
FRP pipe bell and spigot joints are essential in FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) piping systems, providing a secure and reliable method for connecting pipes. These joints are designed to offer leak-free connections, ensuring the integrity of fluid transport. The bell end is flared, while the spigot end is tapered to fit precisely into the bell. This design facilitates easy assembly and strong adhesion when used with the appropriate adhesive. The use of FRP pipe bell and spigot joints in piping systems results in a more durable and corrosion-resistant installation, ideal for various industrial applications where long-term performance and minimal maintenance are crucial. FRP pipe bell and spigot connections with O-ring fittings offer strong, leak-proof joints using standard or precision fittings for various applications.
What is FRP Pipe Bell and Spigot
FRP pipe bell and spigot joints play a crucial role in connecting fiberglass-reinforced plastic pipes, ensuring they perform optimally in a variety of applications. These joints are designed to provide secure, leak-free connections that enhance the overall durability and reliability of FRP piping systems. The bell and spigot system consists of a bell end, which is flared, and a spigot end, which is tapered to fit snugly into the bell. This design not only simplifies the installation process but also creates a robust joint capable of withstanding high pressures and various environmental conditions. Utilizing the proper adhesive during installation ensures a strong bond, making bell and spigot frp pipe joints an excellent choice for industries that demand long-lasting, corrosion-resistant piping solutions.
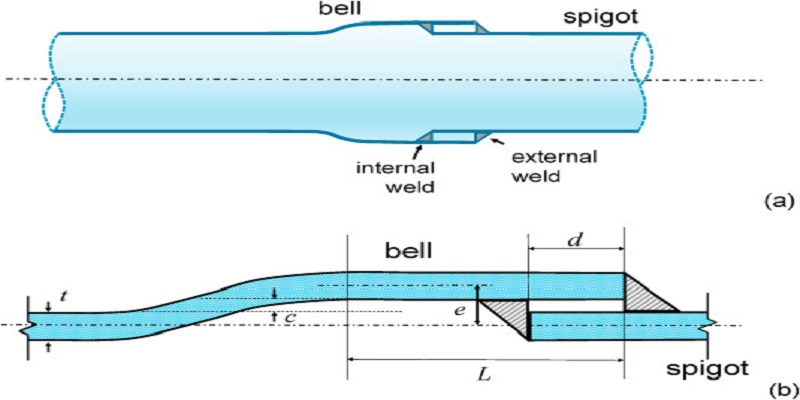
FRP pipe bell and spigot systems are integral to the efficient installation and performance of fiberglass-reinforced plastic piping systems. They ensure a leak-free, durable connection suitable for various applications. In these systems, the bell end of the pipe is slightly flared, while the spigot end is tapered. This configuration facilitates easy assembly, allowing the spigot to fit securely into the bell with the help of adhesive. By using the right methods and materials, these joints provide long-lasting performance and enhance the overall strength and reliability of the piping network.
FRP Pipe Bell and Spigot Various Data Meanings
What is the FRP Pipe Fittings Catalogue
The FRP pipe fittings catalogue is a comprehensive guide that showcases a wide range of fittings available for use in FRP piping systems. These fittings include various types of elbows, tees, reducers, and couplings that are designed to work seamlessly with FRP pipe bell and spigot joints. GangLong Fiberglass offers a diverse selection of fittings to accommodate different pipe sizes and configurations, ensuring that every piping system can be customized to meet specific requirements. The catalogue is an invaluable resource for engineers and installers, providing detailed specifications for each fitting, including dimensions, pressure ratings, and material properties. Understanding the offerings within the FRP pipe fittings catalogue enables the selection of the right components for creating efficient and durable piping networks.
Interpreting the FRP Pipe Size Chart
Understanding the FRP pipe size chart is vital for selecting the right FRP pipe bell and spigot fittings. The chart provides detailed information on the different sizes of FRP pipes, including their inner and outer diameters, wall thickness, and pressure ratings. By referring to the size chart, installers can ensure that they select fittings that match the pipes they are working with, resulting in joints that are both secure and durable. The size chart is also helpful in determining the appropriate adhesive quantity needed for each joint, as larger pipes may require more adhesive to create a strong bond. Utilizing the FRP pipe size chart from GangLong Fiberglass ensures that the piping system is built to withstand operational demands, providing long-term reliability and performance.
The Significance of the FRP Pipe O.D. Chart
The FRP pipe O.D. (Outer Diameter) chart is a critical reference tool that provides the precise external dimensions of FRP pipes. Accurate knowledge of the pipe’s outer diameter is essential when selecting the appropriate FRP pipe bell and spigot fittings, as it ensures a proper fit and effective sealing of the joint. The chart lists various pipe sizes along with their corresponding outer diameters, allowing installers to quickly identify the correct fittings for their specific application. Using the FRP pipe O.D. chart simplifies the process of matching pipes and fittings, ensuring that the bell and spigot joint will be secure and leak-free. For a more detailed and precise selection, the FRP Pipe Schedule Chart can also be used in conjunction with the O.D. chart, as it provides important information on the pipe’s wall thickness and pressure ratings. This chart is particularly important when working with GangLong Fiberglass products, as it helps maintain consistency and integrity throughout the entire piping system, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance.
FRP Pipe Specifications for Bell and Spigot Joints
The specifications of FRP pipes play a significant role in the performance of bell and spigot joints. GangLong Fiberglass offers pipes with various specifications tailored to meet the requirements of different applications. These specifications include the pipe’s diameter, wall thickness, pressure rating, and temperature resistance. When selecting FRP pipe bell and spigot joints, it is essential to consider these specifications to ensure compatibility and reliable performance. For instance, pipes used in high-pressure applications should have a thicker wall and a higher pressure rating to withstand the operational stresses. The bell and spigot fittings must also be designed to accommodate these specifications, providing a tight seal that prevents leakage. Understanding the specifications of GangLong Fiberglass pipes and matching them with the appropriate bell and spigot fittings ensures the longevity and effectiveness of the piping system.
Guidelines for Matching Pipe Sizes for Optimal Joint Integrity
Ensuring the integrity of FRP pipe bell and spigot joints depends on matching the pipe sizes correctly. Here are some essential guidelines for achieving optimal joint integrity:
Accurate Measurement: Always measure the outer diameter of the pipe using precise tools. Refer to the FRP pipe O.D. chart for the correct dimensions and match the bell and spigot sizes accordingly.
Selecting Compatible Fittings: Choose fittings from the FRP pipe fittings catalogue that correspond to the pipe’s dimensions. This ensures a tight fit between the bell and spigot, which is crucial for a secure joint.
Adhesive Application: Apply the adhesive uniformly on both the bell and spigot surfaces. Ensure the adhesive covers the entire bonding area to prevent leaks and joint failures.
Proper Alignment: During installation, align the spigot with the bell carefully to avoid any misalignment that could compromise the joint’s strength.
Curing Time: Allow sufficient curing time for the adhesive to set and create a robust bond. The curing process is essential for the joint’s long-term performance.
By following these guidelines, installers can achieve optimal joint integrity, ensuring that the FRP pipe bell and spigot connections remain secure and leak-free.
FRP Pipe Bell and Spigot Installation
Preparation for FRP Pipe Bell and Spigot Installation
Proper preparation is key to the successful installation of FRP pipe bell and spigot joints. The process involves several steps that ensure the joints are clean, properly aligned, and ready for bonding.
Surface Cleaning: Clean the surfaces of the bell and spigot to remove any dust, grease, or debris that could interfere with the adhesive bond. Use a solvent recommended by GangLong Fiberglass for optimal cleaning results.
Sanding: Sand the bonding surfaces of the bell and spigot using 60 to 80 grit sandpaper. This creates a roughened surface that promotes better adhesion. Ensure that both surfaces are evenly sanded for a uniform bond.
Dry Fit Check: Before applying adhesive, perform a dry fit check by inserting the spigot into the bell to ensure proper alignment and fitment. Make any necessary adjustments to achieve the correct fit.
Marking Alignment: Mark the pipe and fitting to indicate the correct insertion depth. This helps maintain alignment during the bonding process.
By thoroughly preparing the FRP pipe bell and spigot joints, installers can create a strong and durable connection that will perform reliably under operational conditions.

Techniques for Joining FRP Pipe Bell and Spigot
The joining of FRP pipe bell and spigot involves specific techniques to ensure a secure and durable connection.
Alignment and Positioning: Align the spigot with the bell carefully before inserting it. Misalignment can result in an uneven joint that may compromise the pipe’s performance.
Insertion Process: Gently insert the spigot into the bell using steady pressure. For larger pipe sizes, use mechanical aids such as come-alongs or hydraulic cylinders to facilitate insertion while maintaining alignment.
Rotation for Adhesive Spread: Rotate the spigot slightly as it is being inserted into the bell. This action helps distribute the adhesive evenly, ensuring complete coverage of the bonding surfaces.
Locking the Joint: Secure the joint by applying pressure until the spigot reaches the marked alignment depth. Ensure that there is no visible forward movement, indicating that the joint is locked in place.
These techniques are essential for creating a watertight and durable FRP pipe bell and spigot joint that can withstand various operational conditions.
Curing Process for FRP Pipe Bell and Spigot Joints
The curing process is crucial in achieving the full strength of FRP pipe bell and spigot joints. Proper curing allows the adhesive to set and bond the surfaces securely.
Curing Time and Temperature: The curing time for the adhesive depends on the ambient temperature. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations provided by GangLong Fiberglass to determine the appropriate curing time for your specific conditions. Higher temperatures may reduce curing time, while lower temperatures may require longer curing periods.
Use of Heating Collars: For faster curing, use an electric heating collar around the joint. The heating collar provides uniform heat, accelerating the curing process and enhancing the adhesive bond’s strength.
Post-Cure Inspection: After the curing process is complete, inspect the joint for any signs of movement or gaps. A properly cured joint should be solid and free of defects that could lead to leaks.
The curing process is essential for ensuring that the FRP pipe bell and spigot joints can withstand operational stresses and provide long-term reliability.
Techniques for Creating a Secure Bell and Spigot Joint
Creating a secure FRP pipe bell and spigot joint requires precise techniques to ensure a strong, leak-free connection. The process involves the following steps:
Dry Fitting: Before applying adhesive, perform a dry fit by inserting the spigot into the bell to check the alignment and fitment. This step helps identify any adjustments needed for a proper fit.
Marking Insertion Depth: Mark the spigot to indicate the correct insertion depth. This mark acts as a guide during the joining process, ensuring the spigot is inserted to the right depth within the bell.
Inserting the Spigot: After applying adhesive, carefully insert the spigot into the bell. Use a slight rotating motion to spread the adhesive evenly. Ensure the spigot is inserted to the marked depth.
Applying Pressure: Apply consistent pressure on the joint to secure the bond. For larger pipe sizes, mechanical aids like come-alongs or hydraulic cylinders can be used to facilitate the joining process.
Curing: Allow the adhesive to cure according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Curing times may vary depending on the adhesive type and ambient temperature. Proper curing is essential for achieving the full strength of the joint.
By following these techniques, installers can create a secure FRP pipe bell and spigot joint that provides reliable performance and durability.
Field Installation of FRP Pipe Bell and Spigot Joints
Field installation of FRP pipe bell and spigot joints requires careful planning and execution to ensure a successful outcome. The process includes:
Site Preparation: Prepare the installation site by ensuring it is clean and free from debris. Lay out the pipes and fittings in the sequence of installation.
Cutting and Tapering: If custom pipe lengths are required, use appropriate tools to cut the FRP pipes to the desired length. Taper the ends of the pipes as needed to fit into the bell and spigot joints.
Joint Assembly: Follow the techniques for adhesive application and joint assembly. Use alignment tools if necessary to ensure that the pipes are correctly positioned.
Curing and Inspection: Allow the joints to cure completely before subjecting them to operational pressures. Inspect the joints for proper alignment and sealing.
Adhesive Application for Bell and Spigot Joints
The application of adhesive is a critical step in the installation of FRP pipe bell and spigot joints. Proper adhesive application ensures a secure bond that can withstand the demands of the piping system.
Surface Preparation: Clean the surfaces of the bell and spigot to remove any dust, grease, or debris. Sand the surfaces lightly using 60 to 80 grit sandpaper to create a rough texture, which helps the adhesive bond more effectively.
Mixing the Adhesive: Mix the adhesive according to the manufacturer’s instructions provided by GangLong Fiberglass. Ensure that the adhesive is mixed thoroughly to achieve the desired consistency and bonding strength.
Uniform Application: Apply a generous amount of adhesive evenly on the spigot and the inside of the bell. Use a brush or applicator to spread the adhesive uniformly, covering the entire bonding surface. Avoid applying too much adhesive, as it may lead to excess squeeze-out during the jointing process.
Insertion and Bonding: Carefully insert the spigot into the bell while rotating it slightly to distribute the adhesive evenly. Press the joint together until it reaches the marked alignment depth. Hold the joint in place until the adhesive sets.
Excess Adhesive Removal: Remove any excess adhesive from the joint area to ensure a clean finish. This prevents any interference with the pipe’s performance or appearance.

FRP Pipe Bell and Spigot: Sealant Options for Leak-Proof Connections
Socket-and-spigot joints are one of the most widely used methods for connecting fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP) pipes, providing a strong, reliable, and flexible solution for a variety of industrial applications. These joints rely on effective sealants to ensure that the connection remains leak-proof and withstands the pressures of fluid and gas transport. Two of the most common sealants used in these connections are O-rings and REKA gaskets. Let’s explore both in detail:
O-rings in FRP Pipe Bell and Spigot Connections
O-rings are one of the most effective sealants used in FRP pipe bell and spigot joints, particularly in larger diameter pipes. The O-ring is typically made of elastic materials such as rubber or synthetic compounds, and it is installed in parallel grooves located on the plug (spigot) of the joint. When the plug is inserted into the bell (the receiving part of the joint), the O-rings are compressed against the flat seat area within the bell, creating a tight, reliable seal.
The compression of the O-rings ensures that the joint is leak-proof, even under varying pressures and conditions. This method is particularly advantageous because of the O-ring’s ability to accommodate slight misalignments between the pipe ends while maintaining an effective seal. The O-ring seal is also relatively easy to replace or maintain, making it a cost-effective solution over the long term.
In terms of application, O-rings are suitable for various industrial settings, including water treatment plants, sewage systems, and chemical processing plants, where large-diameter FRP pipes need to be securely connected and sealed. The O-ring method is also popular in systems that require flexibility and durability in sealing, especially when pipes are exposed to different temperatures, pressure fluctuations, or corrosive materials.
REKA Gasket in FRP Pipe Bell and Spigot Connections
The REKA gasket is another sealant used in FRP pipe bell and spigot joints, though it is less common than O-rings. The REKA gasket was originally developed in the 1930s for use in asbestos pipes, making it a time-tested solution for pipe sealing. Over time, it has been adapted and is now widely used in fiberglass and other materials for industrial piping systems.
The REKA gasket is typically a flat, resilient sealing material made of rubber or a rubber-like compound. It is designed to be placed between the bell and the spigot of the pipe joint, where it creates a seal once compressed. This type of gasket is known for its ability to resist high pressures, temperatures, and chemicals, making it ideal for industries where pipes must endure harsh conditions, such as oil and gas transport, chemical processing, and power generation.
What makes the REKA gasket particularly advantageous is its long service life and ability to maintain its sealing integrity even in extreme operating environments. It is capable of providing an airtight, watertight seal under demanding conditions, including exposure to high-pressure flows, aggressive chemicals, and fluctuating temperatures. Moreover, the REKA gasket’s design allows for ease of installation and replacement, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
While REKA gaskets are more commonly used in industrial applications requiring resistance to extreme conditions, they are also preferred for systems with high mechanical loads, where the gasket’s durability and pressure-resisting properties are essential.
Comparison of O-rings and REKA Gaskets
Both O-rings and REKA gaskets offer unique advantages depending on the specific needs of an application. O-rings are generally easier to replace and offer flexibility in accommodating slight misalignments during installation, making them ideal for a broad range of general-purpose applications. They are well-suited for scenarios where ease of maintenance and cost-efficiency are paramount.
On the other hand, REKA gaskets excel in more demanding environments where high pressure, temperature extremes, or chemical exposure are common. Their superior resistance to harsh conditions makes them the preferred choice for critical industrial systems that require long-term reliability and performance.
The choice between O-rings and REKA gaskets in FRP pipe bell and spigot connections ultimately depends on the specific demands of the system. O-rings are excellent for large-diameter pipes requiring flexible, cost-effective sealing solutions, while REKA gaskets provide superior sealing performance in extreme conditions. Both sealants are crucial in ensuring that the pipe joints remain strong, secure, and leak-proof, contributing to the overall durability and efficiency of FRP piping systems.
The Strength of Fibercast FRP Pipe in Industrial Settings
Significance of FRP Pipe O.D.
The outer diameter (O.D.) of an FRP pipe is a vital parameter that determines the compatibility of the pipe with various fittings, including FRP pipe bell and spigot joints. A precise match between the pipe’s O.D. and the bell and spigot fittings is essential for creating a secure, leak-proof joint. The O.D. also influences the FRP pipe pressure rating and structural integrity of the piping system. GangLong Fiberglass offers a range of FRP pipes with different O.D. sizes to cater to various industrial requirements. The correct O.D. ensures that the adhesive bonds effectively, providing a strong connection that can withstand operational stresses, including pressure fluctuations and temperature variations.
What is the FRP Pipe O.D. (Outer Diameter) Chart
The FRP pipe O.D. chart is an essential reference that displays the external dimensions of various FRP pipes. It plays a critical role in the selection of FRP pipe bell and spigot fittings. The chart offers a clear view of the pipe’s outer diameter, which is crucial for ensuring compatibility between the pipe and the fittings. For more comprehensive details, the FRP pipe data can also be consulted, as it provides additional specifications such as pressure ratings, wall thickness, and material properties. With the correct outer diameter information and data, installers can select bell and spigot joints that fit perfectly, thus preventing leaks and ensuring a solid connection. The FRP pipe O.D. chart typically includes various sizes of pipes, detailing their corresponding outer diameters. It serves as a guide for engineers and installers to match the appropriate fittings with the pipes in a project.
How to Read and Utilize an FRP Pipe O.D. Chart
The FRP pipe O.D. chart is a straightforward tool that lists various pipe sizes alongside their corresponding outer diameters. Here’s how to read and use the chart effectively:
Locate the Pipe Size: Find the size of the FRP pipe you are using or intend to use in the piping system. This size is typically specified in inches or millimeters.
Identify the O.D.: Match the pipe size with its corresponding outer diameter on the chart. The O.D. is usually listed in millimeters or inches, providing an accurate measurement for selecting fittings.
Select Compatible Fittings: Once the O.D. is known, choose the appropriate FRP pipe bell and spigot fittings from the GangLong Fiberglass catalogue that match the pipe’s outer diameter. This ensures a proper fit and effective sealing.
Cross-Check for Accuracy: Verify that the selected bell and spigot fittings are compatible with the pipe’s O.D. This step is crucial to avoid mismatches that could lead to leaks or joint failure.
Using the FRP pipe O.D. chart simplifies the selection process and ensures that the piping system is assembled correctly, with joints that are secure and durable.
Importance of O.D. in Ensuring Compatibility with Bell and Spigot Joints
The outer diameter of an FRP pipe directly affects the fitment of the FRP pipe bell and spigot joints. A mismatch in size can result in an improper seal, leading to potential leaks or joint failure. Therefore, it is crucial to select bell and spigot fittings that precisely match the pipe’s O.D. When the outer diameter of the pipe aligns with the bell and spigot fittings, it ensures that the adhesive can bond effectively, creating a watertight seal. This compatibility is vital for maintaining the structural integrity of the piping system, especially in applications that involve the transport of fluids under pressure.
How Density of FRP Pipe Impacts Performance and Durability
Ensuring Long-Term Performance of FRP Pipe Bell and Spigot Joints
To ensure the long-term performance of FRP pipe bell and spigot joints, several factors need to be considered during installation and maintenance:
Proper Installation: Follow the recommended installation procedures provided by GangLong Fiberglass. This includes correct adhesive application, curing, and ensuring that the pipe and fittings are free from defects.
Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the joints for signs of wear, damage, or leaks. Early detection of issues allows for timely repairs, preventing potential failures.
Temperature and Pressure Management: Ensure that the piping system operates within the specified temperature and pressure limits. Excessive conditions can compromise the integrity of the joints over time.
Preventive Maintenance: Implement a maintenance schedule that includes cleaning, inspection, and any necessary repairs. Preventive maintenance helps extend the life of the FRP pipe bell and spigot joints.
By adhering to these practices, the integrity and performance of FRP pipe bell and spigot joints can be maintained over an extended period, ensuring a reliable and efficient piping system.
GangLong Fiberglass FRP Pipe Fittings for Bell and Spigot Joints
GangLong Fiberglass offers a wide range of FRP pipe fittings specifically designed for bell and spigot joints. These fittings are manufactured to high-quality standards, ensuring compatibility with various pipe sizes and applications. The GangLong Fiberglass catalogue includes fittings such as elbows, tees, reducers, and couplings, all designed to work seamlessly with FRP pipe bell and spigot joints. Each fitting is engineered to provide a precise fit and strong bond, contributing to the overall integrity of the piping system. Using GangLong Fiberglass fittings ensures that the piping system is equipped with components that are built to withstand the demands of industrial environments, providing long-lasting performance.
Cutting FRP Pipe with Precision: Tools and Techniques to Use
FRP Pipe Bell and Spigot: Alternative Connection Methods and Their Advantages
In addition to the socket-and-spigot joint, which is commonly used for connecting FRP pipes with strong, leak-proof seals, there are several other connection methods for FRP pipes. These methods vary in terms of installation, flexibility, strength, and suitability for specific applications. Below are the primary alternatives to the socket joint, along with their advantages and disadvantages compared to the socket-and-spigot connection.
Butt and Strap Fittings
Butt and strap fittings are a popular alternative to socket joints for FRP pipes. In this method, the ends of two pipes are joined by aligning them in a straight line, followed by welding or bonding them together using a coupling or strap around the joint. This method is often used for smaller diameter pipes or where there is a need for a quick, strong connection.
Advantages:
- Simple and cost-effective for small diameter pipes.
- Strong and reliable connection, suitable for lower-pressure applications.
- No need for O-rings or gaskets, reducing the chances of leaks from seal failure.
Disadvantages:
- Requires precise alignment of the pipe ends.
- Not as flexible as socket joints, especially in larger systems where slight misalignments may occur.
- Can be more labor-intensive and require special equipment for welding or bonding.
Applicable Situations: Butt and strap fittings are often used in smaller pipelines or systems where ease of assembly and cost-effectiveness are key factors. This method is ideal for non-critical applications with lower pressure and less demanding environmental conditions.
Flanged Connections
Flanged connections involve attaching a flange to the end of each FRP pipe, and then bolting the two flanges together using gaskets to create a leak-proof seal. This method is commonly used for larger diameter pipes or systems requiring high-pressure ratings.
Advantages:
- Flanged connections provide a very strong and durable joint, especially for larger pipes.
- Ideal for high-pressure applications, and allows for easier disassembly and maintenance, as bolts can be undone to separate the pipes.
- Flanges allow for flexibility in aligning pipes during installation.
Disadvantages:
- More expensive than other methods, particularly when large or custom flanges are required.
- Installation is more time-consuming due to the need for precise alignment and bolting.
- Requires more space and is bulkier compared to socket joints.
Applicable Situations: Flanged connections are commonly used in industries where high-pressure or high-temperature conditions are common, such as chemical plants, water treatment facilities, and oil and gas pipelines. These connections are ideal when frequent maintenance or disassembly of the piping system is needed.
Threaded Connections
Threaded connections involve screwing the ends of the pipes into threaded fittings, creating a sealed joint. This method is typically used for smaller FRP pipes and is popular in systems where precise alignment and tight connections are important.
Advantages:
- Simple and quick installation for small diameter pipes.
- Allows for easy disconnection and reconfiguration of the pipe system.
- Cost-effective for lower-pressure applications.
Disadvantages:
- Limited to smaller diameter pipes due to the difficulty of threading large pipes.
- Threaded connections are not as reliable for high-pressure systems.
- Over time, threads can wear out, leading to leaks or reduced strength.
Applicable Situations: Threaded connections are ideal for small, low-pressure systems such as residential plumbing, irrigation systems, or in situations where pipes need to be frequently disassembled or reconfigured.
Fusion Bonding (Butt Fusion)
Fusion bonding, or butt fusion, is a method where the ends of FRP pipes are heated and then pressed together to form a permanent bond. This is often used in thermoplastic piping systems, including FRP, when a strong, seamless joint is required.
Advantages:
- Creates a strong, permanent bond that is resistant to high pressures and environmental factors.
- Ideal for applications where the pipes must be leak-proof over long periods.
- Provides a smooth, continuous inner surface, which reduces the chances of buildup or blockages.
Disadvantages:
- Requires specialized equipment to heat and press the pipe ends together.
- Limited flexibility for reconfiguration, as the bond is permanent and cannot be undone.
- More expensive due to the equipment and labor required for fusion bonding.
Applicable Situations: Fusion bonding is often used in large-scale industrial applications such as chemical pipelines, wastewater systems, and high-pressure systems. It is ideal when a permanent, high-strength connection is needed, and maintenance or disassembly is not anticipated.
Compression Fittings
Compression fittings are another method where a pipe is connected to a fitting by compressing a gasket or rubber seal around the pipe’s exterior. The fitting then secures the pipe in place using mechanical pressure.
Advantages:
- Easy to install and requires no welding or gluing.
- Can be disassembled and reassembled if necessary.
- Suitable for a range of pipe sizes and pressures.
Disadvantages:
- Less reliable than welded or flanged connections under high pressure or extreme environmental conditions.
- Gaskets can wear out over time, potentially leading to leaks.
Applicable Situations: Compression fittings are commonly used in residential and light commercial plumbing applications where disassembly might be needed for maintenance or changes to the system.
Comparison with Socket and Spigot Joints
The socket-and-spigot joint method stands out for its ease of use, flexibility, and ability to accommodate slight misalignments, especially in large diameter pipes. Compared to other methods:
- Socket joints are typically quicker and easier to install, particularly when dealing with pipes that need to be connected in tight spaces or locations requiring flexibility during installation.
- Flanged and butt fusion connections are stronger, ideal for high-pressure systems, and provide long-lasting seals but are more complex and expensive to install.
- Threaded connections and compression fittings are better suited for smaller pipes and less demanding applications, offering ease of disassembly but generally not suitable for high-pressure or critical applications.
While FRP pipe bell and spigot joints offer many advantages, including ease of installation and flexibility, the best connection method depends on the specific requirements of the application. For high-pressure, large-scale, or permanent installations, flanged connections or fusion bonding may be the preferred options. However, for simpler, low-cost, or maintenance-heavy projects, butt and strap fittings, threaded connections, and compression fittings are valuable alternatives to consider. Each method has its unique strengths and is suited to particular environments, and understanding these differences will help ensure that the right connection method is chosen for optimal performance.
FAQs about Frp Pipe Bell And Spigot
FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) pipes offer several advantages, such as corrosion resistance and light weight. However, they also have certain limitations. One of the common problems is their vulnerability to mechanical damage. FRP pipes are strong but can be more susceptible to cracking or breaking under heavy impact or pressure compared to metal pipes. Additionally, they may suffer from issues related to UV degradation if not properly coated or shielded from sunlight. Over time, exposure to ultraviolet light can weaken the material, making it less durable. Another concern is their relatively higher cost, especially for specialized installations, and the need for expert handling during installation to avoid damage.
Bell and spigot pipes are widely used in water distribution systems, sewage systems, and drainage projects. The bell and spigot design allows for a watertight seal, making them ideal for transporting liquids without leakage. These pipes are often utilized in underground installations due to their ease of assembly and ability to handle various loads, including soil pressure. Bell and spigot pipes are also employed in irrigation systems and stormwater management systems, where a secure, leak-resistant connection is essential. The bell (a flared-out end) fits over the spigot (a straight end), creating a reliable, sturdy joint that can endure changes in temperature and pressure.
FRP pipes are known for their long service life due to their resistance to corrosion, chemical degradation, and other environmental factors. In optimal conditions, FRP pipes can last anywhere between 50 to 70 years, depending on the type of application and exposure to external elements. The material’s resistance to corrosive substances such as acids and salts makes FRP pipes a popular choice for industries like wastewater treatment and chemical processing, where longevity is a priority. Regular maintenance, proper installation, and protection from excessive mechanical stress can further enhance their lifespan, making them a cost-effective solution for long-term projects.
FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) pipes and PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes differ in material composition, strength, and application. FRP pipes are made by combining fiberglass with a resin matrix, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and higher pressure tolerance compared to PVC pipes. This makes FRP pipes ideal for use in industries like chemical processing, water treatment, and offshore applications, where durability and resistance to harsh environments are critical. On the other hand, PVC pipes are made from a plastic polymer and are lightweight, easy to install, and cost-effective, which makes them popular in residential plumbing and sewer systems. However, PVC is more prone to degradation under UV exposure and has a lower tolerance for extreme temperatures and chemical exposure than FRP pipes. When considering applications, FRP pipes are better suited for demanding environments, while PVC pipes are ideal for general-purpose use.
FRP pipe stands for Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic pipe. This type of pipe is made by reinforcing a plastic matrix (typically polyester or vinyl ester resin) with fiberglass strands, creating a lightweight yet incredibly strong pipe. FRP pipes are designed to offer superior durability, resistance to corrosion, and high tensile strength, making them ideal for industries such as chemical processing, water treatment, and oil and gas transportation. The reinforcement of fiberglass allows FRP pipes to withstand high pressures and extreme environmental conditions, including exposure to harsh chemicals and temperatures. The versatility of FRP pipes makes them a preferred choice in industries that require long-lasting, low-maintenance piping solutions. The use of fiberglass in their construction gives them exceptional mechanical properties, allowing them to be used in a wide range of applications where traditional metal or plastic pipes may fail.

As the editor of GangLong Fiberglass, I have years of experience and in-depth research, focusing on cable tray products, fiberglass solutions, and grille systems. I incorporate years of industry insights and practical experience into every content, committed to promoting the progress of the industry. At GangLong Fiberglass, my commitment is reflected in every product, from innovative cable trays to durable fiberglass solutions and sturdy grille systems. As an authoritative voice in the industry, my goal is to provide valuable information to professionals and businesses and promote forward-looking solutions.


