- Home
- Aluminium Cable Tray
Straight Aluminium Cable Tray – Wire and Cable Management
Aluminium Cable Tray made of aluminum are lighter and resist corrosion widely used in power plant, petroleum industries.
Lightweight aluminium cable tray CSA/UL/NEMA certified with straight sections, side rails, hardware and horizontal/vertical fittings. Made from aluminum alloy, they balance strength, corrosion resistance, and carrying capacity. FRP cable tray provide a similar lightweight and corrosion-resistant option for various applications. Aluminium trays are ideal for environments like power plants and chemical facilities, where reducing structural load is important. For tougher conditions, stainless steel cable tray offer superior strength and durability.
With over 20 years of experience, GangLong Fiberglass offers a wide range of cable management products, including aluminium and stainless steel trays, FRP cable ladder, and metal framing. Known for long-term corrosion resistance and strength, GangLong’s solutions are suitable for both small and large-scale projects, backed by advanced manufacturing and excellent customer support.
Simplifying Your Life: Key Functionalities

| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Aluminium Cable Tray |
| Material | Aluminium Alloy, Cold-Rolled Steel Plate, Stainless Steel |
| Surface Finish | Electrostatic Spraying, Galvanized, Hot-Dip Zinc, Powder Coated, Anodized |
| Width Options | 50mm - 1200mm |
| Length Options | 0.6m - 6m |
| Thickness | 0.8mm - 3.0mm |
| Side Rail Height | 25mm - 400mm (customizable) |
| Max Working Load | Varies according to size |
| Color | Silver, Black, White, Grey, or Custom Color |
| Application | High and low voltage power cable laying, Large diameter cable support, Industrial, Construction, Network, Renewable energy (Solar Systems) |
| Installation Type | Overhead, Floor-mounted, Wall-mounted |
| Heat Dissipation | Excellent ventilation for cooling and cable longevity |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, suitable for humid and chemical-exposed environments |
| Weight | Lightweight, easy to install |
| Accessories | Cable Trunking, Ladders, Perforated Cable Tray, Wire Mesh Tray, Raceway Systems |
| Sample Service | Free sample available |
| MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) | 100 pieces |
| Durability | Long-lasting, suitable for harsh environments |
| Brand | GangLong Fiberglass |
| Port of Origin | Hebei, China |
| Packaging | Standard export packaging or as per customer request |
News
- Exploring the Benefits of Carbon Fiber Apparel
- How to Work with Carbon Fiber Successfully
- Carbon Fiber Suit: The Future of Lightweight Armor
- Is Carbon Fiber Armor the Future of Protection?
- Why White Carbon Fiber is Popular in Automotive Design
- Transparent Carbon Fiber Sheets: Strength Meets Clarity in Design
- Chopped Carbon Fiber Mat for Lightweight Reinforcement
- Carbon Fiber EG Hatch: Upgrade Your Civic Today
- The Benefits of Using Structural Carbon Fibre in Engineering
- How Many Layers of Layered Carbon Fiber Are Needed?
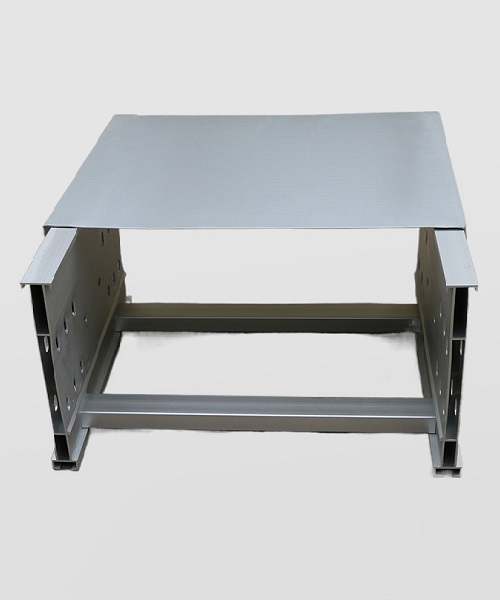

Aluminium Cable Tray Sizes
Aluminum cable trays are widely used in electrical systems to support and route cables. They are known for their lightweight, corrosion resistance, and durability. Below is a detailed description of the common sizes and specifications of aluminum cable trays:
Types of Aluminum Cable Trays
- Ladder Type: Composed of two longitudinal side rails connected by individual rungs, suitable for heavy cables or outdoor installations.
- Perforated Type: Flat bottom trays with perforations for ventilation, ideal for indoor applications with medium to lightweight cables.
- Solid Bottom Type: Fully enclosed trays for complete cable protection against environmental factors.
- Wire Mesh Type: Made of interconnected wires, often used for low-voltage or communication cables.
Standard Dimensions
The sizes of aluminum cable trays are typically based on the following parameters:
Width:
Common options include 100 mm, 150 mm, 200 mm, 300 mm, 450 mm, 600 mm, 750 mm, and 900 mm. The width selection depends on the volume and type of cables to be supported.Height (Depth):
Typical depths are 25 mm, 50 mm, 75 mm, 100 mm, and 150 mm. Deeper trays are ideal for larger cable diameters or bundled cables.Length:
Standard tray lengths are 2.5 meters, 3 meters, or 6 meters. Tray length may vary based on installation requirements or specific project needs.- Thickness:
The thickness of aluminum cable trays varies to meet strength and load requirements, with standard thickness ranging from 1.5 mm to 3.0 mm, or more for heavy-duty trays.
Load Classifications:
- Light Duty: Supports small bundles of cables, often used in office or commercial buildings.
- Medium Duty: Suitable for most industrial applications.
- Heavy Duty: For heavy cables, typically used in power plants, oil refineries, or large infrastructure projects.
Accessories and Fittings:
To ensure proper cable management and secure installation, the following accessories are available in matching sizes:
- Bends: Horizontal, vertical, or angled to change the direction of cable trays.
- Tees and Crosses: For branching cables in multiple directions.
- Reducers: Adjust tray width to accommodate different cable bundle sizes.
- Covers: Available in solid, perforated, or vented designs to protect cables.
Compliance Standards:
Aluminum cable trays are manufactured according to standards like:
- NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association).
- IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission).
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials).
Benefits of Aluminium Cable Tray
Aluminium cable trays are widely preferred in electrical installations for their numerous advantages, making them a popular choice for both industrial and commercial applications. Below are the expanded benefits of aluminium cable trays:
Lightweight
Aluminium cable trays are significantly lighter than steel or other metal trays, which makes them easier to handle and transport. Their lightweight nature reduces labor costs and simplifies the installation process, especially in large-scale projects or areas where structural support is limited. This makes them a cost-effective option for projects requiring large volumes of cable management.
Corrosion Resistance
Aluminium naturally resists corrosion, even in harsh environments such as industrial facilities, coastal areas, or chemical plants. This corrosion resistance eliminates the need for additional coatings or treatments to protect the trays from rust. As a result, aluminium cable trays provide a long-lasting solution, reducing maintenance costs and increasing the lifespan of electrical installations.
Durability
While lightweight, aluminium is a durable material that can withstand mechanical stress and harsh environmental conditions. It is capable of supporting high loads and performing well in demanding environments, making it suitable for various applications, including industrial, commercial, and residential installations. Its strength and resilience ensure that it remains a reliable choice for cable management systems.
Low Maintenance
Thanks to their corrosion resistance, aluminium cable trays require minimal maintenance. They retain their integrity and appearance over time, reducing the need for repairs or replacements. This translates into lower long-term maintenance costs and ensures that the system remains efficient without frequent upkeep, providing additional cost savings for users.
Thermal Conductivity
Aluminium offers excellent thermal conductivity, helping dissipate heat generated by cables more effectively. This property improves the safety and efficiency of electrical installations, as it reduces the risk of overheating and ensures that cables remain within their safe operating temperature range. Enhanced thermal management is especially crucial for high-power electrical systems.
Cost-Effective
Although aluminium trays may have a higher initial cost compared to some other materials, their long-term advantages make them cost-effective. The benefits of aluminium, including durability, low maintenance, and ease of installation, contribute to lower overall project costs and increased return on investment over the trays’ lifespan. This makes them an economical choice in the long run.
Environmentally Friendly
Aluminium is a highly recyclable material, making aluminium cable trays an environmentally friendly choice. By using recycled aluminium, the environmental footprint of manufacturing is reduced. Additionally, aluminium’s durability and long lifespan contribute to sustainability, as fewer replacements are needed over time, minimizing waste.
Ease of Installation
The lightweight and flexible nature of aluminium trays allows for easy cutting, drilling, and assembly during installation. This simplicity reduces installation time and labor costs. Aluminium cable trays are quicker to install than heavier alternatives, allowing for faster project completion, especially in large installations or where time constraints are a factor.
Non-Magnetic
Aluminium is a non-magnetic material, which means it does not interfere with electrical signals. This feature is particularly valuable in installations involving sensitive electronic equipment or communication systems. By avoiding magnetic interference, aluminium trays help maintain the integrity of signals and ensure smooth operation of electrical systems.
Aesthetic Appeal
Aluminium cable trays have a clean, modern appearance that suits a variety of installations. Their natural finish resists tarnishing, providing a professional and polished look. This makes them ideal for open installations in visible areas, ensuring that the cable management system looks as good as it performs.
Fire Resistance
Aluminium is non-combustible, providing an added layer of safety in installations where fire resistance is critical. This property ensures that aluminium trays can help prevent the spread of fire in the event of an electrical fault, enhancing the safety of electrical systems and contributing to fire protection standards in sensitive environments.
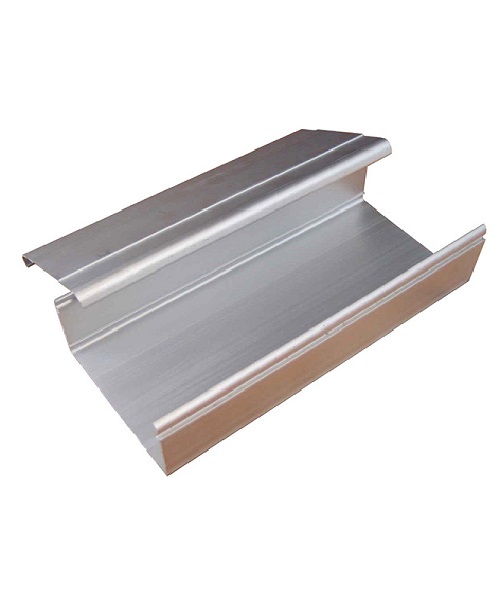
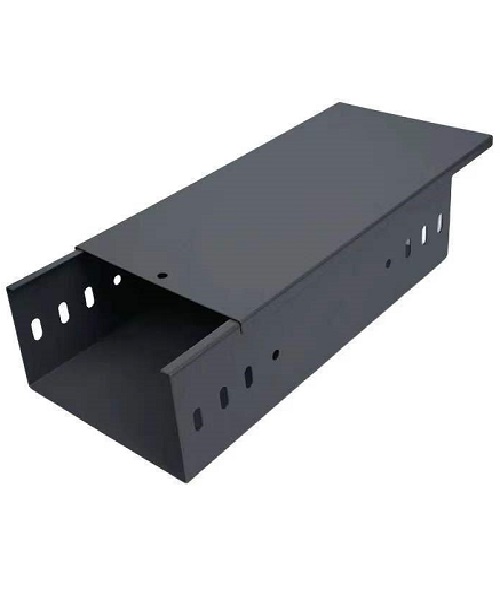


Standards of Aluminium Cable Tray
Aluminum cable trays are governed by several standards that ensure their quality, safety, and performance in electrical installations. Key standards include:
NEMA VE 1: Metal Cable Tray Systems
NEMA VE 1 specifies the requirements for metal cable trays, including aluminum. It covers construction, testing, and performance for compliance with the Canadian Electrical Code (CE Code) and National Electrical Code® (NEC). These standards ensure that aluminum trays meet the necessary safety and operational criteria for efficient cable management in electrical systems.
NEMA VE 2: Metal Cable Tray Installation Guidelines
NEMA VE 2 provides installation guidelines for metal cable trays, including aluminum models. The standard outlines shipping, handling, storing, and installation procedures. It ensures the trays are installed safely and comply with relevant regulations, supporting the proper function of cable management systems in electrical and communication systems, reducing the risk of installation errors and system failures.
IEC 61537: Cable Management – Cable Tray Systems and Cable Ladder Systems
IEC 61537 specifies the requirements for cable tray systems, including aluminum trays, used to support cables and other electrical equipment. It includes testing and performance criteria for safe, reliable cable management in electrical and communication systems. The standard ensures that aluminum trays maintain structural integrity and meet quality requirements under various environmental conditions, contributing to the overall safety and efficiency of the installation.
BS EN 61537: Cable Management – Cable Tray Systems and Cable Ladder Systems
BS EN 61537 aligns with IEC 61537 and provides specifications for cable tray systems, including those made from aluminum. It covers mechanical strength, electrical continuity, and corrosion resistance, ensuring the trays perform effectively in diverse conditions. The standard ensures that aluminum trays provide reliable support for cables while maintaining long-term durability, safety, and efficiency in electrical and communication systems installations.
Eurocode 9: Design of Aluminium Structures
Eurocode 9 provides guidelines for designing aluminum structures, which can be applied to aluminum cable tray systems. Though not specific to trays, the guidelines ensure that aluminum components are structurally sound and meet safety standards. The code helps manufacturers design trays that can safely handle loads and endure environmental conditions, ensuring the overall stability and strength of aluminum cable tray systems in industrial and commercial installations.
Wholesale Aluminium Cable Tray Price List
Aluminum cable trays are essential components in electrical installations, offering lightweight and corrosion-resistant solutions for cable management. The pricing of these trays varies based on factors such as type, size, material thickness, and manufacturer. Below is an overview of common types and their approximate price ranges:
Types of Aluminum Cable Trays
- Ladder Type: Features two longitudinal side rails connected by rungs, suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Perforated Type: Flat-bottom trays with perforations for ventilation, ideal for indoor use.
- Solid Bottom Type: Fully enclosed trays providing maximum cable protection.
- Wire Mesh Type: Constructed from interconnected wires, often used for low-voltage or communication cables.
Approximate Price Ranges
Ladder Type:Prices typically range from $4 to $9.67 per meter, depending on specifications and manufacturer.
Perforated Type:Prices generally range from $0.9 to $9 per piece, varying with size and material thickness.
Solid Bottom Type:Pricing information is less commonly listed online; it’s advisable to contact suppliers directly for quotes.
Wire Mesh Type:Prices range from $0.8 to $9.9 per piece, depending on dimensions and manufacturer.
Factors Influencing Prices
- Size: Wider and deeper trays require more material, increasing costs.
- Material Thickness: Thicker trays offer higher load capacities but are more expensive.
- Surface Finish: Additional treatments like powder coating or anodizing can add to the price.
- Manufacturer and Brand: Reputable brands may charge premium prices for quality assurance.
- Order Quantity: Bulk purchases often come with discounts.
Purchasing Tips
- Compare Suppliers: Review multiple manufacturers to find competitive pricing and quality.
- Request Quotes: For large projects, obtain detailed quotes to understand cost breakdowns.
- Check Certifications: Ensure products meet relevant standards (e.g., NEMA, IEC) for safety and performance.
Ganglong Fiberglass are among the pioneers in the industry, engaged in manufacturing, supplying and exporting Aluminum Cable Trays for our revered customers. The offered cable trays are designed with utmost precision, with the aid of optimum quality aluminum procured from known vendors. Owing to their sturdy structure and excellent heat resistance, these trays are widely acknowledged.
Bulk Order Discounts and Customization Costs
- Discounts: Many manufacturers offer tiered pricing for bulk orders, such as 5% off for 500 meters or 10% off for 1,000 meters.
- Customization: Special designs, extra coatings, or specific sizes may add 10%–30% to standard prices.
Wholesale aluminium cable trays are available at various price points depending on type, size, and customization. Buyers should consider material quality, durability, and supplier reliability when making bulk purchases. For the best pricing, it’s advisable to compare quotes from multiple manufacturers and negotiate based on order quantity.
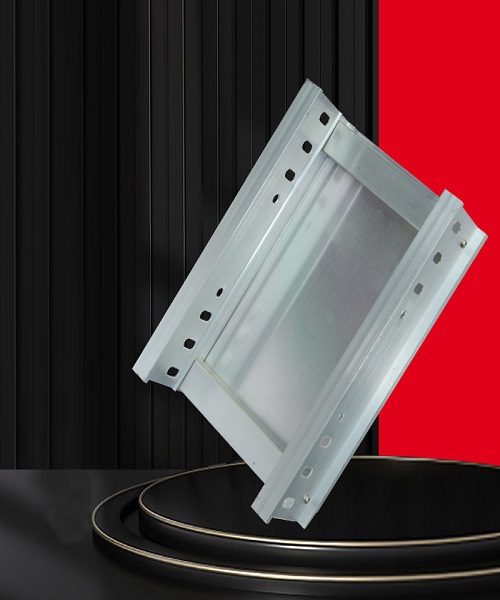

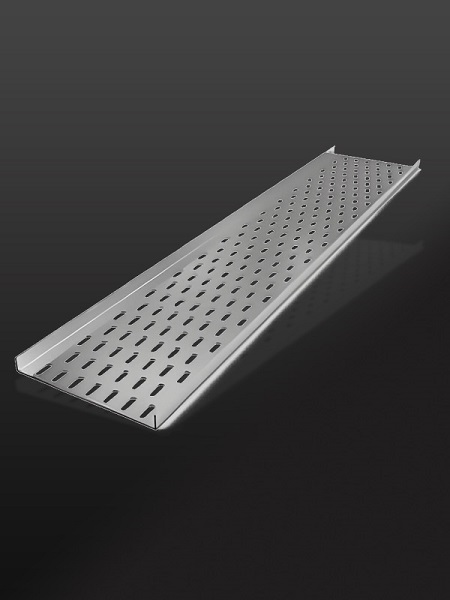
Straight Aluminium Cable Tray: Wire and Cable Management
Straight aluminium cable trays are an essential component of wire and cable management systems. They are widely used in commercial, industrial, and residential applications for organizing, supporting, and protecting electrical cables. Here’s a detailed overview of their features and advantages:
Definition
A straight aluminium cable tray is a continuous support system designed to route and manage electrical cables. These trays are typically straight in design, available in various widths and depths, and made from lightweight, corrosion-resistant aluminium.
Features and Benefits
Lightweight and Strong
Aluminium is lightweight, making it easy to handle, transport, and install. Despite being lightweight, aluminium has a high strength-to-weight ratio, allowing it to support heavy cable loads efficiently. This combination of low weight and strength reduces installation time and labor costs, making it a preferred choice for many cable management applications that require strength without added weight.
Corrosion Resistance
Aluminium is naturally resistant to corrosion, even in harsh environments like coastal regions, industrial plants, and outdoor installations. This natural resistance eliminates the need for additional coatings or treatments, ensuring that the trays remain durable and reliable over time. The corrosion-resistant properties of aluminium also reduce maintenance costs, making it a long-lasting solution in environments exposed to moisture and chemicals.
Heat Dissipation
Aluminium has excellent thermal conductivity, which helps dissipate heat efficiently. This makes aluminium cable trays ideal for systems handling high current loads, as they prevent the risk of cable overheating. Proper heat dissipation ensures that cables remain within safe operating temperatures, enhancing the longevity and performance of the electrical system and reducing the chances of overheating-related failures.
Versatile Design
Straight aluminium cable trays are available in various sizes and can be customized with accessories like bends, tees, and reducers. This versatility allows the trays to be adapted to complex and dynamic electrical systems, ensuring they meet specific installation requirements. The flexible design ensures that aluminium trays can be used for a wide range of applications, from simple cable runs to intricate, customized layouts.
Aesthetic and Professional Appearance
Aluminium trays offer a clean, modern look, making them suitable for exposed installations in offices, commercial spaces, and public buildings. Their natural finish resists tarnishing, giving installations a professional and polished appearance. This aesthetic appeal makes aluminium trays a great choice for environments where the cable management system is visible and where maintaining a professional look is important.
Non-Magnetic and Non-Sparking
Aluminium is non-magnetic, which ensures there is no interference with sensitive electronic equipment or communication systems. Additionally, aluminium is non-sparking, providing added safety in environments where flammable materials are present. These properties make aluminium trays ideal for hazardous areas, such as chemical plants, power stations, and other industrial applications where safety and the integrity of equipment are critical.
Applications
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings such as factories, refineries, and manufacturing plants, aluminium cable trays are essential for managing large volumes of power and data cables. Their corrosion resistance and strength make them ideal for harsh environments. These trays are designed to withstand heavy loads, environmental stresses, and the rigorous demands of industrial equipment, ensuring reliable and safe cable management systems in complex industrial processes.
Commercial Applications
In commercial environments like office buildings, shopping malls, and data centers, aluminium cable trays are used to organize cables for both power distribution and communication systems. Their lightweight nature and customizable design make them suitable for managing cables in expansive commercial buildings. Aluminium trays help maintain a neat and organized system, contributing to the overall efficiency of electrical setups, and ensuring easy access for maintenance and modifications.
Residential Applications
For high-end residential projects, aluminium cable trays are used to ensure efficient cable organization within the home. These trays are particularly beneficial for large homes with sophisticated wiring systems, such as those with integrated home automation, security systems, or audio-visual setups. Their aesthetic appeal, along with their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, makes them ideal for maintaining an organized and visually clean cable system in residential spaces.
Special Environments
Aluminium cable trays are also used in special environments where high resistance to corrosion, temperature extremes, or environmental stresses is needed. This includes chemical plants, offshore platforms, and other facilities with harsh operating conditions. In such environments, aluminium’s corrosion resistance ensures that the trays will maintain their integrity over time, even when exposed to chemicals, saltwater, or high temperatures, providing long-lasting and reliable cable management solutions.
Wire and Cable Management
- Routing: Provides a clear path for cables, ensuring neat and organized installations.
- Support: Prevents sagging and damage by evenly distributing cable weight.
- Protection: Shields cables from physical damage, reducing wear and tear.
- Expansion: Simplifies adding or removing cables during system upgrades.
Straight aluminium cable trays are a highly efficient solution for wire and cable management, offering durability, versatility, and safety. Their lightweight design, combined with excellent thermal and corrosion resistance, makes them an ideal choice for a wide range of electrical installations.
Thank you for your interest in our products. To receive our pricelist or for any inquiries, please fill out the form below. We will get back to you within 24 hours.
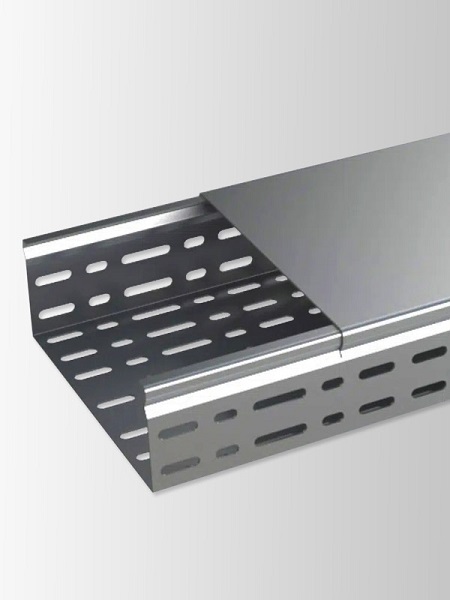
Aluminium Cable Tray Manufacturers: GangLong Fiberglass
GangLong Fiberglass is a leading manufacturer recognized for its comprehensive range of aluminium cable trays and robust product offerings. Known for providing high-quality, durable, and well-engineered trays, GangLong Fiberglass caters to diverse industrial needs. With a reputation for excellence in cable management systems, we supply trays designed to meet both standard and specialized requirements, offering flexibility and performance. As a global leader, we specialize in customizable trays made from high-performance materials, ensuring they are suitable for a wide range of applications.
Certifications
At GangLong Fiberglass, we prioritize quality and safety. Our aluminium cable trays are manufactured to meet stringent industry standards and certifications, such as ISO and UL. These certifications ensure that our products comply with international quality requirements, providing customers with peace of mind regarding the safety, durability, and performance of our cable management systems. Our commitment to maintaining high standards guarantees reliable products for any installation.
Product Range
GangLong Fiberglass offers a diverse selection of aluminium cable trays in various sizes and configurations. From standard trays to highly customizable solutions, we cater to specific project requirements. Whether you need trays for heavy-duty industrial applications or lighter commercial installations, we have options designed to handle different cable volumes and environmental conditions. Our versatile range ensures that we can meet the unique needs of every client, providing tailored solutions that are both functional and cost-effective.
After-Sales Support
Reliable after-sales support is essential for ensuring the proper installation, maintenance, and operation of cable management systems. GangLong Fiberglass provides comprehensive technical support and customer service to assist clients throughout the product lifecycle. Our expert team is available to guide customers during installation, troubleshoot issues, and address any product-related queries. Our dedication to customer satisfaction ensures that you receive ongoing assistance to maximize the performance and longevity of our aluminium cable trays.
What is Aluminum Ladder Cable Tray?
An Aluminum Ladder Cable Tray is a type of cable management system designed to support and organize electrical cables, especially in industrial and commercial installations. It is constructed with two longitudinal side rails connected by transverse rungs, creating a ladder-like structure. The use of aluminum makes it lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and durable, making it ideal for various environments.
Key Features of Aluminum Ladder Cable Trays
Aluminum ladder cable trays are a widely used solution for organizing and supporting cables in electrical installations. Below are the key features and advantages of aluminum ladder cable trays:
Material
Aluminum ladder cable trays are made from high-quality aluminum, known for its excellent corrosion resistance. This material is lightweight, making the trays easy to handle and install, while also providing good thermal conductivity. The inherent corrosion resistance of aluminum ensures that these trays are ideal for use in environments where exposure to moisture, chemicals, or harsh conditions is common. Additionally, the lightweight nature of aluminum reduces the overall structural load, making it easier to support and install without compromising strength.
Design
Side Rails: The side rails of the ladder tray provide structural integrity and load-bearing capacity, ensuring the system can support heavy cables without sagging. The side rails also help maintain the tray’s rigidity, even in challenging environments.
Rungs: The rungs are positioned at regular intervals, typically 6 to 12 inches apart, allowing cables to be easily attached while providing adequate air circulation around the cables. This open design enhances heat dissipation, reducing the risk of overheating. The rungs also provide a simple means for securing cables, ensuring a neat and organized installation.
Sizes
Aluminum ladder cable trays come in a variety of sizes to accommodate different cable loads and installation needs. They are available in various widths, ranging from 100 mm to 1000 mm, to cater to both small and large-scale cable installations. Depths typically range from 25 mm to 150 mm, depending on the cable size and quantity. Standard tray lengths are usually 2.5 meters or 3 meters, but custom lengths can be provided to suit specific project requirements. This variety of sizes ensures that the trays can be tailored to meet the demands of any electrical installation.
Load Capacity
Aluminum ladder cable trays are designed to support medium to heavy cable loads, including power cables, control cables, and communication cables. The robust design, combined with the strong material, allows these trays to handle large volumes of cables without compromising the integrity of the system. The trays provide a secure and stable platform for cables, even in industrial environments that require high cable support capacity.
Ventilation
The open design of aluminum ladder cable trays ensures excellent ventilation, promoting air circulation around the cables. This airflow helps dissipate heat generated by the cables, which is crucial for maintaining safe operating temperatures. Efficient heat dissipation reduces the risk of cable overheating, ensuring the reliability and longevity of the electrical system. This feature is especially important for installations involving high-power cables or systems that operate under heavy loads.
Applications
- Industrial Settings: Power plants, factories, and refineries.
- Commercial Buildings: For structured wiring systems.
- Marine and Offshore: Due to its corrosion resistance.
- Electrical Distribution Systems: For routing and supporting power and control cables.
Accessories
- Horizontal and Vertical Elbows: To change cable tray direction.
- Reducers: To connect trays of different widths.
- Splice Plates: To join sections of the tray.
- Covers: Optional covers for additional cable protection.
The Aluminum Ladder Cable Tray is a versatile and efficient solution for managing and supporting cables in a wide range of environments, offering a balance of strength, durability, and ease of installation.


Installing Aluminium Cable Tray
Installing aluminium cable trays requires careful planning and adherence to safety standards to ensure proper cable support, protection, and organization. Below is a step-by-step guide for installing aluminium cable trays effectively:
Pre-Installation Planning
Site Assessment
- Survey the site to determine the cable tray path.
- Identify potential obstacles, such as beams, pipes, or existing equipment.
- Confirm that the structure can support the cable tray system.
Cable Tray Design
- Choose the appropriate size and type of aluminium cable tray based on the cable load and layout.
- Plan for expansion by allowing extra capacity in the tray design.
- Incorporate accessories such as bends, tees, and reducers for complex routing.
Compliance with Standards
- Ensure compliance with relevant standards like NEMA VE 1/VE 2, IEC 61537, and local electrical codes.
- Verify grounding and bonding requirements for electrical safety.
Materials and Tools
Required Materials
- Aluminium cable trays (straight sections, fittings, and accessories)
- Support systems (hangers, brackets, or cantilever arms)
- Fasteners, bolts, and clamps
- Insulating materials (if required)
Tools
- Measuring tape
- Level
- Drill
- Screwdriver
- Hacksaw or power saw for cutting aluminium trays
- Safety gear (gloves, goggles, and helmets)
Installation Steps
Marking the Route
- Mark the cable tray route on walls, ceilings, or floors using chalk lines or laser tools.
- Ensure a straight and level path with appropriate clearance from other systems.
Installing Supports
- Install brackets, hangers, or cantilever arms at regular intervals (typically 1.5–2 meters, or as specified in the design).
- Secure supports to the structure using bolts or anchors.
- Verify that the supports are level and properly aligned.
Assembling the Cable Tray
- Cut aluminium trays to the required lengths if necessary.
- Assemble straight sections and fittings (bends, tees, etc.) using couplers and bolts.
- Ensure all connections are secure and aligned.
Mounting the Tray
- Place the assembled cable tray on the supports.
- Secure the tray to the brackets or hangers using clamps or fasteners.
- Maintain the required spacing between adjacent trays and other systems.
Cable Routing
- Lay cables in the tray carefully to avoid tangling or damage.
- Group cables based on type (e.g., power, communication) and separate them with dividers if needed.
- Avoid overfilling the tray; follow the fill capacity guidelines.
Securing Cables
- Use cable ties or clamps to secure cables at regular intervals.
- Leave some slack for thermal expansion and contraction.
Electrical and Safety Considerations
Grounding
- Ground the aluminium cable tray to ensure electrical safety.
- Use grounding straps or connectors as per the design.
Insulation
- Use insulating materials if the cables are sensitive to temperature changes or require additional protection.
Fire Safety
- Maintain clearances from flammable materials.
- Follow firestop procedures at walls or floor penetrations.
Inspection and Testing
Visual Inspection
- Check for proper alignment, secure connections, and adequate support spacing.
- Verify that cables are routed and secured correctly.
Load Testing
- Confirm the cable tray system can support the expected load without sagging.
Final Testing
- Test the grounding system for electrical continuity.
- Inspect for compliance with design specifications and safety codes.
Maintenance
- Regularly inspect the cable tray for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Clean debris or dust that may accumulate in the tray.
- Update cable routing and tray configurations as needed during system upgrades.
Tips for Success
- Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installation.
- Use proper tools and techniques to avoid damaging the aluminium trays.
- Coordinate with other trades (e.g., HVAC, plumbing) to prevent conflicts.
By following these steps, you can ensure a safe, efficient, and compliant installation of aluminium cable trays for effective wire and cable management.
FAQs about Aluminium Cable Tray
What should aluminum cable trays be coated with?
Are aluminum cables good?
How to clean an aluminum cable tray?
What is the difference between a cable ladder and a cable tray?
Which cable tray material is best for corrosive environments?
What are the safety procedures in installing cable trays?
What is aluminum cable tray used for?
Industrial and Commercial Buildings: To support power, control, and communication cables in environments where corrosion resistance is essential.
Outdoor Installations: Due to aluminum's natural resistance to corrosion, aluminum trays are often used in outdoor settings, including power plants, chemical plants, and offshore installations.
High-Vibration Environments: Aluminum’s lightweight nature makes it suitable for environments with high vibrations, such as in transportation and manufacturing facilities, where a lower mass reduces stress on supports and anchors.
What are the disadvantages of aluminum cables?
Lower Conductivity: Aluminum has lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, meaning that larger aluminum cables are required to carry the same current as copper cables.
Oxidation: Aluminum forms an oxide layer when exposed to air, which can increase electrical resistance at connections if not properly managed.
Mechanical Strength: Aluminum is more prone to breaking or becoming brittle under stress compared to copper, making it less suitable for environments with frequent bending or physical stress.
Connection Issues: Special care is needed when connecting aluminum wires, as improper connections can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards.
Thermal Expansion: Aluminum expands more than copper when heated, which can loosen connections over time, necessitating regular inspection and maintenance.
Why is aluminium good for cables?
Lightweight: Aluminum is about one-third the weight of copper, making it easier to handle and install, especially in large-scale applications.
Cost-Effective: Aluminum is generally less expensive than copper, making it a cost-effective alternative for electrical wiring, particularly in large installations.
Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer that resists corrosion, making it suitable for outdoor and corrosive environments.
Abundant Availability: Aluminum is more abundant than copper, leading to lower material costs and more stable pricing.
What is the NEC code for cable tray support?
Does aluminum cable rust?
What are aluminum trays used for?
Food Packaging and Serving: Commonly used in the food industry for packaging, baking, and serving food, thanks to their lightweight and non-reactive nature.
Electrical Cable Management: Aluminum cable trays are used to support and organize electrical cables in industrial, commercial, and outdoor environments, offering corrosion resistance and ease of installation.
Transporting Materials: Lightweight and durable, aluminum trays are used in various industries for transporting tools, equipment, and materials.
Aerospace and Automotive: Due to their light weight and strength, aluminum trays and components are used in vehicles and aircraft to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency.
When should l use aluminum wiring?
Large-Scale Power Distribution: In applications where the size and weight of copper cables would be prohibitive, such as in overhead transmission lines or large feeder cables.
Cost-Sensitive Projects: When budget constraints make aluminum a more viable option compared to copper, especially in large installations.
Outdoor and Corrosive Environments: Due to its corrosion resistance, aluminum wiring is suitable for outdoor installations or in environments where moisture and corrosive elements are present.
Retrofits in Older Buildings: Aluminum wiring can be used as a replacement for existing wiring if proper connections are made and the system is regularly inspected.
What do you put on aluminum wire connections?
Anti-Oxidant Compound: Apply an anti-oxidant paste or compound, such as Noalox or Ox-Gard, to the aluminum wire connections to prevent oxidation and ensure good electrical contact.
Aluminum-Compatible Connectors: Use connectors specifically designed for aluminum wire, such as AL/CU (Aluminum to Copper) rated connectors, which are designed to handle the different expansion rates of aluminum.
Torque Wrench: Use a torque wrench to tighten connections to the manufacturer's specified torque, ensuring a secure connection that accommodates aluminum's thermal expansion properties.
What is the difference between cable tray and raceway?
Design:
Cable Tray: An open or semi-open structure used to support and organize multiple cables, allowing for ventilation and easy access.
Raceway: A fully enclosed channel, often rectangular, used to protect cables from environmental factors and physical damage.
Applications:
Cable Tray: Used in industrial and commercial settings where large numbers of cables need to be supported and where flexibility and accessibility are important.
Raceway: Used in environments where cables need to be concealed and fully protected, often in office buildings or areas where aesthetics and safety are priorities.
Accessibility:
Cable Tray: Provides easy access for cable installation, maintenance, and upgrades.
Raceway: Offers limited accessibility, as the cables are enclosed, making modifications more challenging.
What is another name for a cable tray?
What is the difference between cable duct and cable tray?
Design:
Cable Duct: An enclosed channel, often made of plastic or metal, used to route and protect cables along walls, ceilings, or floors. It keeps cables hidden and protected from external damage.
Cable Tray: An open or semi-open structure used to support and organize cables over longer distances, allowing for ventilation and easy access.
Applications:
Cable Duct: Used where cables need to be concealed and protected from physical damage, often in commercial or residential buildings for aesthetic and safety reasons.
Cable Tray: Used in industrial and commercial environments where large numbers of cables need to be supported, managed, and easily accessible for maintenance and upgrades.
Accessibility:
Cable Duct: Offers less accessibility, as cables are enclosed and more difficult to modify once installed.
Cable Tray: Provides easier access for adding, removing, or rearranging cables as needed.
Is aluminium cable cheaper than copper?
What is the downside of aluminum wiring?
Oxidation: Aluminum oxidizes when exposed to air, forming a non-conductive layer that can increase resistance and cause connections to overheat if not properly treated.
Thermal Expansion: Aluminum expands more than copper when heated, which can lead to loose connections over time, increasing the risk of electrical fires.
Lower Conductivity: Aluminum has lower electrical conductivity than copper, so larger diameter wires are needed to carry the same current.
Brittleness: Aluminum is more prone to becoming brittle and breaking, especially at connections where repeated stress or bending occurs.
Special Handling: Aluminum wiring requires special connectors and anti-oxidant compounds to ensure safe and reliable connections, which can complicate installation and maintenance.
Why is aluminium not used for electrical wiring?
Why use aluminium instead of copper?
Cost-Effectiveness: Aluminum is significantly cheaper than copper, making it a more economical choice for large-scale power distribution.
Weight: Aluminum is much lighter than copper, which makes it easier to handle and reduces the overall weight load in structures, particularly important in overhead power lines and large cable installations.
Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer, making it resistant to corrosion, which is beneficial in outdoor and industrial environments.
What is the disadvantage of aluminium cable compared to copper cable?
Lower Conductivity: Aluminum has only about 60% of the conductivity of copper, requiring larger cables to carry the same amount of current.
Thermal Expansion: Aluminum expands more when heated, which can cause loose connections and potential safety hazards over time.
Oxidation: The formation of aluminum oxide can increase resistance at connections, leading to overheating if not properly managed.
Mechanical Strength: Aluminum is less durable than copper and more prone to fatigue, making it more likely to break or become damaged over time.
What is the advantage of aluminium cable?
Cost Savings: Aluminum is cheaper than copper, making it a cost-effective choice for large installations.
Lightweight: Aluminum is lighter than copper, which reduces the physical load on structures and makes installation easier.
Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum's natural oxide layer provides protection against corrosion, particularly useful in outdoor and industrial environments.
Abundance: Aluminum is more abundant than copper, ensuring a stable supply and more consistent pricing.
Why is aluminium nowadays replacing copper for use in electrical cables?
Economic Considerations: The lower cost of aluminum makes it attractive for large-scale power distribution projects, particularly where budget constraints are significant.
Weight Advantages: Aluminum’s lighter weight reduces structural loads and simplifies transportation and installation, especially in overhead power lines.
Material Availability: Aluminum’s greater abundance compared to copper ensures a more stable and sustainable supply chain.
Is aluminum wiring a big deal?
How to tell if wire is copper or aluminum?
Color: Strip away the insulation to reveal the metal. Copper wire will appear reddish-brown, while aluminum wire will be silvery-gray.
Weight: Copper is denser and heavier than aluminum, so copper wire will feel heavier compared to aluminum wire of the same size.
Markings: Check for markings on the insulation. Aluminum wires are often marked with ""AL"" or ""Aluminum,"" whereas copper wires might have no such marking.
What is stronger, copper or aluminum?
When to use aluminium wire?
Large Power Distribution: Ideal for overhead power lines and large feeder cables where weight and cost savings are significant factors.
Cost-Constrained Projects: When the budget is a primary concern, aluminum wire offers a more economical alternative to copper.
Corrosive Environments: Aluminum is often used in environments where corrosion resistance is important, such as in outdoor installations or industrial settings.
High-Voltage Applications: Aluminum is frequently used in high-voltage transmission lines due to its light weight and cost advantages.
How much does it cost to replace aluminum wiring with copper?
Can luse aluminium wire for AC?
Does aluminum cable tray need to be grounded?
Why is aluminum wire not used in residential electrical wiring?
Oxidation: Aluminum oxidizes when exposed to air, forming a non-conductive layer that can increase resistance at connections, leading to overheating and potential fire hazards.
Thermal Expansion: Aluminum expands more than copper when heated, which can cause connections to loosen over time, further increasing the risk of electrical fires.
Historical Issues: In the 1960s and 1970s, many homes were wired with aluminum, and a significant number of fires were attributed to faulty aluminum wiring. This led to a shift back to copper wiring, which is considered safer for residential use.
Connection Reliability: Aluminum wiring requires special connectors and techniques, and improper installation can lead to dangerous conditions.
What is the NEC code for cable tray grounding?
Does tray cable need to be in conduit?
Exiting the Tray: If tray cable exits the cable tray and enters a hazardous location, a conduit might be required to provide additional protection.
Mechanical Protection: In environments where the cable is subject to potential mechanical damage or where additional protection is needed, a conduit might be required.
Always consult the NEC and local codes to determine whether conduit is required in specific situations.
Should you earth cable tray?
Is it necessary to provide tie down cables installed in a cable tray?
Maintaining Organization: Keeping the cables neatly organized within the tray.
Preventing Sagging: Securing the cables prevents them from sagging, which can cause mechanical strain and potential damage.
Avoiding Abrasion: Tying down cables reduces the risk of abrasion against the tray edges, which could compromise the cable insulation over time.
Ensuring Compliance: NEC and other standards often require cables to be secured at regular intervals to ensure a safe and reliable installation.
Can you attach a ground wire to aluminum?
Use of Compatible Connectors: Use connectors specifically designed for aluminum, such as AL/CU (Aluminum to Copper) rated connectors, to ensure a safe and reliable connection.
Anti-Oxidant Compound: Apply an anti-oxidant compound to the connection point to prevent oxidation, which can increase resistance and reduce the effectiveness of the ground.
Proper Installation: Ensure that the connection is tight and meets the torque specifications recommended by the manufacturer to account for aluminum’s thermal expansion properties.
Can Aluminium cable be used underground?
What aluminum wire can be buried?
Type USE (Underground Service Entrance) Cable: Designed for underground installations, typically used for supplying power from the utility to a residential or commercial building.
Type URD (Underground Residential Distribution) Cable: Often used for distributing power from transformers to residential properties.
These cables are manufactured with moisture-resistant insulation and are designed to withstand the harsh conditions of underground installations.
Do you have to pigtail aluminum ground wire?
Ensure Compatibility: Many electrical devices and connectors are not rated for direct connection with aluminum wire, so a copper pigtail is used to make the final connection.
Prevent Oxidation: Using a copper pigtail helps prevent issues with oxidation at the connection point, which can lead to increased resistance and overheating.
Do l need to replace aluminum wiring?
Condition: If the aluminum wiring is in good condition and has been properly installed with the correct connectors and anti-oxidant compounds, it may not need to be replaced. However, it should be regularly inspected.
Safety Concerns: If the aluminum wiring has shown signs of overheating, loose connections, or if it was installed before current safety standards were developed, it may be advisable to replace it with copper wiring.
Insurance Requirements: Some insurance companies may require the replacement of aluminum wiring due to its history of causing fires, so check with your insurance provider.
If replacement is necessary, it’s important to have it done by a qualified electrician to ensure safety and compliance with local codes.
Is cable tray cheaper than conduit?
What are the 3 main types of cable tray?
Ladder Cable Tray: Consists of two side rails with cross rungs resembling a ladder, providing maximum ventilation and support for large, heavy cables. It is commonly used in industrial environments.
Perforated Cable Tray: Features a flat bottom with holes or slots, allowing for some ventilation while providing more continuous support than ladder trays. It is widely used in commercial and light industrial settings.
Solid Bottom Cable Tray: A completely enclosed tray that offers maximum protection for cables from external damage but provides no ventilation. It is used where cables need to be shielded from environmental factors or where falling debris is a concern.
Can l run thhn in cable tray?
Which cable tray is best?
Ladder Cable Tray: Best for heavy-duty, industrial applications where ventilation is critical and long spans need to be covered.
Perforated Cable Tray: Best for environments where a balance of support, protection, and ventilation is needed, commonly in commercial and light industrial applications.
Solid Bottom Cable Tray: Best for environments where maximum protection from external elements is necessary, such as areas with falling debris or dust.
Can you run cable tray wire in conduit?
What is the difference between cable raceway and cable tray?
Design:
Cable Raceway: An enclosed, often rectangular channel used to protect and conceal cables along walls, floors, or ceilings. It is typically used where cables need to be hidden for aesthetic reasons.
Cable Tray: An open or semi-open structure used to support and organize cables over long distances, providing easy access for maintenance and ventilation.
Applications:
Cable Raceway: Used in environments where cables need to be fully enclosed and protected, often in office buildings or places where aesthetics and safety are important.
Cable Tray: Used in industrial and commercial settings where large volumes of cables need to be supported, organized, and easily accessible.
What is the difference between cable trunking and cable tray?
Design:
Cable Trunking: A fully enclosed rectangular or square channel used to route and protect cables along walls or ceilings, keeping them hidden and protected from physical damage.
Cable Tray: An open or semi-open structure used to support and manage cables over longer distances, allowing for ventilation and easy access.
Applications:
Cable Trunking: Typically used where cables need to be concealed for aesthetic reasons or protected from mechanical damage, often in commercial or residential buildings.
Cable Tray: Used in industrial or commercial environments where large numbers of cables need to be supported and where accessibility and flexibility are important.
Accessibility:
Cable Trunking: Offers less accessibility for cable maintenance and upgrades, as cables are enclosed.
Cable Tray: Provides easier access for adding, removing, or rearranging cables as needed.
Is metal or PVC conduit cheaper?
What are the disadvantages of solid bottom cable tray?
Poor Ventilation: Solid bottom trays do not allow air circulation around the cables, which can lead to overheating, especially for high-current applications.
Heavier Weight: These trays are typically heavier than other types, making them more challenging to install and requiring stronger support structures.
Limited Access: Adding, removing, or modifying cables is more difficult because the cables are enclosed, making maintenance more cumbersome.
Moisture Accumulation: In humid environments, moisture can collect inside the tray, potentially leading to corrosion or cable damage over time.
What is the most cheap type of conduit?
What is the difference between cable tray and wireway?
Design:
Cable Tray: An open or semi-open structure used to support and organize multiple cables along a route, allowing for ventilation and easy access.
Wireway: An enclosed rectangular channel, often with a removable cover, used to protect and route a smaller number of cables, providing more protection than a cable tray.
Applications:
Cable Tray: Used in industrial and commercial settings where large numbers of cables need to be supported over long distances and easy access is required.
Wireway: Used in applications where cables need more protection from physical damage, often in control rooms or smaller installations.
Accessibility:
Cable Tray: Provides easy access for maintenance and cable modifications.
Wireway: Offers access through removable covers but is more enclosed than a cable tray.
Is tray cable rated for conduit?
Thank you for your interest in our products. To receive our pricelist or for any inquiries, please fill out the form below. We will get back to you within 24 hours.
