- Home
- Cable Tray
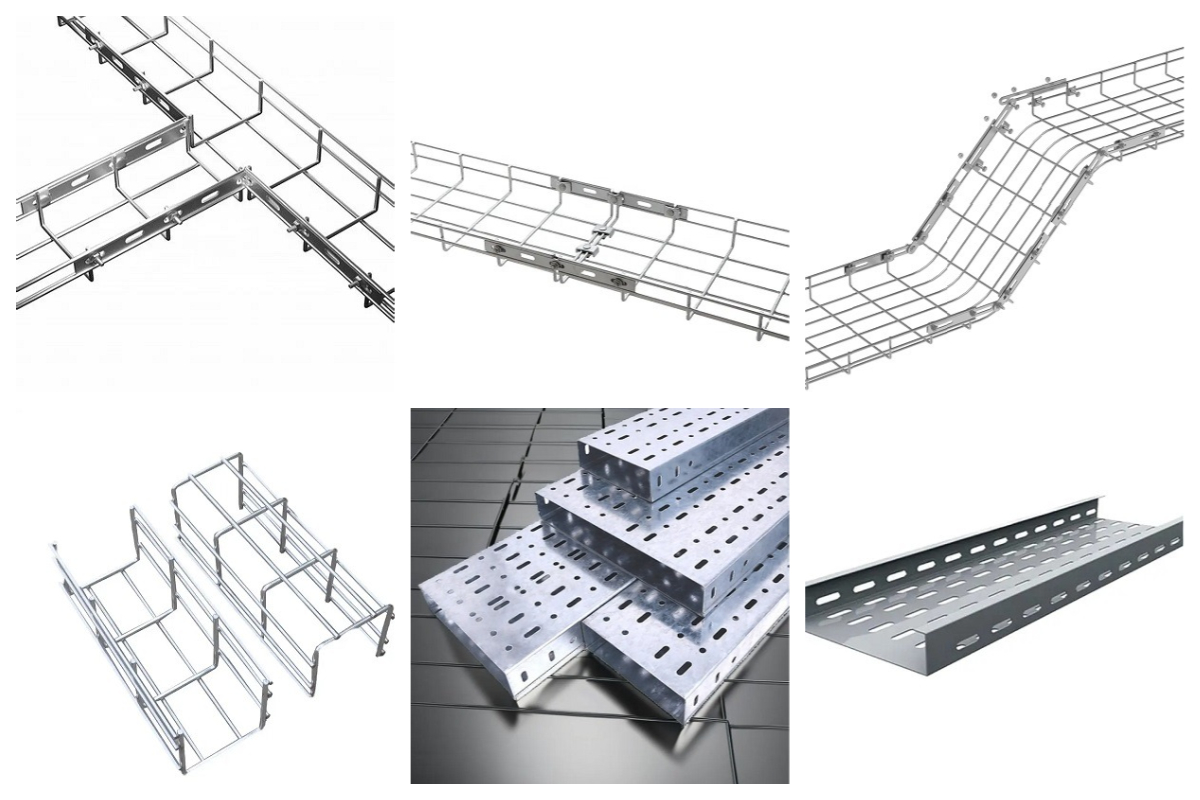
Wire Mesh Cable Tray and Ladder Systems
Sturdy wire mesh cable tray system for data centers & commercial use. Supports 12A/12B loads. Includes prefab assemblies & ladder trays. Our Wire Mesh Cable Trays, precision-engineered from welded steel wire with 24 years of research and over 76,000 miles worldwide, handle everything from oil-rig power routes to data-center cabling. GangLong Fiberglass offers a range of cable-management solutions—stainless steel, aluminum, and FRP cable tray—backed by exceptional quality and service. Essential for modern infrastructure, these cost-effective tray systems provide safe, organized support for electrical and data cables in offices, hospitals, factories, data centers, and warehouses, ensuring cable integrity, hazard prevention, and long-term performance.
News
- Exploring the Benefits of Carbon Fiber Apparel
- How to Work with Carbon Fiber Successfully
- Carbon Fiber Suit: The Future of Lightweight Armor
- Is Carbon Fiber Armor the Future of Protection?
- Why White Carbon Fiber is Popular in Automotive Design
- Transparent Carbon Fiber Sheets Two Sided Gloss Twill
- Epoxy-Compatible Chopped Carbon Fiber Mat
- Carbon Fiber EG Hatch: Upgrade Your Civic Today
- The Benefits of Using Structural Carbon Fibre in Engineering
- How Many Layers of Layered Carbon Fiber Are Needed?
Thank you for your interest in our products. To receive our pricelist or for any inquiries, please fill out the form below. We will get back to you within 24 hours.
Simplifying Your Life: Key Functionalities
| Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Place of Origin | Hebei, China |
| Brand Name | GangLong Fiberglass |
| Product Name | Cable Tray |
| Material | Galvanized Steel, Galvanized Steel, Aluminum, 304/316 Stainless Steel, FRP |
| Finish | HDG, Powder Coating, E-plating |
| Wire Diameter | Customizable |
| Width | Customizable |
| Length | Customizable |
| Color | Black, Silver or Customized |
| Side Rail Height | Customizable |
| Maximum Working Load | Depends on Size |
| Minimum Order Quantity | For Standard Sizes, All Quantities Can Be Met |
| Certification | CE, NEMA, ISO, UL, ABS |
| Quality | Guaranteed |
| Features | Anti-corrosion |
| Applications | Industrial, Construction, Cable Management, Cable Rack, Cable Laying, Cable Routing |
What is a Cable Tray?
Definition and Purpose
A Cable Tray is a structural system used to support and manage electrical cables in a variety of settings, from industrial plants to commercial buildings. It serves as a pathway that holds and organizes cables, providing protection from physical damage, environmental conditions, and accidental interference. The primary purpose of a Cable Tray is to ensure that cables are securely routed and accessible for maintenance, thereby enhancing the safety and efficiency of the electrical system. By using a Cable Tray, you can effectively manage large volumes of cables, keep them orderly, and facilitate easier inspections and modifications.
Basic Components and How They Support and Organize Electrical Cables
A typical Cable Tray system includes several key components:
Tray Sections: The main body of the system, which can be designed as ladder trays, perforated trays, or solid bottom trays. Each design has unique advantages based on the type of cables being managed and the specific requirements of the installation.
Supports and Hangers: These are used to secure the Cable Tray to walls, ceilings, or floors. Proper support ensures that the tray maintains its integrity and alignment, preventing sagging or displacement.
Covers: Optional components that protect cables from dust, debris, or environmental hazards. Covers also help to prevent accidental contact with the cables.
Accessories: Additional elements such as brackets, clamps, and connectors that facilitate the installation and configuration of the Cable Tray system. These accessories help in creating custom pathways and ensuring a stable and secure setup.
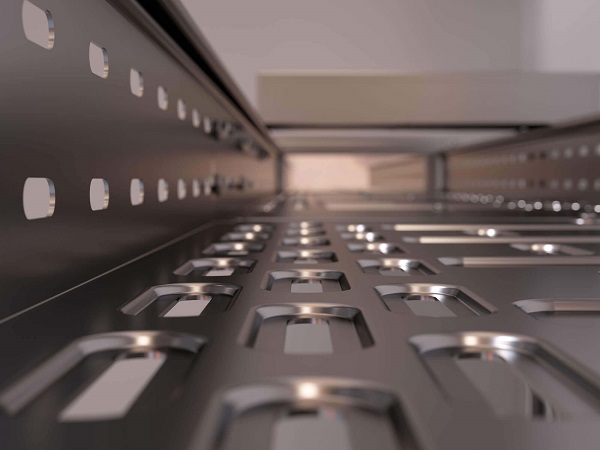
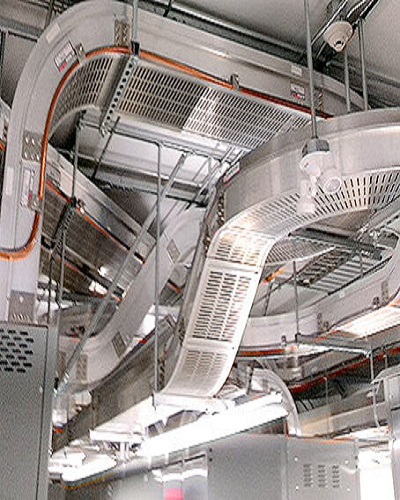


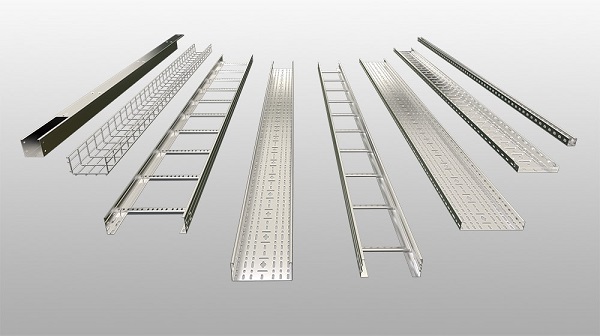
Types of Cable Trays
Cable trays are integral to the organization and management of electrical cables and wires. They come in various designs, each tailored to meet specific requirements based on cable type, installation environment, and load capacity. Understanding the distinct types of cable trays will help you select the most appropriate solution for your needs.
Ladder Cable Tray
Design: Side Rails with Rungs
The ladder cable tray features a design reminiscent of a ladder, consisting of two parallel side rails connected by a series of rungs. This configuration creates a supportive framework that holds the cables securely while allowing for easy access and airflow. The spacing between the rungs provides sufficient support for the cables, reducing the risk of sagging and ensuring stability.
Best Suited For: Heavy Cables, Long Spans, and High-Volume Applications
Ladder cable trays are particularly effective for applications requiring support for heavy cables, long spans, or a high volume of cables. The robust design of the ladder cable tray can handle significant cable loads and spans long distances without compromising structural integrity. This makes it ideal for industrial settings, large commercial buildings, and data centers where extensive cable management is required.
Advantages: Easy Access, Minimal Accumulation of Moisture, and Good Airflow
One of the key advantages of ladder cable trays is the ease of access they provide. The open design allows for straightforward inspection, maintenance, and modifications of the cable system. Additionally, the ladder design minimizes the accumulation of moisture and debris, reducing the risk of corrosion and enhancing the longevity of the cables. The good airflow around the cables helps in dissipating heat, which is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing overheating.
Perforated Cable Tray
Design: Ventilated Bottom with Holes
Perforated cable trays are characterized by their bottom surface, which is perforated with holes or slots. This ventilated design facilitates airflow around the cables, helping to keep them cool and preventing the buildup of heat. The perforations also allow for easy mounting of the cables and accessories, enhancing the overall flexibility of the cable management system.
Best Suited For: Industrial Facilities, Data Centers, and Commercial Buildings
Perforated cable trays are well-suited for use in industrial facilities, data centers, and commercial buildings. Their ventilated design makes them ideal for environments where heat dissipation is a concern, and where the ability to quickly modify and maintain the cable system is advantageous. The flexibility provided by the perforated design also allows for the easy addition or reconfiguration of cables as needed.
Advantages: Easy Maintenance, Robust Protection, and Flexibility in Installation
The perforated cable tray’s design simplifies maintenance and modifications. The holes allow for easy access to the cables and connections, making adjustments straightforward. Additionally, the robust construction provides adequate protection for the cables against physical damage and environmental factors. The flexibility in installation offered by the perforated design makes it adaptable to various configurations and mounting options.
Solid Bottom Cable Tray
Design: Continuous Solid Surface
Solid bottom cable trays feature a continuous solid surface across their base. This design provides a completely enclosed pathway for the cables, offering enhanced protection from environmental elements and potential damage. The solid bottom helps in containing the cables and preventing debris or contaminants from coming into contact with them.
Best Suited For: Environments Needing Enhanced Protection, Such as Healthcare Facilities and Industrial Settings
Solid bottom cable trays are ideal for environments where enhanced protection of the cables is critical. This includes healthcare facilities, where cleanliness and protection from contaminants are essential, as well as industrial settings where cables might be exposed to harsh conditions or potential physical damage. The solid bottom ensures that the cables are shielded from external factors that could affect their performance and longevity.
Advantages: Improved Safety, Reduced Electromagnetic Interference, and Durability
The solid bottom design of these cable trays offers several benefits. It improves safety by providing a secure enclosure that prevents accidental contact with live cables. Additionally, the solid surface helps in reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can be important for maintaining signal integrity in sensitive environments. The durability of the solid bottom cable tray ensures long-lasting performance, even in challenging conditions.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Cable Tray
Selecting the right cable tray involves evaluating several factors to ensure that the tray meets the specific needs of your installation. Each consideration impacts the performance, safety, and longevity of the cable management system. Below are the key considerations to keep in mind when choosing a cable tray:
Size and Capacity
Cable Volume: Assess the volume of cables that the tray needs to accommodate. This includes evaluating the number and size of cables that will be routed through the build cable trays. Proper assessment ensures that the trays can effectively manage the cable volume while maintaining organization and accessibility. A tray with insufficient capacity can lead to overcrowding, which can compromise cable performance and accessibility.
Tray Load Capacity: The load capacity of a cable tray refers to its ability to support the weight of the cables. Ensure that the tray you select can handle the combined weight of all cables without bending or sagging. This involves considering both the static load (the weight of the cables) and any dynamic loads (such as potential movement or vibrations).
Spacing and Layout: The spacing between supports and the layout of the tray also affect its performance. Proper spacing is essential to maintain structural integrity and prevent excessive bending.
Material Types
Metal (e.g., Galvanized Steel, Stainless Steel, Aluminum) vs. Non-Metallic (e.g., Fiberglass)
The material of the cable tray plays a significant role in its suitability for different environments and applications.
Metal Cable Trays: Common metals used in cable trays include galvanized steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
Galvanized Steel: This material is known for its corrosion resistance and strength. It is suitable for indoor environments and areas with moderate exposure to moisture.
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel cable trays offer superior corrosion resistance and are ideal for harsh environments where exposure to chemicals or extreme conditions is a concern.
Aluminum: Aluminum trays are lightweight yet strong and resistant to corrosion. They are often used in applications where weight reduction is important, and they perform well in various environmental conditions.
Non-Metallic Cable Trays: Fiberglass is a common non-metallic material used in cable trays.
Fiberglass: Fiberglass cable trays are highly resistant to corrosion, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. They are suitable for environments where metal trays might corrode or degrade over time. Fiberglass trays also offer the advantage of being lightweight and easy to install.
Environmental Factors
Choosing Trays Based on Exposure to Moisture, Chemicals, and Temperature Variations
Environmental conditions significantly impact the selection of a cable tray. Consider the following factors when choosing the right cable tray for your installation:
Exposure to Moisture: In environments where trays are exposed to high levels of moisture or potential flooding, opt for materials with high corrosion resistance, such as stainless steel or fiberglass. Galvanized steel trays may also be suitable for moderate moisture conditions but may require additional protective coatings.
Chemical Exposure: For environments with exposure to chemicals, choose materials that can withstand chemical corrosion. Fiberglass trays and stainless steel cable tray are typically preferred in such settings due to their chemical resistance properties. These materials ensure the safe and effective management of cables in environments where exposure to harsh chemicals is a concern.
Temperature Variations: Extreme temperature fluctuations can affect the performance and durability of cable trays. Ensure that the material you select can handle the temperature range of the installation environment. Fiberglass trays are often used in extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, due to their thermal stability.
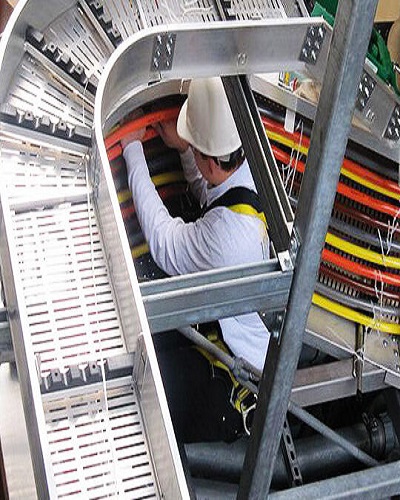

Cable Tray of Industry-Specific Applications
Cable trays are essential components used in numerous industries for the efficient organization and support of electrical cables. Each industry has unique requirements, and selecting the appropriate cable tray is crucial to ensuring the optimal performance, safety, and compliance with regulatory standards. Below are the primary applications of cable trays in various sectors:
Industrial Cable Trays
In manufacturing plants, cable trays are essential for organizing and supporting the electrical cables that run across production lines, machine control systems, and power distribution networks. These trays help ensure that cables are neatly arranged and protected, reducing the risk of damage while supporting high electrical loads commonly found in industrial settings.
Cable Tray for Data Centers
In data centers, cable trays are critical for managing the dense network of cables used to connect servers and other IT infrastructure. By organizing cables effectively, they help improve airflow, reduce cable clutter, and ensure easier access for maintenance. This organization is especially crucial in data centers, where system performance and uptime are paramount.
Cable Tray in Commercial Construction
In commercial construction, cable trays not only serve a functional role but also need to be integrated seamlessly into the building’s design. Whether concealed within walls, ceilings, or designed to match the aesthetic of the interior, cable trays must meet both aesthetic preferences and building code compliance. This ensures the system is not only effective but also maintains the visual integrity of the space.

Popular Suppliers and Products
GangLong Fiberglass‘s Cable Trays
GangLong Fiberglass is recognized for its comprehensive range of cable tray solutions that cater to diverse industrial and commercial needs. GangLong Fiberglass’s cable trays are well-regarded for their durability, ease of installation, and adherence to industry standards.
Product Range: GangLong Fiberglass offers a broad selection of cable trays, including cable ladder, stainless steel cable tray, aluminium cable tray, cable tray fittings, FRP cable tray and FRP cable ladder. Our products are designed to handle various load capacities and environmental conditions, making them suitable for both heavy-duty and standard applications.
Market Position: GangLong Fiberglass has established a strong market position through its commitment to quality and innovation. Our products are widely used in industrial plants, commercial buildings, and data centers. GangLong Fiberglass is known for its reliability and has earned a reputation for providing solutions that enhance cable management efficiency and safety.
Compliance and Standards
Ganglong Fiberglass ensures all products meet or exceed industry standards, including:
- NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association)
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories) Certification
- CTI (Cable Tray Institute) Compliance
- CSA (Canadian Standards Association) Approval
Unique Features and Advantages
Ganglong Fiberglass cable trays come equipped with advanced features such as:
- Tray Covers – Protection against environmental elements and mechanical damage.
- Wire Management Accessories – Organized and secure cable routing.
- Custom Fabrication – Tailored solutions based on application needs.
- Strong Logistics Support – Efficient delivery and inventory management.
Cable Tray Innovations
The field of cable tray design is continually evolving, with innovations aimed at improving performance, ease of use, and adaptability. Here are some of the key trends and technologies shaping the future of cable trays:
Smart Cable Management: Advances in smart technology are being integrated into cable trays, such as sensors that monitor cable conditions, temperature, and load. These smart systems can provide real-time data and alerts, facilitating proactive maintenance and optimizing cable management.
Modular and Flexible Designs: The trend towards modular and flexible cable tray systems allows for easier customization and scalability. Modular designs enable quick reconfiguration and expansion, making them ideal for dynamic environments where changes are frequent.
Sustainable Materials: There is a growing emphasis on using eco-friendly materials in cable tray production. Innovations include the use of recycled metals and sustainable non-metallic materials, such as fiberglass composites that reduce environmental impact.
Enhanced Safety Features: New safety features are being incorporated into cable tray designs to improve protection and compliance with safety regulations. This includes features like integrated grounding systems and fire-resistant materials.
Improved Aesthetics: As aesthetic considerations become more important in commercial and public spaces, cable tray designs are evolving to include more visually appealing options. This includes trays with customizable finishes and designs that blend seamlessly with building interiors.
Cable Tray of Installation and Maintenance Tips
Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial for ensuring the effectiveness and longevity of cable trays. By following best practices during installation and adhering to a maintenance schedule, you can optimize the performance of your cable tray system. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you with both installation and maintenance.
Best Practices for Installing Different Types of Cable Trays
Ladder Cable Tray
Ladder cable tray installation starts with a clear layout plan. Ensure trays are supported with hangers or brackets spaced according to specifications. Align side rails and secure them firmly for stability. Use adjustable hangers where needed for varied heights. Cables should be laid evenly without sharp bends or tension. Leave enough space around cables for airflow and cooling. A well-supported and balanced ladder tray system helps prevent overheating and allows for future cable system expansion.
Perforated Cable Tray
Perforated cable trays should be mounted on level brackets with proper alignment. The perforations make it easier to attach cable ties and accessories, keeping cables secure and organized. Installers should avoid overcrowding cables and maintain open airflow through the tray. This type of tray is ideal for installations that may require frequent changes or additions. Its flexible design allows for easy upgrades while ensuring the cable system stays neat, accessible, and efficient in day-to-day operation.
Solid Bottom Cable Tray
Solid bottom trays require full-length support to prevent sagging. Alignment is critical to ensure proper load handling. In dusty or moist environments, seal joints with gaskets or sealant to block contaminants. Place cables carefully to avoid crowding, which can complicate maintenance or cause damage. Avoid overfilling, and maintain an organized layout for better airflow and inspection access. This installation approach protects sensitive cables and ensures reliability over time in challenging conditions.
Regular Maintenance to Ensure Longevity and Performance
Routine Inspections
Visual Checks: Conduct regular visual inspections of the cable tray system to identify any signs of damage, corrosion, or wear. Check for loose fittings, sagging trays, or any obstructions that might impact performance.
Cable Condition: Inspect the condition of the cables within the trays. Look for signs of wear, such as fraying or insulation damage, and address any issues promptly to prevent potential failures.
Cleanliness: Keep the cable trays and surrounding areas clean and free of debris. Dust and debris can accumulate in trays, affecting airflow and increasing the risk of overheating. Regular cleaning helps maintain optimal conditions for the cables.
Preventive Maintenance
Tightening and Adjustments: Periodically check and tighten any loose bolts, fasteners, or supports. Ensure that the cable tray remains securely attached and properly aligned.
Corrosion Protection: For metal cable trays, inspect and maintain protective coatings to prevent corrosion. Reapply protective coatings or paint as needed to extend the life of the trays.
Upgrades and Reconfigurations: As your cable management needs evolve, consider upgrading or reconfiguring the cable trays. Add or adjust trays to accommodate new cables or changes in the layout, ensuring that the system remains effective and organized.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Overloading: Address any issues related to overloading by redistributing cables or adding additional trays as needed. Overloaded trays can lead to structural problems and impact cable performance.
Heat Build-Up: If you notice excessive heat build-up, ensure that the tray design allows for adequate airflow. Consider using trays with better ventilation or implementing additional cooling solutions if necessary.
Damage Repair: Repair any damaged sections of the cable trays promptly to prevent further issues. Replace or repair damaged trays, supports, or accessories to maintain system integrity.

Stainless Steel Cable Tray
What is a Stainless Steel Cable Tray?
A stainless steel cable tray is a structural system used to support and organize insulated cables in industrial, commercial, and residential settings. Made from high-quality stainless steel, it offers excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and durability. Its lightweight design allows for easy installation, while its robust structure ensures long-term performance, even in harsh or demanding environments. It is ideal for safe, efficient cable management.
Applications of Stainless Steel Cable Tray
Chemical Processing Plants
In chemical plants, equipment must endure harsh substances like acids, solvents, and corrosive gases. Stainless steel cable trays are ideal for such settings, as they withstand chemical exposure without degrading. This helps maintain electrical system reliability and reduces maintenance costs. They are often used in areas with frequent spills, high temperatures, and heavy-duty processes, providing a long-lasting cable management solution in highly reactive or aggressive environments.
Outdoor and Coastal Installations
Stainless steel cable trays are perfect for outdoor and coastal installations where exposure to moisture, UV rays, and salty air can cause rapid deterioration. They are commonly used on rooftops, bridges, offshore rigs, and near seaports. Their corrosion resistance ensures long service life, even in extreme climates. By preventing rust and structural failure, these trays offer a dependable solution for long-term cable support in open-air or marine environments.
Heavy-Duty Industrial Applications
Heavy industries like mining, power generation, and large-scale manufacturing rely on stainless steel cable trays for supporting high-load cables. These trays offer excellent mechanical strength, preventing sagging or structural damage under weight. Their durability helps minimize downtime and ensures safety in environments with vibration, heat, or mechanical impact. They are essential in installations where both structural integrity and resistance to wear are crucial for continuous operation.
Advantages and Characteristics
Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel’s natural resistance to rust and oxidation makes these trays ideal for wet, humid, or chemically aggressive environments. They perform reliably in coastal areas, food processing plants, and chemical facilities where other materials might degrade quickly. This corrosion resistance ensures safety, reduces maintenance costs, and extends the life of the entire cable support system under harsh operating conditions.
Extended Service Life
One of the most valued features of stainless steel cable trays is their long lifespan. Unlike galvanized or painted systems that may wear or chip over time, stainless steel retains its integrity with minimal degradation. Its resistance to environmental stressors means fewer replacements and repairs, resulting in lower long-term costs and fewer disruptions to operations, especially in critical infrastructure environments.
Lightweight Design
Despite their strength, stainless steel cable trays are relatively lightweight, making them easier to transport, handle, and install. This advantage reduces labor time and the need for heavy lifting equipment on-site. The ease of handling is particularly beneficial in overhead installations or retrofit projects where maneuverability is limited, improving safety and project efficiency.
Structural Strength and Stability
Stainless steel trays are designed to carry heavy cable loads without bending or warping. Features such as reinforced side rails and swivel flanges enhance structural stability, especially in dynamic or vibration-prone environments. Their rigidity allows them to span greater distances with fewer supports, optimizing layout flexibility while maintaining system integrity under load.
Types of Stainless Steel Cable Trays
Stainless steel cable trays come in various designs to meet different structural and environmental requirements. Each type offers unique benefits depending on the installation scenario and cable load.
Standard Stainless Steel Cable Trays
Best suited for light to moderate cable loads, standard trays offer a clean, corrosion-resistant solution for routing control and communication cables in sanitary or indoor environments. Their lightweight design makes them easy to install and maintain.
Heavy-Duty Return Flange Series
Designed for large-diameter or high-voltage cables, these trays feature reinforced side flanges and increased wall height. Common in industrial plants and energy facilities, they deliver superior structural support and resist deformation under heavy loads.
Wire Mesh (Basket Type) Stainless Steel Trays
Wire mesh trays are made of stainless steel rods welded into a basket shape. They are lightweight, flexible, and easy to cut or bend during installation. Commonly used in commercial buildings, data centers, and areas with frequent system upgrades, they allow fast and adaptable cable routing with excellent ventilation.
FAQs about Cable Tray
What are the three types of cable trays?
Ladder Cable Tray: This type features two parallel side rails connected by horizontal rungs. The open design allows for excellent airflow, making it ideal for managing heavy cables and long spans. It is particularly useful in industrial settings where frequent maintenance or modifications are required.
Perforated Cable Tray: Characterized by a base with perforations or slots, this tray facilitates ventilation and easy attachment of cable management accessories. It is suitable for environments where heat dissipation and flexibility in cable management are critical, such as in data centers and commercial buildings.
Solid Bottom Cable Tray: This tray has a continuous solid base, providing enhanced protection against dust, moisture, and other contaminants. It is ideal for applications where additional safety and protection of cables are required, such as in healthcare facilities or harsh industrial environments.
When to use a cable tray?
What is the difference between a tray cable and a regular cable?
What does a cable tray look like?
Ladder Type Cable Tray: Resembles a ladder with two parallel side rails connected by crossbars or rungs, offering excellent ventilation and easy cable installation.
Solid-Bottom Cable Tray: A continuous, flat-bottom tray that provides maximum protection for cables but less ventilation.
Perforated Cable Tray: Similar to solid-bottom trays but with holes or slots that allow for some ventilation while still providing protection.
Wire Mesh Cable Tray: Made from a grid of wires forming a basket-like structure, offering high flexibility and good ventilation, commonly used for data and communication cables.
These trays are typically made of materials like steel, aluminum, or fiberglass, and are designed to be mounted on walls, ceilings, or under floors.
What is the advantage of using cable trays?
Flexibility: Cable trays allow for easy changes and expansions in cable installations, making it simpler to add or reroute cables as needed.
Cost-Effectiveness: They can be more cost-effective than conduit systems, particularly in large installations, due to their ease of installation and modification.
Improved Airflow: Open designs like ladder or wire mesh trays provide excellent ventilation, which helps in dissipating heat generated by cables, reducing the risk of overheating.
Ease of Maintenance: Cable trays provide easy access to cables, making it simpler to perform maintenance, repairs, or upgrades without disrupting other cables.
Enhanced Safety: They help in organizing cables, reducing the risk of tripping hazards, and preventing physical damage to cables.
What do cable trays carry?
Power Cables: For transmitting electrical power to different parts of a building or facility.
Data Cables: For transmitting digital data, commonly used in networking and communication systems.
Control Cables: For controlling machinery, equipment, or systems in industrial settings.
Communication Cables: For telecommunication and broadcasting systems.
Fiber Optic Cables: For high-speed data transmission in communication networks.
Specialty Cables: Such as instrumentation cables, which are used in specific applications like monitoring and control systems.
How do l choose a cable tray?
Load Capacity: Determine the weight of the cables and select a tray that can support the total load without bending or sagging.
Material: Choose a material that suits the environment. For example, steel offers strength, aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, and fiberglass is non-conductive and resistant to corrosion.
Tray Type: Depending on your needs, choose between ladder, solid-bottom, perforated, or wire mesh trays. Ladder trays are best for high ventilation, solid-bottom for maximum protection, and wire mesh for flexibility.
Environment: Consider environmental factors such as exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures, and choose a tray that can withstand these conditions.
Installation Space: Ensure the tray fits the available space and can be easily mounted in the desired location.
Regulatory Compliance: Make sure the tray meets relevant industry standards and local building codes.
What is the difference between cable duct and cable tray?
On the other hand, a cable tray is an open system that supports and organizes cables without completely enclosing them. Cable trays allow for better ventilation and easier access to the cables but provide less protection compared to ducts. The choice between a duct and a tray depends on the specific needs of the installation, such as the level of protection required and the importance of ventilation and accessibility.
Which type of cable tray is best?
Ladder Tray: Best for applications requiring excellent ventilation and easy cable access, commonly used in industrial settings.
Solid-Bottom Tray: Ideal for environments where cables need maximum protection from dust, moisture, or physical damage.
Perforated Tray: Provides a balance between protection and ventilation, suitable for a variety of environments.
Wire Mesh Tray: Best for data and communication cables where flexibility and airflow are crucial, often used in data centers and commercial installations.
Each type has its strengths, so the choice depends on factors like the type of cables, environmental conditions, load requirements, and ease of maintenance.
What are the five basic cable trays fittings?
Elbow/Bend Fitting:
Description: Used to change the direction of the cable tray system horizontally or vertically. These come in various angles like 90°, 45°, or custom angles.
Application: Useful when the cable tray needs to turn around corners or navigate obstacles.
Tee Fitting:
Description: Allows the cable tray to branch off into two directions, forming a ""T"" shape.
Application: Used when cables need to be routed to different locations from a single path.
Cross Fitting:
Description: A four-way fitting that enables the cable tray to split into four directions.
Application: Ideal for complex cabling systems that require multiple routing paths.
Reducer Fitting:
Description: Used to transition from a wider cable tray to a narrower one or vice versa.
Application: Helps in adjusting the size of the cable tray to accommodate varying cable volumes.
Coupler Fitting:
Description: Connects two sections of cable tray together in a straight line, ensuring continuity of the tray system.
Application: Essential for extending the length of the cable tray installation.
What are the four kinds of trays?
Ladder Tray:
Description: Resembles a ladder with spaced rungs and provides excellent ventilation and easy cable access.
Advantages: Most common for heavy-duty applications.
Solid-Bottom Tray:
Description: A fully enclosed tray with no gaps, providing maximum protection for cables.
Advantages: Ideal for environments where cables need to be protected from contaminants.
Perforated Tray:
Description: Similar to a solid-bottom tray but with perforations for ventilation and drainage.
Advantages: Balances protection with the need for airflow.
Wire Mesh/Basket Tray:
Description: Made from a grid of wires, creating a basket-like structure that is flexible and easy to install.
Advantages: Lightweight, provides excellent ventilation, and is ideal for routing data and communication cables.
What is the difference between cable tray and raceway?
Description: An open support system used to manage and organize cables. It allows easy access to cables and good ventilation.
Applications: Ideal for large installations where cables may need to be rerouted or accessed frequently.
Raceway:
Description: A fully enclosed conduit that provides a protected pathway for cables. It shields cables from external conditions such as dust, moisture, and physical damage.
Applications: Used in environments where cables need more protection, such as in walls, floors, or exposed outdoor areas.
What is the difference between a perforated cable tray and a channel cable tray?
Description: A cable tray with a series of holes or slots in its base and sides to allow ventilation and drainage.
Advantages: Provides some protection while enabling airflow and reducing weight.
Channel Cable Tray:
Description: A U-shaped tray, typically with solid sides and bottom, that fully encloses the cables on three sides.
Advantages: Offers more protection than a perforated tray but less ventilation, making it suitable for environments where cables need to be shielded from dust or debris.
What is the standard size of cable tray?
Width: Common widths are 100mm (4 inches), 150mm (6 inches), 300mm (12 inches), 450mm (18 inches), 600mm (24 inches), and up to 900mm (36 inches).
Height: The height of the side rails commonly ranges from 25mm (1 inch) to 150mm (6 inches).
Length: Standard lengths are typically 2.4 meters (8 feet) or 3 meters (10 feet).
The specific size required depends on the volume and type of cables being supported, as well as the load-bearing requirements.
What are the disadvantages of a solid bottom cable tray?
Limited Ventilation: Since the tray is fully enclosed, it restricts airflow around the cables, which can lead to heat buildup and potential overheating, especially in high-power applications.
Heavier Weight: Solid-bottom trays are generally heavier than perforated or ladder trays, making them more challenging to install, especially in overhead applications.
Higher Cost: The solid construction often makes these trays more expensive due to the increased material required and the need for stronger supports.
Reduced Flexibility: The solid bottom limits access to cables once they are installed, making maintenance, modifications, or expansions more difficult.
What is another name for a cable tray?
What is the difference between cable tray and channel tray?
Description: An open system that supports cables along their length, providing easy access and ventilation. Common types include ladder, perforated, and wire mesh trays.
Applications: Suitable for large-scale installations where cables need to be frequently accessed or rerouted.
Channel Tray:
Description: A U-shaped tray that encloses cables on three sides, offering more protection than an open cable tray but less ventilation.
Applications: Used in environments where cables need to be shielded from external factors like dust, but less frequent access is required.
What is the difference between cable trunking and cable tray?
Description: An enclosed rectangular or square conduit that fully encases and protects cables. Typically made of metal or plastic, it is used to route and organize cables in a neat and concealed manner.
Applications: Ideal for environments where cables need to be hidden or protected from external damage, such as in walls, floors, or ceilings.
Cable Tray:
Description: An open support system that holds and organizes cables along their length, allowing easy access and ventilation.
Applications: Used in industrial and commercial settings where large volumes of cables need to be managed, and frequent access is required.
The choice between cable trunking and cable tray depends on the need for protection, accessibility, and the environment in which the cables are being installed.
What is the difference between a cable ladder and a cable tray?
Description: A cable ladder is a type of cable tray that consists of two parallel side rails connected by rungs or crossbars at regular intervals, resembling a ladder.
Advantages: It provides excellent ventilation for cables, allowing heat to dissipate easily. The open structure makes it easy to route and secure cables, and it is ideal for long cable runs that require support but also need frequent access for maintenance or changes.
Applications: Commonly used in industrial and commercial settings where large volumes of cables need to be supported over long distances, especially in environments that require good airflow around the cables to prevent overheating.
Cable Tray:
Description: The term ""cable tray"" is more general and encompasses various types of cable support systems, including ladder trays, solid-bottom trays, perforated trays, and wire mesh trays.
Advantages: Depending on the type, cable trays can offer varying levels of protection, ventilation, and flexibility. For example, solid-bottom trays provide maximum protection but limited ventilation, while perforated trays offer a balance between protection and airflow.
Applications: Used in a wide range of environments, from industrial plants to commercial buildings, for organizing and supporting electrical and communication cables.
In summary, a cable ladder is a specific type of cable tray designed for maximum ventilation and easy cable access, while ""cable tray"" is a broader term that includes multiple designs with different features.
Can you stack wires in cable tray?
Weight Distribution: When stacking wires, it’s essential to ensure that the weight is evenly distributed across the tray to prevent sagging or deformation of the tray, which could lead to cable damage.
Cable Separation: Different types of cables, especially those carrying different voltage levels, should be separated to avoid interference. In some cases, separators or dividers can be used within the tray to maintain this separation.
Ventilation: Stacking cables can reduce ventilation and increase the risk of overheating, especially in high-density installations. Proper planning is needed to ensure adequate airflow around the cables.
Compliance: Always follow local electrical codes and standards (like the NEC in the United States) when stacking cables in a tray, as there may be specific regulations on how cables should be arranged.
Is cable tray considered a raceway?
Raceway: A raceway is a physical pathway that facilitates the routing of electrical wiring in a building or structure, protecting the wires and organizing them in a manner that meets code requirements.
Cable Tray as a Raceway: Cable trays are a form of raceway that provides an open support system for electrical and communication cables. Unlike enclosed raceways like conduits, cable trays offer more flexibility and accessibility, allowing for easier installation, maintenance, and modifications.
Why are cables tied down in cable tray?
Stability: Tying down cables ensures they remain in place and do not shift or move, which can prevent mechanical damage or wear over time.
Organization: Properly secured cables are easier to manage and maintain, reducing the risk of tangling or crossing, which could lead to interference or difficulty in troubleshooting.
Safety: Loose cables can pose safety hazards, such as tripping or falling, and in some cases, might even lead to electrical faults if they come into contact with sharp edges or other hazards.
Compliance: Electrical codes often require that cables be secured at regular intervals to prevent sagging and ensure the integrity of the installation.
Does cable tray need to be grounded?
Electrical Safety: Grounding the cable tray ensures that any stray electrical current that might result from damaged insulation or faults is safely conducted to the ground, reducing the risk of electrical shock or fire.
Code Compliance: Electrical codes, such as the NEC (National Electrical Code) in the United States, typically require that metal cable trays be properly grounded as part of the overall grounding system for the installation.
Lightning Protection: In some installations, grounding the cable tray can also provide a path for lightning strikes to safely dissipate, protecting both the cables and the structure.
What is the purpose of a cable tray?
Cable Support: Cable trays prevent cables from sagging and provide a stable support system, which helps maintain the integrity of the wiring over time.
Organization: Cable trays help to organize multiple cables, making it easier to identify and maintain them. This is especially important in large installations with numerous cables.
Flexibility: Cable trays allow for easy modifications, such as adding or removing cables, without the need for extensive rewiring. This is especially valuable in environments where systems frequently change.
Ventilation: Certain types of cable trays, like ladder trays, allow for good airflow around the cables, helping to dissipate heat and reduce the risk of overheating.
Protection: While not fully enclosed, cable trays still offer some level of protection against mechanical damage, dust, and debris, depending on the type of tray used.
Which cable tray is best?
Ladder Tray:
Best For: Applications requiring excellent ventilation and easy access to cables, such as in industrial settings with long cable runs.
Advantages: Provides maximum airflow, easy to install and modify, suitable for high-power cables that generate heat.
Solid-Bottom Tray:
Best For: Environments where cables need protection from dust, moisture, or mechanical damage.
Advantages: Offers maximum protection, ideal for sensitive or delicate cables, suitable for areas with a high level of contamination.
Perforated Tray:
Best For: Situations requiring a balance between protection and ventilation, commonly used in commercial buildings.
Advantages: Provides some protection with improved airflow, lighter than solid-bottom trays, easier to install.
Wire Mesh/Basket Tray:
Best For: Data centers, communication rooms, or areas with frequent cable changes.
Advantages: Highly flexible, excellent ventilation, easy to install, ideal for low-voltage and data cables.
Ultimately, the choice depends on factors such as the type of cables, environmental conditions, load requirements, and the need for accessibility and future modifications.
What is the difference between cable tray and conduit?
Description: A cable tray is an open support system used to organize and route multiple cables within a building or industrial facility. It allows easy access to cables and provides ventilation, which helps prevent overheating.
Advantages: Easier to install and modify, supports large volumes of cables, and offers better ventilation for heat dissipation.
Applications: Commonly used in industrial and commercial environments where cables need to be rerouted or accessed frequently.
Conduit:
Description: A conduit is a fully enclosed, tubular raceway system that protects cables from external elements such as dust, moisture, and mechanical damage. Conduits can be made from metal, plastic, or other materials and are typically used for individual cables or small groups of cables.
Advantages: Provides maximum protection against environmental hazards, and is often required in areas with strict safety codes.
Applications: Suitable for environments where cables need to be completely enclosed and protected, such as in walls, underground, or in hazardous locations.
Is cable tray cheaper than conduit?
Does tray cable need to be in conduit?
Does cable have to be in conduit?
Can l run thhn in cable tray?
THHN cables must be part of a larger assembly, such as in a bundle or within an appropriate jacketed tray cable.
The installation must comply with local codes, such as the NEC (National Electrical Code), which may have additional requirements regarding spacing, support, and protection.
Directly running single THHN conductors in a cable tray without additional protection or bundling is generally not allowed unless specifically permitted by code.
What is the spacing between cables in a cable tray?
Current Carrying Capacity: Proper spacing is essential to prevent overheating and ensure adequate ventilation.
Voltage Level: Higher voltage cables may require more spacing to avoid interference.
Local Codes: Codes like the NEC provide guidelines for spacing based on factors such as cable type and load.
Typical Spacing: For power cables, a common practice is to maintain a gap of at least one cable diameter between adjacent cables. In some cases, dividers may be used to maintain separation and organize cables.
How do you pull a cable through a cable tray?
Preparation: Ensure the cable tray is clean, free of debris, and properly supported. Identify and plan the route, including any bends or junctions.
Lay Out the Cable: Lay the cable out along the route to avoid tangling and ensure correct orientation.
Use Rollers or Guides: For longer runs or heavy cables, use rollers or cable guides to minimize friction and prevent damage to the cable.
Pulling the Cable: Start pulling the cable manually or using a mechanical puller. Pull slowly and steadily to avoid kinking or damaging the cable.
Securing the Cable: Once in place, secure the cable using cable ties or clamps at regular intervals, ensuring that it is properly supported and that there is no sagging.
Does cable tray count as a raceway?
Does cable tray require bonding?
What are the 3 main types of cable tray?
Ladder Cable Tray:
Description: Consists of two parallel side rails with rungs or crossbars spaced at regular intervals, resembling a ladder.
Advantages: Provides excellent ventilation, easy access to cables, and is ideal for long cable runs that require frequent modifications.
Solid-Bottom Cable Tray:
Description: A tray with a continuous, flat-bottom surface that completely supports the cables without any gaps.
Advantages: Offers maximum protection against dust, debris, and physical damage, making it suitable for environments requiring high levels of protection.
Perforated Cable Tray:
Description: Similar to a solid-bottom tray but with holes or slots in the base and sides to allow ventilation and drainage.
Advantages: Provides a balance between protection and ventilation, suitable for a variety of environments.
What type of cable can be used in cable tray?
Tray Cable (TC): Specifically designed for use in cable trays, often used for power, control, and communication wiring.
THHN/THWN Cable: Can be used in trays if bundled or jacketed, following code requirements.
Fiber Optic Cables: Commonly used in data centers and communication installations.
Power Cables: Used for electrical power distribution.
Instrumentation Cables: Used in industrial settings for monitoring and control.
Low-Voltage Cables: Such as communication and data cables, can also be installed in cable trays.
It’s important to choose cables that are rated for tray use and comply with local codes and standards.
Is it necessary to provide tie down cables installed in a cable tray?
Prevents Movement: Securing the cables ensures they stay in place, preventing shifting or tangling that could lead to mechanical damage.
Maintains Organization: Properly tied cables are easier to manage and maintain, especially in large installations.
Safety: Reduces the risk of tripping hazards and potential interference between different types of cables.
Compliance: Electrical codes often require cables in trays to be secured at regular intervals to ensure the integrity of the installation.
Which cables should not be in the same tray?
High-Voltage and Low-Voltage Cables: Should not be mixed, as high-voltage cables can induce interference in low-voltage lines.
Power Cables and Communication/Data Cables: Mixing these can lead to electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can disrupt data transmission.
Fire-Rated Cables and Non-Fire-Rated Cables: Should be separated to maintain the integrity of fire-rated systems in case of an emergency.
Cables with Different Insulation Ratings: May need to be segregated based on their voltage and temperature ratings to prevent degradation of the insulation material.
In some cases, dividers or separate trays may be used to maintain proper separation between incompatible cable types. Always refer to local electrical codes and standards for specific requirements.






