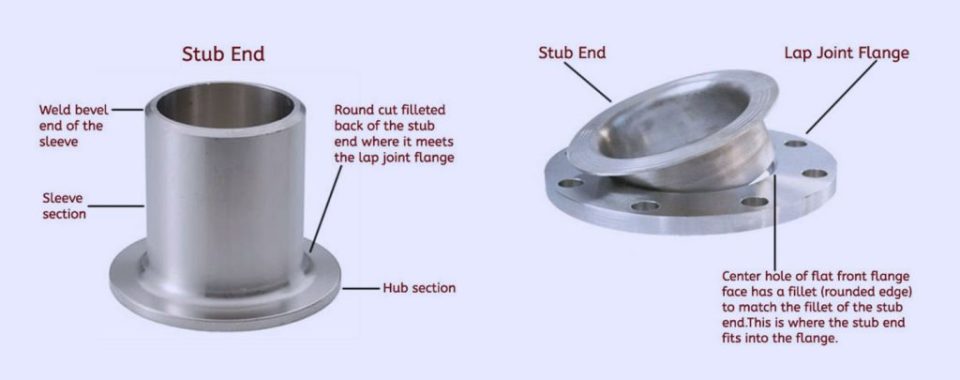
An FRP pipe stub end is a crucial component in piping systems used to connect FRP pipes to flanges. It consists of a short length of FRP pipe with one flared end that allows easy connection to a flange, creating a strong, secure joint. The use of an FRP pipe stub end enhances the system’s resistance to corrosion and chemical exposure, making it ideal for industrial applications. Additionally, the lightweight nature of FRP materials simplifies handling and installation while maintaining durability and long-lasting performance. This component plays a vital role in ensuring reliable, leak-free connections in demanding environments. FRP pipe stub ends provide corrosion resistance, connect pipes to fittings, and allow flange rotation for easy alignment and system adjustments.
What is an FRP Pipe Stub End?
An FRP pipe stub end is a critical component used in piping systems, primarily when a detachable connection between pipes is needed. It is a short piece of FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic) pipe that has one flared end designed to work with a lap joint flange. The stub end allows for easy disconnection and reassembly of pipes, which is especially useful in systems that require regular maintenance or in situations where the pipe needs to be detached without removing the entire assembly. The FRP pipe stub end offers flexibility, strength, and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for a variety of industrial applications.
At GangLong Fiberglass, we manufacture FRP pipe stub ends to fit a wide range of pipe diameters and pressure ratings, ensuring that they meet the specific needs of different projects. These components are used in conjunction with flanges to create strong, leak-resistant joints that are easy to assemble and disassemble.
The frp pipe stub end is a crucial component used in piping systems, particularly in applications involving Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) pipes. These stub ends are typically paired with backing flanges and play a pivotal role in joining two sections of piping without needing welding. They provide flexibility in installation, making it easier to detach or replace sections of pipe when necessary.
The stub end works by allowing the flange to rotate independently of the pipe itself, which is advantageous in many industrial applications. Additionally, frp pipe stub ends help prevent issues like leakage or stress on the pipes, providing a secure yet adjustable connection.

The Key of Role of FRP Pipe Stub Ends in Piping Systems
FRP pipe piles from GangLong Fiberglass are also highly customizable, including options for Centrifugally Cast Fiberglass Pipe, allowing for tailored solutions to meet specific project requirements.They are used in conjunction with lap joint flanges to create connections that are both durable and easy to disconnect. This makes them ideal for systems that require frequent inspection or maintenance, such as those found in chemical plants, wastewater treatment facilities, and power plants.
Flexibility and Maintenance
One of the main benefits of using an FRP pipe stub end is the flexibility it provides in piping systems. Because the stub end allows for easy disconnection, it simplifies the process of removing sections of the pipe for inspection, cleaning, or repair. Instead of having to cut through the pipe or remove the entire section, the flanged connection can be easily disassembled by loosening the bolts on the flange. This saves both time and labor, particularly in large-scale industrial systems where regular maintenance is required.
Strength and Durability
Despite their flexibility, FRP pipe stub ends are designed to offer excellent strength and durability. The materials used in FRP pipes, including fiberglass and resin, provide high resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for transporting aggressive chemicals, wastewater, and other corrosive fluids. Similar to FRP pipe piles, these stub ends are manufactured to ensure they can withstand the same pressures and environmental conditions as the pipes they are connected to, ensuring the overall integrity of the system.
How about the Different Types of FRP Pipe Stub Ends?
FRP pipe stub ends come in various types, depending on the design of the flange and the specific requirements of the piping system. Understanding the different types of stub ends can help in selecting the appropriate one for a given application.
Standard Stub End
The standard FRP pipe stub end is designed for use with a lap joint flange. It features a flared or “stub” end that fits into the flange, allowing the pipe to be easily disconnected when needed. The standard stub end is commonly used in systems where the pipe will need to be frequently disassembled or where future modifications are expected.
Long Stub End
A long FRP pipe stub end is similar to the standard version but features a longer body. This type of stub end is used when additional length is required to connect two pipes or to provide additional support in certain areas of the piping system. Long stub ends are often used in high-pressure systems where additional reinforcement is needed.
Short Stub End
A short FRP pipe stub end is designed for applications where space is limited. It has a shorter body compared to the standard version, making it ideal for compact piping systems. Short stub ends are often used in systems where pipes need to be tightly spaced or where there are physical constraints on the installation.
Advantages of Using FRP Pipe Stub Ends in Industrial Applications
FRP pipe stub ends offer several key advantages in industrial applications, particularly in systems where durability, flexibility, and resistance to corrosion are important.
Corrosion Resistance
One of the main reasons FRP pipe stub ends are used in industrial applications is their resistance to corrosion. FRP materials are naturally resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and solvents. This makes them ideal for use in chemical processing plants, wastewater treatment facilities, and other environments where corrosion is a significant concern. By using FRP pipe stub ends, operators can reduce the risk of leaks, corrosion-related failures, and costly maintenance.
Lightweight and Easy Installation
Another advantage of using FRP pipe stub ends is their lightweight nature. Compared to metal alternatives, FRP components are much lighter, making them easier to handle and install. This can lead to significant labor savings, especially in large-scale piping systems where heavy lifting equipment may otherwise be required. The lightweight nature of FRP also reduces the overall load on the piping system, which can extend the life of the system and reduce maintenance costs.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Despite their lightweight nature, FRP pipe stub ends offer a high strength-to-weight ratio. This means that they are strong enough to handle high pressures and demanding environmental conditions, yet light enough to be easily transported and installed. The combination of strength and flexibility makes FRP stub ends a popular choice for a wide range of industrial applications.
How FRP Pipe Stub Ends Work with Lap Joint Flanges
FRP pipe stub ends are most commonly used in conjunction with lap joint flanges. The lap joint flange is a type of flange that slides over the stub end and is used to bolt two sections of pipe together. The design of the lap joint flange allows for the easy disconnection of the pipes by loosening the bolts, making it an ideal solution for systems that require frequent disassembly or modification.
Creating a Detachable Joint
The main function of the FRP pipe stub end and lap joint flange combination is to create a strong, detachable joint between two sections of pipe. The stub end fits into the flange, and the flange is then bolted to a matching flange on the adjacent pipe section. This creates a secure, leak-resistant connection that can be easily disassembled when needed. In similar applications, fiberglass tube end fittings can also be used to ensure a robust and secure connection between pipe sections, providing additional flexibility and ease of assembly. Because the flange is not permanently attached to the pipe, the joint can be quickly and easily taken apart, making maintenance and modifications simple.
Allowing for Pipe Movement
Another advantage of using FRP pipe stub ends with lap joint flanges is that they allow for a certain degree of movement within the piping system. This is particularly important in systems where thermal expansion or ground movement is a concern. The flexibility of the lap joint flange and stub end connection allows the pipes to move slightly without compromising the integrity of the connection, reducing the risk of damage or failure in the system.
How about the Advantages of Using FRP Lap Joint Flanges?
FRP lap joint flanges, when used with FRP pipe stub ends, offer several key benefits that make them popular in various industrial applications. Their design allows for flexibility, ease of installation, and reusability, which is essential in environments where frequent maintenance is required.
Ease of Alignment
One of the major advantages of using FRP lap joint flanges is their ease of alignment. Because the lap joint flange is not welded directly to the pipe, it can rotate freely around the FRP pipe stub end. This rotation allows for easy alignment with the corresponding flange during installation, making it simpler to bolt the sections together. In large systems where precise alignment is necessary, this feature helps reduce installation time and effort.
Reusability of the Backing Flange
Another benefit of using FRP lap joint flanges is the reusability of the backing flange. Since the flange is not permanently attached to the pipe, it can be reused even after the pipe section has been removed or replaced. This reduces material costs, especially in systems that undergo frequent modifications or replacements. The ability to reuse the flange without sacrificing the strength of the joint makes it an economical choice for many industrial applications.
Flexibility in Installation
FRP lap joint flanges provide flexibility in installation, which is especially important in systems that require frequent adjustments. The detachable nature of the FRP pipe stub end and the flange connection allows for easy changes to the piping layout or modifications to the system. Whether adding new components or reconfiguring existing ones, the combination of the FRP pipe stub end and lap joint flange provides a practical solution that simplifies the process.
Applications of FRP Pipe Stub Ends in Various Industries
FRP pipe stub ends are used in a wide variety of industries due to their versatility, strength, and corrosion resistance.
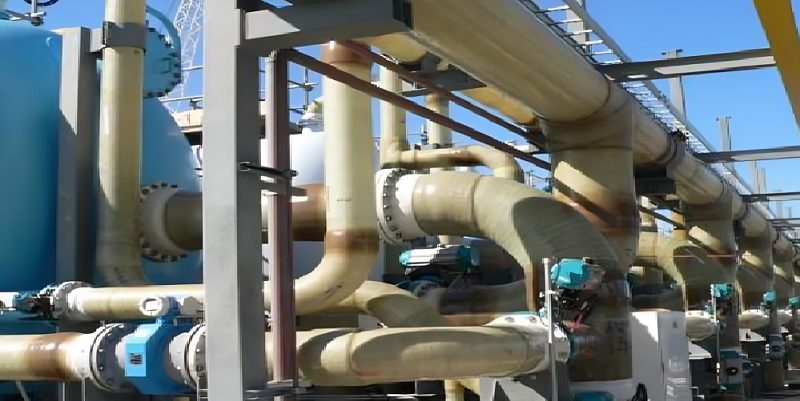

Some of the most common applications include:
Chemical Processing
In chemical processing plants, where pipes are exposed to aggressive chemicals and high temperatures, FRP pipe stub ends are used to create flexible, corrosion-resistant connections. The ability to easily disassemble and reassemble the piping system is a significant advantage in environments where regular maintenance is required. Generally,FRP pipe stub ends have temperature limits ranging from 140°F (60°C) for polyester resin to 250°F (121°C) for epoxy resin, ensuring reliable performance in high-temperature environments.
Water and Wastewater Treatment
FRP pipe stub ends are also commonly used in water and wastewater treatment facilities. These systems often handle aggressive fluids, including sewage and industrial wastewater, which can quickly corrode metal pipes. FRP components, including stub ends, offer excellent resistance to corrosion, significantly extending the life expectancy of the piping system. Additionally, the easy disconnection of stub ends allows operators to perform routine inspections and cleanings without disrupting the entire system, further contributing to the long-term durability and efficiency of the infrastructure.
Power Generation
In power plants, FRP pipe stub ends are used in cooling systems, steam lines, and other areas where high temperatures and pressures are present. The strength and durability of FRP materials make them well-suited for these demanding applications, while the flexibility of the stub end and lap joint flange connection allows for easy maintenance and system modifications.
How about the Customization of FRP Pipe Stub Ends?
At GangLong Fiberglass, we offer customized FRP pipe stub ends to meet the specific requirements of each project. Whether the system requires standard, long, or short stub ends, we can produce components that are tailored to the size, pressure rating, and environmental conditions of the application.
Custom Diameters and Lengths
FRP pipe stub ends can be manufactured in a wide range of diameters and lengths, depending on the needs of the system. Whether a large-diameter pipe is needed for a high-capacity fluid transport system or a smaller-diameter pipe for a compact industrial application, GangLong Fiberglass can produce stub ends that fit perfectly into the overall design of the piping system.
Resin and Fiber Selection
The type of resin and fiberglass used in the production of FRP pipe stub ends can also be customized based on the chemical and thermal requirements of the application. By selecting the right combination of materials, we can ensure that the stub ends offer the necessary resistance to corrosion, temperature fluctuations, and pressure changes.
Importance of FRP Pipe Span Charts in Industrial Piping
How about an FRP Pipe Stub End?
An FRP pipe stub end is a short segment of Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP) piping used in conjunction with lap joint flanges to provide a detachable, flexible connection in a piping system. It is typically designed with one end flared out, which fits into the lap joint flange to form a secure and easy-to-remove joint. The FRP pipe stub end is essential in systems that require frequent assembly and disassembly for maintenance, inspection, or cleaning. Its use in various industries such as chemical processing, water treatment, and power generation highlights its versatility and efficiency in creating durable yet flexible piping systems.
GangLong Fiberglass specializes in the production of high-quality FRP pipe stub ends that are designed to meet specific industry standards. These components provide excellent resistance to corrosion, pressure, and environmental factors, making them an ideal choice for harsh industrial environments.
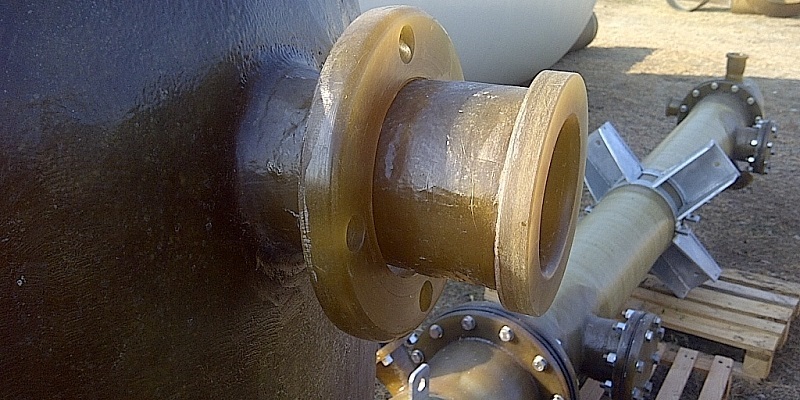

How FRP Pipe Stub Ends Work with Other FRP Fittings
FRP pipe stub ends are often used in conjunction with other FRP fittings, such as elbows, reducers, and tees, to create comprehensive piping systems. These fittings work together to ensure that the system operates efficiently while maintaining flexibility and ease of access for maintenance.
FRP Elbows
FRP elbows are used to change the direction of the piping system, typically at 45 or 90-degree angles. When used with FRP pipe stub ends, elbows allow for the smooth flow of fluids while maintaining the integrity of the joint. The combination of these components ensures that the system remains leak-free and easy to disassemble if necessary.
FRP Reducers
FRP reducers are used to connect pipes of different diameters, allowing for a smooth transition between sections of the system. The FRP pipe stub end can be used in conjunction with reducers to create flexible joints that can be easily modified or replaced. This flexibility is particularly important in systems that experience changes in flow requirements or need to accommodate different pipe sizes.
FRP Tees
FRP tees are used to connect three sections of pipe, allowing for the branching of the system. The use of FRP pipe stub ends with tees ensures that these connections are secure and easy to disassemble when needed. This combination of components is ideal for complex piping systems where multiple branches and connections are required.
Key Manufacturing Processes for FRP Pipe Stub Ends
The production of frp pipe stub ends typically involves filament winding or molding processes, which are critical for achieving the strength and durability needed for high-pressure applications. In filament winding, continuous strands of fiberglass are wound around a rotating mandrel in a specific pattern, ensuring the necessary strength and structural integrity for each frp pipe stub end. The molding process can also be used to create custom dimensions for specific industrial needs, allowing for a tailored solution to unique piping requirements.
Material Composition of FRP Pipe Stub Ends
The primary materials used in making frp pipe stub ends include fiberglass reinforcements and thermosetting resins. These materials are combined in various ratios depending on the desired properties of the end product. The fiberglass provides the necessary strength and rigidity, while the resin acts as a binding agent that offers chemical resistance and overall durability. Common types of resins used include epoxy, vinyl ester, and polyester, each offering specific advantages based on the application.
For instance, epoxy resins are highly resistant to water and chemicals, making them ideal for use in water treatment plants, while vinyl ester resins provide excellent resistance to acidic and alkaline environments. This adaptability in material composition makes frp pipe stub ends highly versatile in a wide range of industries.
Durability and Longevity of FRP Pipe Stub Ends
One of the key reasons industries opt for frp pipe stub ends is their durability and long lifespan. FRP components can last decades with minimal maintenance, making them a cost-effective solution for industries that rely on the integrity of their piping systems. The corrosion-resistant nature of FRP materials ensures that they remain functional even in harsh environments, where metal pipes and fittings might degrade or fail over time. In similar applications, GRP shelter solutions are also used to provide long-lasting protection for equipment and infrastructure, offering comparable durability and resistance to environmental factors, ensuring both piping and related systems maintain their integrity over extended periods.
Additionally, frp pipe stub ends are highly resistant to ultraviolet (UV) light and thermal expansion, which further contributes to their longevity in outdoor or high-temperature settings. This resilience makes them ideal for applications where continuous exposure to sunlight or extreme temperatures would compromise the integrity of other materials.
How Resin Types Impact FRP Pipe Tensile Strength
Installation and Maintenance of FRP Pipe Stub Ends
frp pipe stub ends are relatively easy to install compared to metal alternatives. Their lightweight nature simplifies transportation and handling, reducing labor costs and the risk of injury during installation. The lack of welding requirements also eliminates the need for specialized tools or skilled labor, further streamlining the installation process.
In terms of maintenance, frp pipe stub ends require little upkeep once installed. Routine inspections for wear and tear are typically sufficient to ensure the system remains in optimal condition. Should a replacement or adjustment be needed, the modular design of frp pipe stub ends allows for easy detachment and reassembly, minimizing downtime.
The Key of Choosing the Right FRP Pipe Stub End
Selecting the appropriate frp pipe stub end involves considering various factors, such as the intended application, operating environment, and specific performance requirements. It’s crucial to choose the right type of resin and reinforcement combination to ensure the stub end meets the needs of the system.
For example, in highly corrosive environments, selecting a stub end made with vinyl ester resin may be the best choice, while for high-pressure systems, epoxy-based frp pipe stub ends might offer better performance. Consulting with a reliable manufacturer like GangLong Fiberglass can provide the necessary guidance to make informed decisions about material selection and component specifications.
Compatibility with Other FRP Pipe Components
frp pipe stub ends must be compatible with other components in the piping system to function correctly. This includes ensuring that the dimensions of the stub end align with the backing flange, pipe diameter, and thickness. Incompatible components can lead to leaks, pressure imbalances, or mechanical failures within the system.
Manufacturers like GangLong Fiberglass ensure that their frp pipe stub ends are designed to seamlessly integrate with a wide range of FRP pipe systems, providing a uniform and reliable solution. This compatibility extends to both new installations and retrofits, allowing for easy upgrades or modifications without requiring extensive system overhauls.
Benefits of FRP Pipe Stub Ends for Environmental Sustainability
As industries worldwide move toward more sustainable practices, the use of FRP materials, including frp pipe stub ends, is gaining prominence. FRP components have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to traditional materials like steel or concrete. They are non-toxic, corrosion-resistant, and can be manufactured with minimal waste.
Additionally, their long lifespan reduces the need for frequent replacements, which in turn lowers the overall consumption of raw materials. Companies like GangLong Fiberglass are also developing more eco-friendly resins and processes that further enhance the sustainability of FRP products, making frp pipe stub ends a viable choice for green infrastructure projects.
Applications of FRP Pipe Wet Layup in Industrial Rehabilitation
How to Choose a Suitable FRP Pipe Stub End
Choosing the right FRP pipe stub end requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure compatibility and optimal performance in the intended application. Here’s a detailed guide:
Material Compatibility
Ensure the stub end’s material matches the chemical resistance required for the fluids or gases being transported. FRP materials can be tailored with specific resins to resist various corrosive substances.
Size and Dimensions
Select a stub end with the correct diameter and wall thickness to match the connected pipes and flanges. Refer to industry-standard dimensions for accurate sizing.
Pressure Rating
Verify that the stub end’s pressure rating meets or exceeds the operating pressure of the system.
Temperature Range
Consider the operating temperature of the system. FRP components have specific limits, and exceeding them can compromise performance.
Installation Requirements
Choose a stub end with a design that facilitates easy installation and alignment, especially in systems requiring frequent maintenance or adjustments.
Standards and Certifications
Check for compliance with industry standards, such as ASTM or ASME, to ensure quality and reliability.
Application-Specific Needs
For special applications, such as handling abrasive materials or high-velocity fluids, consult manufacturers for custom options.
By evaluating these factors, users can select an FRP pipe stub end that ensures durability, efficiency, and long-term reliability in their piping systems.
FAQs about Frp Pipe Stub End
FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) pipes and PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes are both commonly used in piping systems, but they have distinct differences in terms of material properties, applications, and performance. One of the main differences is their composition: FRP pipes are made from a combination of fiberglass and resin, while PVC pipes are made from a thermoplastic material known as polyvinyl chloride.
FRP pipes are generally stronger and more durable than PVC pipes, making them suitable for more demanding industrial applications. They have higher resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and extreme environmental conditions. This makes FRP pipes ideal for industries like chemical processing, wastewater treatment, and oil and gas, where exposure to harsh substances and temperatures is common.
On the other hand, PVC pipes are more flexible and easier to install than FRP pipes. They are often used in residential and commercial plumbing, as well as in low-pressure applications like irrigation systems. PVC pipes are lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to most chemicals, but they may not perform well in high-pressure or high-temperature environments compared to FRP pipes.
Another key difference is the installation process. FRP pipes require specialized equipment and skilled labor for installation, especially for large-diameter pipes or complex systems. PVC pipes, however, are easier to handle and join, often requiring only simple tools and fittings. Overall, the choice between FRP and PVC pipes depends on the specific needs of the project, including factors like pressure, temperature, chemical exposure, and installation requirements.
FRP stands for Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic, a composite material widely used in various industrial applications, including piping systems. FRP pipes are made by reinforcing plastic (usually a thermosetting resin like polyester, vinyl ester, or epoxy) with fiberglass fibers. This combination creates a strong, durable material that is resistant to corrosion, chemicals, and other environmental factors.
The use of fiberglass reinforcement in FRP pipes enhances their strength while keeping them lightweight. This makes FRP pipes ideal for applications where traditional materials, like steel or concrete, may not be suitable due to their weight or susceptibility to corrosion. For instance, FRP pipes are commonly used in chemical plants, wastewater treatment facilities, and offshore oil and gas operations, where exposure to harsh chemicals and environmental conditions can rapidly degrade metal pipes.
One of the main advantages of FRP pipes is their versatility. They can be customized to meet specific project requirements, including different sizes, shapes, and wall thicknesses. This makes them a popular choice in industries that require pipes with specialized performance characteristics.
While FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) pipes offer many advantages, including corrosion resistance, light weight, and durability, they also have some limitations and potential problems. One common issue with FRP pipes is their vulnerability to impact damage. Since FRP is a composite material, it may crack or fracture if struck by a heavy object, unlike metal pipes, which can withstand more significant physical force.
Another potential problem is the material’s susceptibility to UV degradation. Prolonged exposure to sunlight can weaken the resin in FRP pipes, causing it to become brittle and less durable over time. This can be mitigated by using protective coatings or installing the pipes underground or in shaded areas.
FRP pipes may also have challenges with installation, especially when compared to more flexible materials like PVC or metal. The installation process requires specialized equipment and skilled labor, particularly for large-scale projects involving joining or repairing FRP pipes. If not handled correctly, improper installation can lead to leaks, joint failures, or even structural weaknesses in the pipe.
A pipe stub end is a short length of pipe with a flange-like collar on one end, used in conjunction with lap joint flanges in piping systems. The stub end allows for easier assembly and disassembly of pipelines, especially when frequent maintenance or inspection is required. For FRP (Fiber-Reinforced Plastic) pipes, stub ends are made of composite materials, providing corrosion resistance and lightweight properties. In an FRP system, stub ends are critical for creating flanged connections while maintaining the material’s chemical and mechanical properties. The smooth surface of the FRP stub end ensures proper sealing with gaskets and compatibility with lap joint flanges. This design is particularly beneficial in industries like chemical processing, where resistance to aggressive substances is essential.
FRP pipe stands for Fiber-Reinforced Plastic pipe, a composite material made by reinforcing plastic resin (typically polyester, vinyl ester, or epoxy) with glass, carbon, or other fibers. FRP pipes are widely used for their excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and durability. These pipes are lightweight yet capable of withstanding high pressures and harsh environmental conditions, making them ideal for industries like chemical processing, wastewater treatment, and marine applications. Compared to traditional materials like steel or concrete, FRP pipes offer advantages in ease of installation, reduced maintenance, and a longer service life. Additionally, their non-corrosive nature makes them suitable for transporting corrosive fluids such as acids, alkalis, or saltwater, ensuring structural integrity over time.
FRP flanges are flange fittings made from Fiber-Reinforced Plastic, designed to connect sections of FRP piping systems. They serve as connection points for valves, equipment, and other pipeline components, ensuring a tight and reliable seal. FRP flanges are manufactured to be lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and capable of handling aggressive fluids and environments. They come in various configurations, including blind, slip-on, and lap-joint types, to suit specific applications. When paired with FRP stub ends, these flanges allow easy assembly and disassembly without compromising the integrity of the piping system. Industries like petrochemical, water treatment, and pulp and paper frequently use FRP flanges due to their ability to resist chemical degradation and operate in extreme conditions while requiring minimal maintenance.
FRP is not inherently stronger than steel but offers unique advantages that make it preferable in specific applications. While steel has higher tensile strength, FRP’s strength-to-weight ratio can exceed that of steel. This means FRP can achieve comparable strength at a fraction of the weight, making it easier to handle and install. Additionally, FRP excels in corrosion resistance, outperforming steel in environments with exposure to chemicals, moisture, or salt. FRP does not rust or degrade over time, which translates to lower maintenance and longer service life in aggressive conditions. However, FRP is not suitable for extremely high-temperature applications where steel’s heat tolerance is unmatched. In piping systems, the choice between FRP and steel depends on factors like operational environment, load requirements, and cost-effectiveness.

As the editor of GangLong Fiberglass, I have years of experience and in-depth research, focusing on cable tray products, fiberglass solutions, and grille systems. I incorporate years of industry insights and practical experience into every content, committed to promoting the progress of the industry. At GangLong Fiberglass, my commitment is reflected in every product, from innovative cable trays to durable fiberglass solutions and sturdy grille systems. As an authoritative voice in the industry, my goal is to provide valuable information to professionals and businesses and promote forward-looking solutions.


