- Home
- Fiberglass Angle
Fiberglass Angle Stock and Structural Shapes
Fiberglass Angle more corrosion resistant alternative to traditional steel or aluminum angle making it a great choice for any environment.
Fiberglass Angles, made from plastic resin reinforced with glass fibers, offer a strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant alternative to traditional metal angles, making them ideal for various industrial and construction applications. They are particularly favored in environments prone to rust and wear, such as wastewater treatment plants, chemical processing facilities, and food processing factories. The structural integrity and longevity of Fiberglass Angles make them a superior choice compared to aluminum, wood, or steel beams. These angles feature a 90° equal leg shape, providing strength and durability while being nonconductive, which is beneficial for insulating sound and temperature in building projects.
GangLong Fiberglass offers corrosion-resistant Fiberglass Angles, available in 10ft or 20ft lengths, ideal for various environments. This material’s adaptability and resistance to harsh conditions make it increasingly popular among builders and engineers for structural support and framing in various demanding settings.
Simplifying Your Life: Key Functionalities
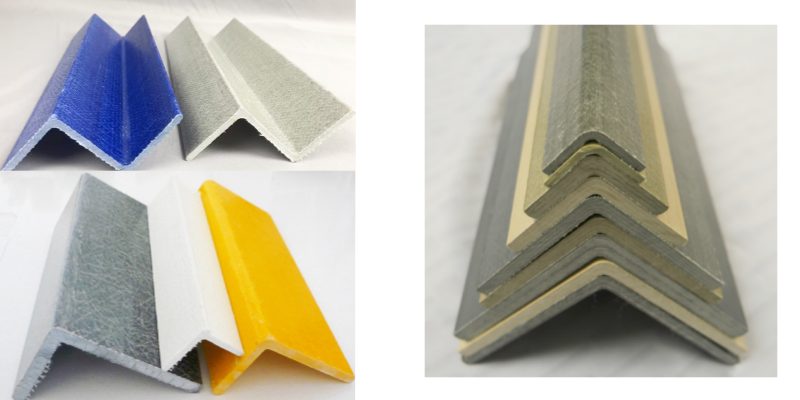
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Fiberglass Angle Bar / FRP GFRP Pultruded Angle Profiles |
| Brand Name | GangLong Fiberglass |
| Place of Origin | Hebei, China |
| Material | Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) / Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic (GFRP) |
| Technique | Pultrusion |
| Shape Options | L-Shape, U-Shape, Customized |
| Surface Treatment | Smooth, Polished, Painted, or Customized |
| Processing Service | Cutting, Bending, Punching, Moulding |
| Feature | Corrosion Resistance, High Strength, Lightweight, UV Resistant, Anti-aging |
| Color Options | Customized Colors (Black, White, Red, Green, Yellow, etc.) |
| Dimensions | Customized (e.g., L-angle, U-angle, Equal Angle beams, etc.) |
| Resin Type | ISO, ORTH, VE, PH |
| Surface Material | Polyester Mat, Needled Mat, Continuous Strand Mat |
| Certificate | ISO9001, 18001, SGS, ASTM |
| OEM Support | Fully Supported |
| Packaging | Normal Packing: Protective Film + Cardboard. Can be customized as per customer requirements |
| Quality Guarantee | High Quality Guarantee |
| Application | Construction, Industry, Architecture, Concrete, General Building Support |
| Bendable | Yes |
| Drawings Support | Yes (Custom Drawings Accepted) |
| Sample Availability | Free Sample Available |
| Packing Details | Cartons, Pallet, Customized Packaging Options Available |
| Delivery Time | Typically 10-15 Days (depending on order size and customization) |
News
- Exploring the Benefits of Carbon Fiber Apparel
- How to Work with Carbon Fiber Successfully
- Carbon Fiber Suit: The Future of Lightweight Armor
- Is Carbon Fiber Armor the Future of Protection?
- Why White Carbon Fiber is Popular in Automotive Design
- Transparent Carbon Fiber Sheets: Strength Meets Clarity in Design
- Chopped Carbon Fiber Mat for Lightweight Reinforcement
- Carbon Fiber EG Hatch: Upgrade Your Civic Today
- The Benefits of Using Structural Carbon Fibre in Engineering
- How Many Layers of Layered Carbon Fiber Are Needed?

What is Fiberglass Angle?
Fiberglass Angle is a structural shape made from fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP), designed to offer strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion and chemicals. It is typically manufactured through a process known as pultrusion, where continuous strands of fiberglass are pulled through a resin bath and then through a heated die to form the desired angle shape. This process ensures that the Fiberglass Angle has consistent quality and high mechanical properties.
The material’s properties make Fiberglass Angle an excellent choice for applications where traditional materials like steel or aluminum might fail due to corrosion or chemical exposure. Its inherent strength allows it to support significant loads while being much lighter than metal alternatives. Additionally, Fiberglass Angle is non-conductive and non-magnetic, making it suitable for use in environments where electrical insulation or non-interference with magnetic fields is required. This combination of properties—strength, durability, and resistance—makes Fiberglass Angle a versatile and reliable material for a wide range of industrial and structural applications.
Structural Fiberglass Angle 90°
A structural fiberglass angle is a versatile reinforcement material made from woven fiberglass fibers combined with a resin matrix. Designed in a right-angle shape (90 degrees), it provides essential structural support for various applications. These angles offer enhanced strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors, making them an ideal choice for both heavy-duty and lightweight applications where traditional materials like steel or aluminum may not perform as effectively.
Material Composition
Fiberglass Reinforcement
Fiberglass angles are primarily made up of woven glass fibers, which are reinforced with a resin matrix. The fiberglass reinforcement provides the material with high strength, making it ideal for structural applications. The glass fibers are arranged in a way that maximizes their load-bearing capacity while maintaining flexibility. This reinforcement process ensures that the material is robust yet lightweight, offering excellent mechanical performance for various structural requirements.
Resin Matrix
The resin matrix in fiberglass angles plays a critical role in binding the glass fibers together and providing the material with its durability and resistance to environmental factors. Common resins used in fiberglass angles include polyester, vinyl ester, and epoxy. Polyester resin is typically used for general-purpose applications, offering good strength and corrosion resistance. Vinyl ester and epoxy resins are often chosen for more demanding environments due to their superior resistance to chemicals, heat, and corrosion.
Polyester Resin
Polyester resin is one of the most commonly used resins in fiberglass profiles, including angles. It provides a cost-effective solution with good corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. The resin is also relatively easy to work with, making it a popular choice for general-purpose applications. Polyester resin, however, may not be as resistant to harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures as vinyl ester or epoxy resins.
Dimensions
Typical Sizes
Fiberglass angles are available in a variety of sizes to suit different applications. The leg lengths of these angles typically range from 1 inch to several inches, depending on the specific requirements of the project. For instance, smaller angles may be used for lighter applications, while larger profiles are designed to bear heavier loads. Custom sizes and configurations are also available to meet specific project needs, allowing for flexibility in the design and construction of various structures and systems.
Thickness
The thickness of fiberglass angles is an important factor in determining their load-bearing capacity. Typical thicknesses range from 1/8 inch to several inches, depending on the intended application. Thicker angles are designed to handle heavier loads, while thinner profiles may be sufficient for lighter structural support. When selecting fiberglass angles, it’s crucial to choose the correct thickness based on the structural requirements, ensuring that the angle can safely support the weight and stresses it will encounter.
Applications
Construction
Fiberglass angles are widely used in the construction industry for structural framing, support beams, and bracing. They are particularly useful in environments where traditional materials like steel would be susceptible to corrosion. Fiberglass angles provide a reliable and durable alternative that resists environmental degradation while offering the necessary strength and support. Their corrosion resistance makes them ideal for use in buildings, bridges, and other structures exposed to moisture or harsh weather conditions, ensuring longevity and reduced maintenance.
Marine
In the marine industry, fiberglass angles are used for boat building and repairs due to their lightweight nature and resistance to water damage. They provide strength and support while being resistant to the harsh effects of seawater and salt. Fiberglass angles offer a corrosion-resistant alternative to metals, which are often prone to rust and degradation in marine environments. Their ability to withstand moisture makes them a preferred material for boat frames, docks, and other marine structures.
Industrial
Fiberglass angles are commonly used in industrial applications such as chemical storage tanks, pipelines, and other facilities where corrosion resistance is critical. The fiberglass material provides the necessary strength to support equipment and structures while maintaining durability in corrosive environments. These angles are ideal for use in industries such as chemicals, oil and gas, and manufacturing, where exposure to harsh substances or extreme conditions requires reliable materials that won’t degrade over time.
Advantages
Lightweight
Fiberglass angles are much lighter than traditional metal angles, such as steel or aluminum, which makes them easier to handle and install. The reduced weight simplifies transportation and decreases labor costs, as workers can more easily lift and position the angles during installation. This lightweight property is particularly valuable in large-scale projects, where significant time and cost savings can be achieved by reducing the need for heavy lifting equipment or extensive labor.
Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Fiberglass angles provide an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, meaning they can support heavy loads while remaining lighter than comparable metal angles. This allows them to deliver the necessary structural support without the added weight that often complicates installation and handling. The ability to achieve high strength with lower weight is especially beneficial for applications where space and weight are limited, such as in aerospace, transportation, and infrastructure projects.
Thermal Insulation
Fiberglass is known for its excellent thermal insulation properties. Fiberglass angles prevent heat transfer, making them suitable for use in environments where temperature control is important. This thermal insulation quality helps reduce energy costs and maintain more stable internal temperatures in buildings and industrial processes. Fiberglass angles are particularly useful in applications where temperature fluctuations can impact equipment performance or where insulation is required to maintain energy efficiency.
Low Maintenance
Fiberglass angles require minimal maintenance compared to traditional metals. While metals may need regular painting, rust prevention, or protective coatings, fiberglass angles are naturally resistant to corrosion, UV damage, and weathering. This low maintenance requirement translates into long-term savings and less downtime for repairs or replacements. Fiberglass angles are ideal for projects where reduced maintenance and long service life are essential, particularly in harsh environments where metals might need frequent attention.
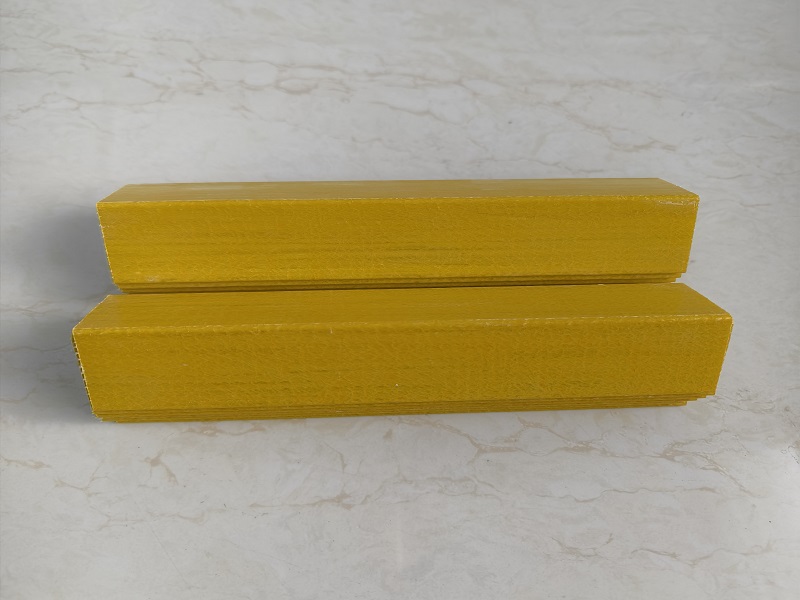


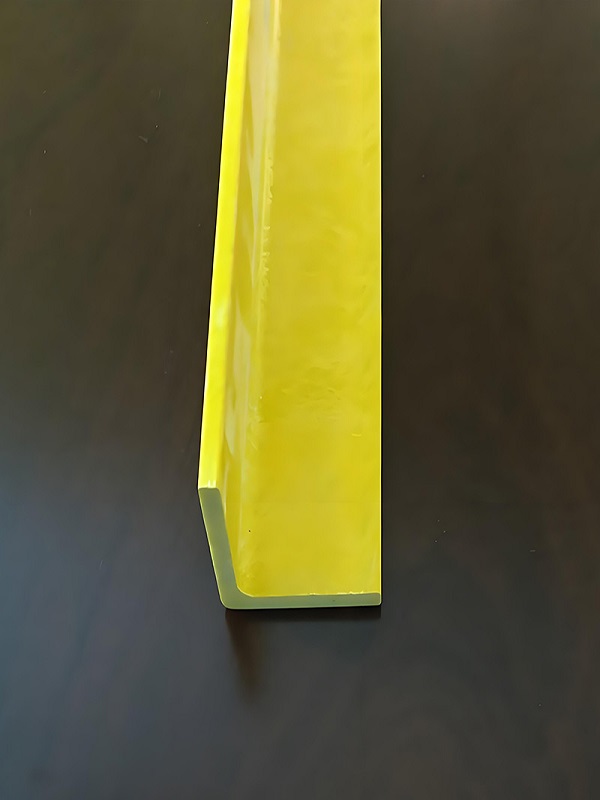
Fiberglass Angle: Equal Leg Angle
An equal leg fiberglass angle is a type of structural angle made from fiberglass, featuring two legs of equal length that meet at a 90-degree angle. This configuration provides balanced strength and support, making it suitable for various structural applications. The equal leg design ensures uniform load distribution, making it an effective solution for reinforcement in numerous industries.
Advantages
Corrosion Resistance
One of the most notable advantages of equal leg fiberglass angles is their superior corrosion resistance. Unlike steel or aluminum angles that degrade over time due to rust, fiberglass angles are immune to corrosion, even in the harshest environments such as marine or chemical processing industries. This property ensures that fiberglass angles retain their strength and integrity for longer periods, reducing maintenance costs and extending the service life of the structure.
Ease of Installation
Equal leg fiberglass angles are easier to handle and install compared to metal counterparts. Their lightweight nature makes them less cumbersome, allowing for quicker and safer installation processes. Additionally, they can be easily cut to size or shaped using standard fiberglass cutting tools, making them a flexible solution for custom applications. This ease of installation translates to reduced labor costs and faster project completion times.
Flexibility in Application
The balanced design of equal leg fiberglass angles makes them highly versatile for a wide range of applications. Whether used for framing, bracing, or structural reinforcement, these angles can be adapted to suit various load-bearing needs. Their equal leg structure provides symmetry, making them ideal for use in both vertical and horizontal applications. This flexibility ensures that fiberglass angles can be used in diverse industries, from construction to marine to industrial facilities.
Installation
Fastening
Equal leg fiberglass angles can be fastened to other components using bolts, screws, or adhesives based on the specific structural needs and load requirements. Given the balanced design of equal leg angles, fastening should ensure that both legs are evenly secured for uniform load distribution. For heavier applications or those requiring high strength, bolts or screws are typically used, while adhesives can be sufficient for lighter or non-load-bearing applications. Proper fastening ensures that the angles maintain their structural integrity under load.
Customization
Fiberglass equal leg angles are easy to customize to suit project specifications. They can be cut, shaped, and drilled with standard fiberglass tools to fit precise dimensions or special designs. This customization is essential for applications where angles need to fit into tight spaces or align with other structural components. The ease of customization allows equal leg angles to be tailored for unique project requirements, whether for irregular angles or specific lengths.
Pre-Installation Checks
Before installation, it’s important to inspect the equal leg fiberglass angles for any surface defects or structural weaknesses. This includes checking for cracks, chips, or any damage that could compromise their strength. Ensuring the angles are the correct length and thickness for the application is also critical, as is confirming the quality of the resin used in manufacturing. Pre-installation checks ensure that the angles will function effectively once installed, maintaining their performance over time.
Installation Tools and Equipment
The installation of equal leg fiberglass angles requires specific tools for cutting, shaping, and fastening. Standard tools such as saws, grinders, and drills can be used to modify the angles as needed. Specialized fiberglass cutting tools help ensure clean edges without compromising the material’s integrity. For fastening, corrosion-resistant bolts, screws, or adhesives are commonly used, depending on the application’s load requirements. Having the right tools ensures a smooth installation process and prevents damage to the fiberglass material.
Considerations
Load Capacity
When selecting equal leg fiberglass angles, it is crucial to ensure they are rated for the intended load. These angles are designed to distribute weight evenly, so it’s essential to match the angle’s load-bearing capacity with the specific demands of the application. Overloading fiberglass angles can compromise their strength and potentially lead to failure. It’s important to check with the manufacturer for load ratings and ensure the fiberglass angles are suitable for the stresses they will encounter in structural applications.
UV Protection
For applications where the equal leg fiberglass angles will be exposed to sunlight, UV inhibitors are essential. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays can degrade the resin, weakening the angle and leading to a loss of structural integrity. Choosing fiberglass angles with built-in UV resistance is vital, especially for outdoor projects or installations in areas with high sun exposure. UV protection ensures the longevity of the material and helps maintain its strength and appearance over time.
Environmental Conditions
The environment in which equal leg fiberglass angles are used significantly impacts their performance. In outdoor or marine environments, the angles must be resistant to not only UV radiation but also moisture and salt exposure. Fiberglass angles made with vinyl ester or epoxy resins provide superior resistance to corrosive environments, making them ideal for harsh conditions. Ensure that the right resin type is selected based on the environmental factors the angles will face, such as chemicals, humidity, or temperature extremes.
Maintenance Requirements
Fiberglass equal leg angles generally require minimal maintenance, thanks to their corrosion resistance and durability. However, it is important to check the angles regularly for signs of wear, such as surface damage or UV degradation. In areas with heavy moisture or exposure to harsh chemicals, periodic inspections for cracks, chips, or any stress-related damage are advisable. While fiberglass doesn’t rust like metal, maintenance may include cleaning, re-coating for UV protection, or replacing angles if they show signs of failure. Regular upkeep ensures the angles maintain their strength and performance throughout their service life.
Thank you for your interest in our products. To receive our pricelist or for any inquiries, please fill out the form below. We will get back to you within 24 hours.
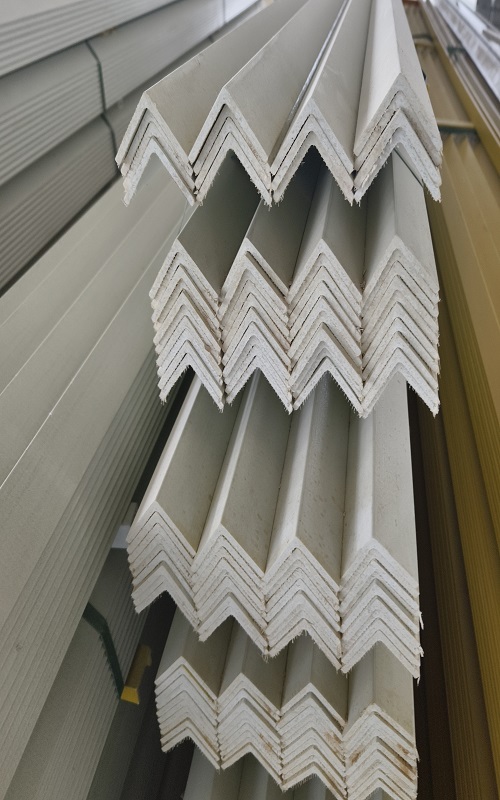
Fiberglass Angle: Structural Shapes
Fiberglass angles, also known as structural angles, are critical components in construction and engineering, available in various shapes tailored to meet different structural needs. Here’s an overview of the primary shape types:
Equal Leg Angles
- Description: Equal leg angles have legs (sides) of the same length, forming a symmetrical “L” shape.
- Dimensions: Commonly available in standard sizes, such as 1″x1″, 2″x2″, and so on, but can also be customized.
- Applications:
- Structural Support: Ideal for framing, bracing, and load-bearing applications where uniform strength is required.
- Versatility: Used in various settings, including buildings, bridges, and mechanical supports.
Unequal Leg Angles
- Description: Unequal leg angles feature one leg longer than the other, creating an asymmetrical shape.
- Dimensions: These angles are available in various configurations, allowing for specific design requirements.
- Applications:
- Custom Support: Designed for situations where different load capacities are needed on each side, such as in specialized frames or equipment supports.
- Load Distribution: Helps in applications where weight or forces are unevenly distributed, providing tailored structural solutions.
Corner Angles
- Description: Corner angles are characterized by rounded or beveled edges, providing a smooth transition between surfaces.
- Applications:
- Aesthetic Design: Commonly used in furniture, architectural details, and interior design, where visual appeal and safety are paramount.
- Safety Features: The rounded edges minimize injury risks, making them suitable for public spaces and high-traffic areas.
Heavy-Duty Angles
- Description: These angles are thicker and more robust than standard fiberglass angles, designed for heavy loads and high-stress applications.
- Applications:
- Industrial Use: Ideal for heavy industrial environments, such as manufacturing plants and construction sites, where structural integrity is critical.
- Support Structures: Often used in frameworks for large machinery, cranes, and equipment that require exceptional strength.
Specialty Shapes
- Description: Fiberglass angles can be custom-manufactured to meet unique specifications and project requirements.
- Applications:
- Tailored Solutions: Used in specialized applications where standard shapes do not meet specific engineering needs, such as unique machinery or custom structural supports.
- Innovative Designs: Engineers can create complex structures by utilizing custom-shaped fiberglass angles.
Fiberglass angles are versatile structural components available in various shapes, including equal leg, unequal leg, corner angles, heavy-duty angles, and specialty shapes. Each type serves specific purposes, making them invaluable in construction, manufacturing, and design. Understanding these shape types and their applications is crucial for selecting the right fiberglass angle to ensure structural integrity and performance in any project.
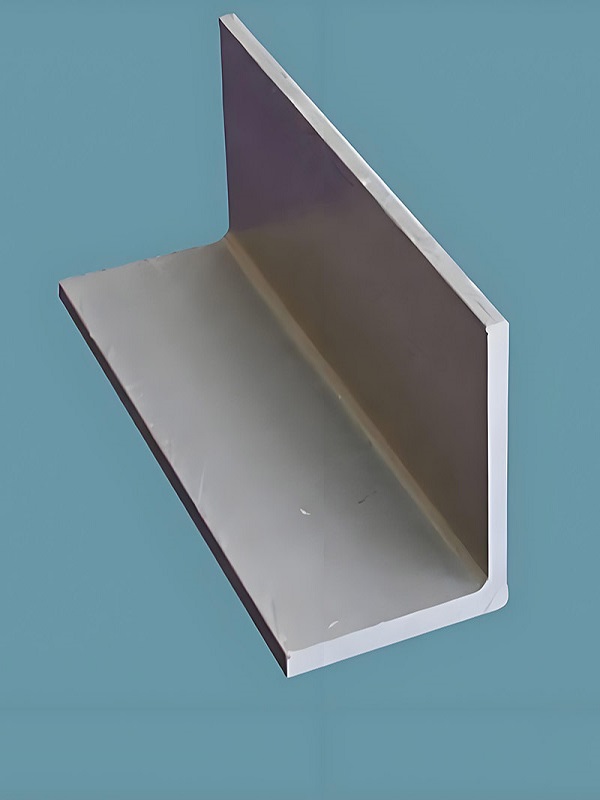

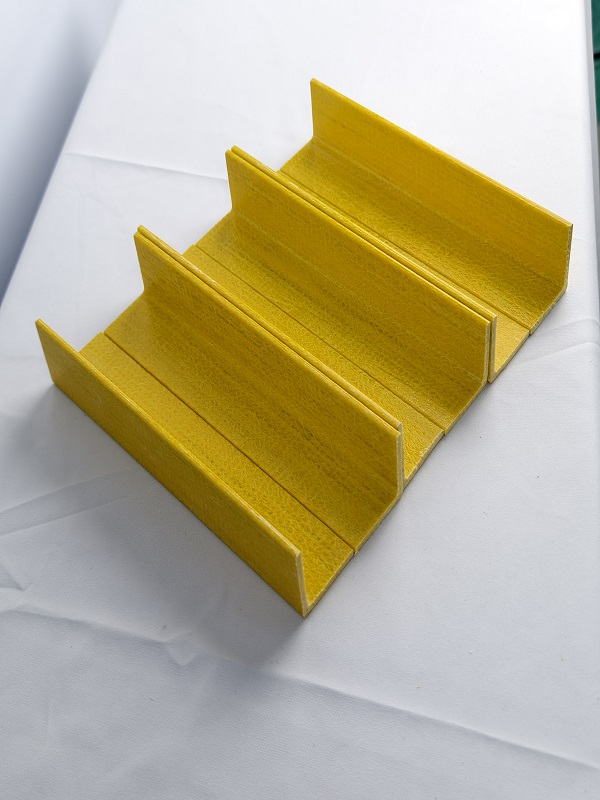
Common Applications of Fiberglass Angle
Fiberglass Angle is a versatile material that finds applications across a wide range of industries due to its unique combination of strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. Here are some of the most common uses of Fiberglass Angle in various settings.
Fiberglass Angle Strips
Fiberglass Angle Strips are commonly used in construction, marine, and industrial environments. In construction, these strips provide structural support and reinforcement for various components, from beams to panels. In marine applications, Fiberglass Angle Strips are favored for their corrosion resistance, making them ideal for use in docks, boat hulls, and other structures exposed to saltwater. In industrial settings, these strips are often used to create durable frameworks that can withstand exposure to chemicals and other harsh conditions without deteriorating.
The Fiberglass Angle Bracket is an essential component in structural support and framing applications. These brackets are widely used in building construction to secure and stabilize joints and connections between different structural elements. Their strength and resistance to corrosion make them ideal for use in both indoor and outdoor settings, ensuring long-lasting performance even in challenging environments. Additionally, Fiberglass Angle Brackets are non-conductive, making them suitable for use in areas where electrical insulation is required, such as in electrical enclosures and control panels. Pultruded Fiberglass Angle is particularly suitable for specialized applications that require electrical insulation and resistance to electromagnetic interference. This type of Fiberglass Angle is often used in the electrical and telecommunications industries, where it provides a safe and reliable solution for supporting and insulating electrical components. The pultrusion process ensures that the Pultruded Fiberglass Angle has consistent properties, making it a dependable choice for critical applications where material integrity is paramount.Fiberglass Angle Bracket
Pultruded Fiberglass Angle
Comparing Fiberglass Angle with Other Materials
When selecting materials for your project, understanding the differences between Fiberglass Angle and other commonly used materials like aluminum and steel is crucial. Each material offers distinct advantages and disadvantages depending on the specific requirements of your application.
Fiberglass Angle vs. Aluminum Angle
Weight: One of the most significant advantages of Fiberglass Angle over aluminum is its weight. While both materials are lightweight compared to steel, Fiberglass Angle is even lighter, making it easier to handle and install. This reduction in weight can lead to lower transportation costs and easier on-site management, especially in large-scale projects.
Strength: Although aluminum is known for its strength, Fiberglass Angle offers comparable strength with the added benefit of flexibility. This flexibility allows Fiberglass Angle to absorb impact better than aluminum, which is more rigid and prone to bending or denting under stress.
Corrosion Resistance: Both materials offer excellent corrosion resistance, but Fiberglass Angle has the edge in environments where exposure to chemicals or saltwater is a concern. While aluminum is resistant to rust, it can still corrode when exposed to certain chemicals or in highly acidic environments. In contrast, Fiberglass Angle is impervious to most chemicals and does not corrode, making it the superior choice for harsh environments like marine or chemical processing settings.
Cost: When it comes to cost, Fiberglass Angle generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to steel, especially when considering the long-term benefits. While steel angles might have a lower upfront cost, they require regular maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion. Over time, these maintenance costs can add up, making Fiberglass Angle the more economical choice in the long run. Durability: Steel is undoubtedly strong and durable, but it is also prone to rust and corrosion, especially in outdoor or moisture-rich environments. Fiberglass Angle, on the other hand, offers excellent durability without the need for protective coatings or regular maintenance. Its inherent resistance to corrosion, moisture, and UV exposure ensures a longer lifespan, even in the most challenging conditions. Application Suitability: Steel angles are often chosen for heavy-duty structural applications where extreme strength is required. However, for applications where weight reduction, corrosion resistance, and low maintenance are priorities, Fiberglass Angle is the better choice. It is particularly suitable for applications in corrosive environments, electrical installations, and situations where weight savings are critical, such as in transportation or aerospace.Fiberglass Angle vs. Steel Angle


Fiberglass Angle Price: What to Expect
When budgeting for your project, understanding the cost of Fiberglass Angle is crucial. The price of Fiberglass Angle can vary significantly depending on several factors, including size, thickness, and the supplier from which you purchase.
Price Range for Fiberglass Angle
The cost of Fiberglass Angle typically ranges from $10 to $30 per foot, depending on the dimensions and thickness of the angle. For example, smaller Fiberglass Profiles, such as a 1-inch by 1-inch Fiberglass Angle with a 1/8-inch thickness, tend to be on the lower end of the price spectrum. These Fiberglass Profiles offer a cost-effective solution for projects requiring lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials without compromising on strength. Their affordability makes them ideal for applications where smaller, yet sturdy, components are needed to maintain structural integrity while keeping costs low. Conversely, larger profiles, such as a 4-inch by 4-inch angle with a 1/4-inch thickness, are more expensive due to the increased material usage and the added strength they provide.
In addition to the basic size and thickness, specialized Fiberglass Angle products, such as those designed for high-strength or corrosion-resistant applications, may also command higher prices. Custom orders or angles made from premium-grade resins could further increase costs, so it’s essential to consider your specific project requirements when estimating expenses.
Several factors can influence the pricing of Fiberglass Angle, and understanding these can help you make more informed purchasing decisions: Supplier: Prices can vary between suppliers, with some offering discounts for bulk purchases or for regular customers. Well-established suppliers like GangLong Fiberglass may have higher prices due to their reputation for quality and service, while smaller, local suppliers might offer more competitive rates. Bulk Purchasing: Buying Fiberglass Angle in bulk can significantly reduce the per-foot cost. Many suppliers offer discounts when you purchase large quantities, which can be particularly beneficial for larger projects. If your project requires a substantial amount of Fiberglass Angle, it’s worth inquiring about bulk pricing options. Shipping Costs: Since Fiberglass Angle is often purchased in long lengths, shipping costs can add up quickly, especially for larger orders. Some suppliers may offer free or discounted shipping for orders above a certain threshold, so it’s worth considering this when comparing prices. If possible, sourcing locally can help you avoid these additional costs. When considering the price of Fiberglass Angle, it’s important to balance cost with quality and reliability. While it might be tempting to opt for the cheapest option, ensuring that the material meets your project’s specifications is vital for long-term success. By comparing prices across different suppliers, considering bulk purchase discounts, and factoring in shipping costs, you can find the best value for your Fiberglass Angle needs.Factors Affecting Pricing
Making the Best Purchasing Decision
Related Products
When working with Fiberglass Angle, there are several related products that can enhance and complement your project. These additional materials, such as Fiberglass Tubes and other pultruded fiberglass shapes, provide versatile solutions that can work in tandem with Fiberglass Angle to meet diverse structural and design needs.
Fiberglass Tube
Fiberglass tube is one of the most commonly used related products. Like fiberglass angle, it is manufactured using the pultrusion process, which ensures consistent quality and strength. Additionally, filament wound fiberglass tubing offers enhanced structural integrity, making it suitable for demanding applications.Fiberglass square tube, along with round profiles, are commonly used in applications requiring structural support, such as frameworks, railings, and handrails. Their lightweight nature, combined with excellent resistance to corrosion and chemicals, makes them a perfect complement to Fiberglass Angle in environments exposed to harsh conditions.
For projects that require both angled and tubular components, Fiberglass Tube can be seamlessly integrated with Fiberglass Angle to create robust structures. For example, in constructing a framework, Fiberglass Tubes can serve as the main vertical supports, while Fiberglass Angles can be used to reinforce joints and provide additional stability.
In addition to Fiberglass Tube, there are several other pultruded fiberglass shapes that can be used alongside Fiberglass Angle to achieve specific design goals. These include: Fiberglass Channel: Ideal for creating strong yet lightweight structural components. Fiberglass Channels are often used in conjunction with Fiberglass Angles to build frameworks, platforms, and walkways that require corrosion resistance and long-term durability. Fiberglass Rod: These solid, cylindrical shapes are perfect for applications requiring additional tensile strength. Fiberglass Rods can be used as reinforcement within structures, complementing Fiberglass Angle by adding strength to areas under significant stress. Fiberglass I-Beam: For heavy-duty applications, Fiberglass I-Beams offer exceptional load-bearing capabilities. These beams are often used in conjunction with Fiberglass Angle in large-scale construction projects, such as bridges, platforms, or industrial flooring, where both vertical and angled support are necessary. The combination of Fiberglass Angle with other pultruded fiberglass shapes allows for greater flexibility and creativity in project design. Whether you’re constructing a complex industrial framework or a simple support structure, using these related products together ensures that you can meet the specific demands of your project. The shared properties of these materials—lightweight, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation—make them ideal partners in a wide range of applications.Other Pultruded Fiberglass Shapes
Complementing Fiberglass Angle in Projects

GangLong Fiberglass Angle Supply
GangLong Fiberglass offers a wide range of high-quality fiberglass angle profiles, engineered for structural applications across various industries. These fiberglass angles feature two legs that form either an L-shaped 90° angle or a Y-shaped angle, making them highly adaptable for construction, architectural, and industrial uses. Their strength, lightweight properties, ease of fabrication, and simple installation make them an excellent alternative to traditional materials like steel and aluminum.
Key Features
Lightweight and Durable
GangLong Fiberglass angles are known for their light weight and exceptional durability. They are significantly lighter than metal alternatives, which reduces transportation costs and simplifies installation. Despite their lighter weight, they maintain a high level of strength and stability, making them ideal for structural applications that require both durability and a reduction in overall weight. This combination of strength and lightness allows for easier handling without compromising performance.
Corrosion Resistance
Fiberglass angles are highly resistant to corrosion, unlike traditional metal materials like steel and aluminum. This makes them particularly useful in environments prone to chemical exposure, moisture, or harsh weather conditions, where metals would normally degrade. With their inherent corrosion resistance, GangLong Fiberglass angles maintain their integrity over time, offering long-term reliability and requiring minimal maintenance. Their ability to withstand corrosion makes them perfect for use in marine, chemical processing, or outdoor environments.
One of the key benefits of fiberglass angles is their low maintenance requirements. Due to their durability, corrosion resistance, and UV stability, these angles do not require frequent upkeep. Unlike metals that may require regular painting, rust removal, or protective coatings, fiberglass angles maintain their appearance and performance over an extended period. This not only reduces maintenance costs but also contributes to a longer service life, making them a cost-effective solution for demanding applications. GangLong Fiberglass angles are treated with UV inhibitors, ensuring they remain unaffected by prolonged exposure to sunlight. UV exposure can degrade many materials, but fiberglass profiles are specially designed to withstand harsh UV rays without losing their mechanical properties. This treatment makes them suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications, ensuring long-lasting performance even in environments with high levels of sun exposure. The UV resistance guarantees that the profiles will not weaken, crack, or discolor over time. The 500 Standard Grade is a general-purpose isophthalic polyester resin system designed to offer excellent corrosion resistance in a variety of environments. It includes UV inhibitors to protect against sunlight degradation, ensuring long-term performance even in outdoor applications. This grade is ideal for general use where fire resistance is not a primary concern but where durability and corrosion resistance are crucial. Its versatility makes it suitable for many industrial and structural uses. The 525 FR/UV Grade is a fire-retardant isophthalic polyester resin system designed to enhance safety by reducing the spread of fire. In addition to its fire-resistant properties, this grade also includes UV inhibitors that protect the resin from environmental degradation. It is an excellent choice for applications requiring both fire protection and UV stability, such as in industrial or commercial settings where both fire safety and exposure to sunlight are a concern. The 625 VE Grade uses a premium vinyl ester resin system, combining fire-retardant properties with superior corrosion resistance. This grade is ideal for demanding environments where fire safety and resistance to aggressive chemicals or corrosion are required. With a UV inhibitor, it also ensures that the fiberglass profiles maintain their strength and integrity in harsh outdoor conditions. The 625 VE Grade is the best choice for applications exposed to severe environments, including marine and industrial uses. Fiberglass angles are frequently used in the construction of walkways and platforms in industrial environments. They provide durable, safe, and non-slip surfaces, making them ideal for environments where employees must work in challenging conditions. Their lightweight nature also simplifies installation, while their corrosion resistance ensures that they will perform reliably over time, even in harsh weather or exposure to chemicals. Fiberglass angles are commonly used as supports and brackets to secure various structures and equipment. Their high strength-to-weight ratio ensures that they provide the necessary support while reducing the overall weight of the structure. Additionally, their corrosion resistance makes them ideal for environments where metal supports might fail due to rust or chemical degradation. Fiberglass angles are a reliable choice for providing long-lasting stability and strength. In structural framing, fiberglass angles offer an excellent alternative to traditional steel and aluminum. They are used to build strong and durable frames for various applications, including scaffolding, framework for buildings, and infrastructure components. Their ability to resist corrosion and their lightweight nature make them particularly valuable for use in corrosive environments, such as marine or chemical processing settings, where metal framing might corrode over time. GangLong Fiberglass angles are manufactured with a combination of glass fiber reinforcements and high-performance thermoset polyester or vinyl ester resin systems. This ensures that every product meets the highest standards of quality and reliability. We use stringent quality control measures throughout the production process to guarantee that our fiberglass profiles perform to expectations, providing you with long-lasting solutions. To enhance corrosion resistance and UV protection, all GangLong Fiberglass products feature a surface veil. This protective layer helps to prolong the life of the profiles by safeguarding them from environmental damage, ensuring that they maintain their strength and durability throughout their service life. With over 100 standard shapes available, GangLong Fiberglass is your go-to supplier for structural FRP needs. Our extensive inventory allows us to offer a wide variety of profiles, ensuring that we can meet the requirements of nearly any project. Whether you need standard sizes or custom configurations, GangLong Fiberglass has the products you need. GangLong Fiberglass angles come in a wide range of sizes, ensuring they meet the strength requirements of your specific application. Our products are stocked at distribution centers located strategically to ensure fast and efficient delivery. With a broad selection of profiles and sizes available, you can easily find the right fiberglass angle for your project, ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Custom sizes are also available to suit unique project needs, ensuring versatility for any construction or infrastructure project. For durable, cost-effective, and low-maintenance structural solutions, trust GangLong Fiberglass angle stock to deliver unmatched performance in even the most demanding environments. Contact us today to find the right fiberglass angle for your project!Low Maintenance
UV Resistance
Available Grades
500 Standard Grade
525 Fire Retardant/UV Resistant Grade
625 VE Grade
Applications
Walkways and Platforms
Supports and Brackets
Structural Framing
Why Choose GangLong Fiberglass?
Quality Assurance
Surface Veil
Extensive Inventory
Custom Sizes and Availability
FAQs about Fiberglass Angle
What is the draft angle for a fiberglass mold?
How do you cut fiberglass insulation at an angle?
What is the FRP angle?
What is fiber angle?
Can you cut FRP with an angle grinder?
Can FRP go directly on studs?
What is the difference between FRP and GRP pole?
How strong are fiberglass l beams?
What are the 4 main types of FRP?
Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP)
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP)
Aramid Fiber Reinforced Polymer (AFRP)
Basalt Fiber Reinforced Polymer (BFRP)
Each type offers different properties suited for specific applications.
Can you screw in FRP?
Does FRP hold up outside?
What does FRP stand for fiberglass?
What specification is FRP?
Does FRP expand in heat?
What are the disadvantages of fiberglass?
Brittleness: Fiberglass can be more brittle and prone to cracking under impact.
Health Risks: Handling fiberglass can cause skin irritation and respiratory issues.
Difficult to Repair: Once damaged, fiberglass can be challenging to repair effectively.
Environmental Concerns: Fiberglass production and disposal have environmental impacts due to its non-biodegradable nature.
Why do people not like fiberglass?
Why can't you touch fiberglass?
Is fiberglass cancerous?
What is the biggest problem with Fibreglass insulation?
Why is fiberglass toxic?
Why is fiberglass bad for skin?
What weakens fiberglass?
Why is fiberglass not sustainable?
How long does fiberglass last?
What are 3 advantages of fiberglass?
Corrosion Resistance: Ideal for use in harsh environments where metal would corrode.
Lightweight: Easier to handle and install compared to metals like steel.
Non-conductive: Safe for electrical applications, reducing the risk of electric shock.
