- Home
- Fiberglass Sheets
In Stock Fiberglass Sheets Supply
Fiberglass Sheets are high-strength laminates made from fiberglass prepreg reinforced with epoxy resin. These sheets are versatile and suitable for various applications, including pattern templates and surface sheeting, where a flat, smooth surface is needed. Manufactured without tints or pigments, the Natural Fiberglass Sheets retains its natural color. Autoclave curing at high temperatures and pressure ensures that these sheets are strong, rigid, and free from voids or waves, unlike wet layup methods. GangLong Fiberglass offers high-strength, lightweight fiberglass sheets with epoxy resin in various sizes and styles, available for fast shipping and easy online ordering.
GangLong Fiberglass offers a complete line of FRP sheets, including Epoxy Fiberglass Sheet, which is known for its superior strength and resistance to chemicals and moisture, making it ideal for a wide range of industrial applications.These sheets exhibit excellent electrical insulating properties, dimensional stability, and superior adhesive qualities, along with high mechanical strength and chemical resistance, even in humid conditions. Fiberglass Sheets are widely used in industrial applications for their strength, durability, and moisture resistance, making them ideal for roofing, construction reinforcement, and insulation. Their lightweight yet strong nature makes them a preferred choice for both residential and industrial projects, offering reliable and versatile solutions across various applications.
News
- Exploring the Benefits of Carbon Fiber Apparel
- How to Work with Carbon Fiber Successfully
- Carbon Fiber Suit: The Future of Lightweight Armor
- Is Carbon Fiber Armor the Future of Protection?
- Why White Carbon Fiber is Popular in Automotive Design
- Transparent Carbon Fiber Sheets Two Sided Gloss Twill
- Epoxy-Compatible Chopped Carbon Fiber Mat
- Carbon Fiber EG Hatch: Upgrade Your Civic Today
- The Benefits of Using Structural Carbon Fibre in Engineering
- How Many Layers of Layered Carbon Fiber Are Needed?
Simplifying Your Life: Key Functionalities
| Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Origin | Hebei, China |
| Brand Name | GangLong Fiberglass |
| Product Name | Fiberglass Sheets |
| Material | Fiberglass |
| Application | Infrastructure |
| Technology | Pultrusion |
| Surface Treatment | Smooth or Polished |
| Processing Services | Bending, Forming, Welding, Cutting, Uncoiling |
| Advantages | Insulation, Fireproof, Anti-corrosion |
| Width | Customizable |
| Length | Customizable |
| Thickness | Customizable |
| Size | Customizable |
| Color | White, Yellow, Gray or Customized |
| Tensile Strength | High |
| Certification | ISO9001 ISO14001 |
| Packaging | Customized Packaging |
What Are Fiberglass Sheets?
Fiberglass sheets are high-strength laminates made from fiberglass prepregs reinforced with high-strength epoxy resins. These sheets are versatile and widely used in applications requiring flat, smooth surfaces, such as pattern templates, surfacing sheets, or structural panels. Their strength and rigidity make them suitable for diverse industrial and construction needs.
Natural fiberglass sheets are manufactured without added tints or pigments, showcasing the natural color of fiberglass. To ensure durability and consistency, they are cured in autoclaves at high temperatures and pressures. This advanced curing process results in rigid sheets with a smooth, lightweight structure, minimal voids, and a flat surface, unlike the uneven results often seen in wet layup processes.
With their robust properties and versatile applications, fiberglass sheets are ideal for projects that demand strong, reliable materials with precise finishes and superior quality.
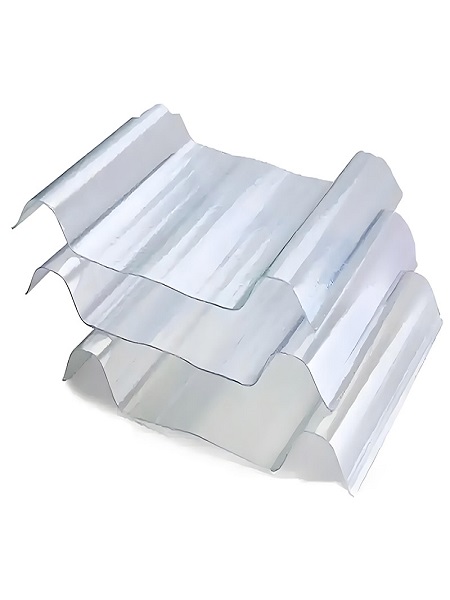
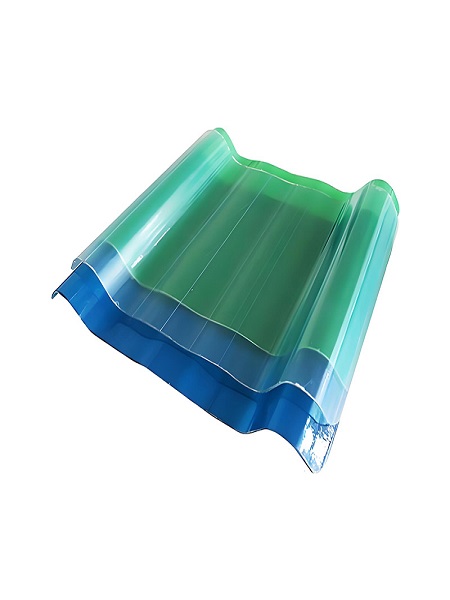


Applications of Fiberglass Sheets
Fiberglass sheets are highly versatile materials, widely utilized across various industries due to their exceptional strength, lightweight nature, and durability. Below are some key applications:
Marine Industry
Fiberglass sheets are commonly used in the construction and repair of boats, hulls, and decks. Their resistance to corrosion, moisture, and harsh environmental conditions makes them an ideal material for marine applications.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, fiberglass sheets are used for body panels, hoods, and other structural components. They provide a lightweight alternative to metals while maintaining strength and impact resistance, contributing to better fuel efficiency and durability.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry benefits from the lightweight yet strong properties of fiberglass sheets. They are used for aircraft interiors, panels, and structural components, where weight reduction is critical without compromising performance or safety.
Industrial Applications
Fiberglass sheets are integral to industrial environments where high-strength, chemical-resistant materials are required. They are used for tanks, ducts, insulation, and equipment housing, offering durability in harsh conditions and prolonged usage.
From marine and automotive to aerospace and industrial applications, fiberglass sheets are indispensable for projects demanding a combination of strength, reliability, and versatility.
Advantages of Fiberglass Sheets
Fiberglass sheets offer a range of advanced properties that make them highly advantageous for various applications across industries. Below are the key benefits:
Exceptional Electrical Insulation
Fiberglass sheets exhibit excellent electrical insulation properties, making them ideal for applications in electronics, power generation, and electrical equipment. Their good dielectric loss properties and electrical strength ensure reliable performance in high-voltage and sensitive systems.
Superior Dimensional Stability
These sheets maintain their shape and structural integrity even under extreme conditions. Their dimensional stability ensures consistent performance, reducing deformation risks in demanding environments.
High Mechanical Strength
Fiberglass sheets possess extremely high mechanical strength, enabling them to withstand heavy loads and impacts. This makes them a preferred choice for structural and load-bearing applications in industries like construction, marine, and aerospace.
Excellent Bonding Properties
The excellent bonding characteristics of fiberglass sheets allow them to adhere well to other materials, facilitating their use in composite structures or layered assemblies.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Fiberglass sheets demonstrate remarkable chemical resistance, withstanding exposure to corrosive substances and harsh environments. They perform reliably not only at room temperature but also under wet or humid conditions, making them suitable for marine, industrial, and outdoor applications.
Durability and Versatility
Combining these properties, fiberglass sheets are a durable, versatile solution for applications demanding strength, reliability, and resistance to environmental stress. Their consistent performance under diverse conditions makes them an indispensable material across industries.

Thank you for your interest in our products. To receive our pricelist or for any inquiries, please fill out the form below. We will get back to you within 24 hours.

Common Sizes of Fiberglass Sheets
Fiberglass sheets are available in a range of sizes to suit different applications, with the most common sizes being 4×8 feet, 5×10 feet, and custom dimensions based on project needs. Each size offers unique advantages and considerations, making them versatile for various industries.
Fiberglass Sheets 4×8
Fiberglass Sheets 4×8 are standard-sized panels measuring 4 feet by 8 feet, making them a convenient option for various projects. These sheets come in different thicknesses, typically ranging from 1/8 inch to 1/2 inch, depending on the intended application. The 4×8 size is popular due to its versatility and ease of handling, providing ample coverage for large areas or sections. The sheets are made by layering fiberglass fibers with resin, which is then cured to create a rigid, durable panel. These panels have numerous fiberglass sheet uses, including applications in construction, automotive, and marine industries, thanks to their strength and lightweight properties.
Advantages of 4×8 Fiberglass Sheets
The 4×8 fiberglass sheet is a popular size due to its versatility and ease of handling. Its dimensions—4 feet by 8 feet—allow for easy transportation and installation, especially for standard building or industrial projects. This size is commonly used for wall panels, roofing, insulation, and boat hulls. The flat, strong surface provides durability without adding significant weight, making it ideal for construction, automotive, and marine applications. Additionally, the size is compatible with standard cutting tools, allowing for customization when needed.
Disadvantages of 4×8 Fiberglass Sheets
While 4×8 fiberglass sheets are versatile, they may not be suitable for larger projects that require fewer seams or continuous coverage. For large-scale applications, such as expansive walls or larger structural components, the 4×8 sheet may require more joints, which could compromise the aesthetic or structural integrity if not properly sealed or reinforced. Additionally, cutting these sheets to fit certain spaces can result in material wastage, especially if the project requires a custom shape or size.
4×8 Fiberglass Sheet Applications
Fiberglass Sheets 4×8 are widely used in construction, manufacturing, and DIY projects due to their strength and lightweight properties. In construction, they are often employed for creating durable partitions, wall panels, and countertops. In manufacturing, these sheets are used for producing parts and components that require high strength and resistance to environmental factors. For DIY enthusiasts, 4×8 fiberglass sheets offer a manageable size for custom projects like crafting, home repairs, or even artistic installations. The benefits of using 4×8 fiberglass sheets include their ease of installation, resistance to moisture, and overall durability, making them an excellent choice for both practical and creative applications.
Fiberglass Sheets 5×10
5×10 fiberglass sheets are a larger variant of fiberglass laminates, measuring 5 feet by 10 feet, and are commonly used in industries requiring a wider coverage area. These sheets are made from fiberglass prepregs reinforced with high-strength epoxy resin, which gives them excellent mechanical strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. The increased size compared to the standard 4×8 sheet allows for greater efficiency in large-scale projects, reducing the need for multiple seams and joints.
Advantages of 5×10 Fiberglass Sheets
Larger Coverage Area
The 5×10 size provides a broader surface area, reducing the number of sheets required for larger projects. This makes installation quicker and more cost-effective, particularly for expansive applications like walls, roofs, or industrial panels.Fewer Seams
With fewer sheets required, the 5×10 fiberglass panels create a more seamless surface. This reduces the potential for leaks, gaps, and structural weaknesses, ensuring a smoother and more aesthetically pleasing result.Increased Strength and Durability
Due to the larger size, 5×10 fiberglass sheets are typically reinforced for greater strength, providing enhanced durability in both structural and environmental conditions. They are resistant to moisture, chemicals, and wear, making them ideal for long-lasting applications.Efficient for Large-Scale Applications
For large-scale or high-volume projects, using 5×10 fiberglass sheets offers operational efficiency by reducing installation time and minimizing waste.
Disadvantages of 5×10 Fiberglass Sheets
Handling and Transportation Challenges
The larger size of 5×10 sheets makes them bulkier and more difficult to handle. Transporting these sheets requires larger vehicles and special equipment, increasing logistics complexity and costs.Limited Customization
While the larger size is efficient for many applications, it may not be suitable for projects that require a more customized fit. Cutting these larger sheets to precise dimensions can result in material wastage.Increased Weight
The 5×10 sheets are heavier than smaller sheets, which can make installation more labor-intensive and may require additional support structures to prevent sagging or bending during the process.
Applications of 5×10 Fiberglass Sheets
Construction and Building Projects
The 5×10 size is commonly used for large construction projects, such as industrial buildings, warehouses, and commercial spaces. Their size makes them ideal for roofing, wall panels, or partitions where wide, flat surfaces are needed.Marine Industry
For boat hulls, decks, and other large components, 5×10 fiberglass sheets are an excellent choice. Their strength and resistance to water and corrosion make them particularly valuable for marine applications.Automotive and Aerospace
In automotive and aerospace industries, 5×10 fiberglass sheets are used to create larger body panels, structural components, and other parts where reducing the number of seams and improving strength is crucial.Industrial Equipment
These sheets are widely used in the manufacturing of tanks, ducts, and enclosures, where durability and chemical resistance are essential. Their larger size allows for fewer joints, which is ideal for large equipment or machinery housing.
Overall, 5×10 fiberglass sheets are an ideal choice for projects requiring a larger, more efficient material with high mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and minimal seams. While they offer numerous advantages in terms of size and durability, they do require more careful handling during transportation and installation.
Custom Sizes of Fiberglass Sheets
Custom-sized fiberglass sheets are tailored for specific projects, minimizing material waste and ensuring precision. These sheets are perfect for intricate designs or unique structures but often come at a higher cost and longer lead time.
Fiberglass Sheets and Resin
Usage of Resin
Fiberglass sheets are often used in conjunction with resin to enhance their strength, durability, and overall performance. The resin acts as a bonding agent that saturates the fiberglass sheets, binding the fibers together and creating a solid, cohesive material. This combination is commonly employed in various applications where reinforced materials are required.
In practical terms, fiberglass sheets and resin are frequently used in industries such as marine construction, automotive repair, and home improvement. For instance, in boat construction, fiberglass sheets are laminated with resin to form a strong, water-resistant hull. In automotive repair, resin-infused fiberglass sheets are used to create durable, lightweight panels. Additionally, in home improvement, resin-coated fiberglass sheets are utilized for making countertops, shower walls, and other surfaces that benefit from the material’s resilience.
Types of Resins
Several types of resins are used with fiberglass sheets, each offering unique benefits depending on the application:
Epoxy Resin: Epoxy resin is known for its excellent adhesive properties and high strength. It cures to a hard, durable finish that is resistant to moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations. Epoxy resin is often preferred in high-performance applications, such as aerospace and marine environments, due to its superior bonding and protective qualities.
Polyester Resin: Polyester resin is another common choice for use with fiberglass sheets. It is more affordable than epoxy resin and provides good strength and durability. Polyester resin cures quickly and is widely used in the automotive industry, for home repair projects, and for creating molds. While it may not offer the same level of chemical resistance as epoxy, it is suitable for many standard applications.
Vinyl Ester Resin: Vinyl ester resin is a type of resin that combines features of both epoxy and polyester resins. It provides excellent resistance to corrosion and impact, making it a good choice for demanding environments. Vinyl ester resin is often used in industries where high performance and durability are required, such as in chemical tanks or pipelines.
Fiberglass Sheets for Roofing
Applications in Roofing
Fiberglass sheets are increasingly used in roofing applications due to their excellent performance and versatility. These sheets are often employed in both residential and commercial roofing projects, offering a lightweight and durable alternative to traditional roofing materials. Fiberglass sheets are utilized in several ways, including as a primary roofing material, for roofing panels, and as part of a composite roofing system.
In roofing, fiberglass sheets are valued for their weather resistance and durability. They are resistant to UV rays, moisture, and extreme temperatures, making them suitable for various climates and environmental conditions. The sheets can be used in flat or pitched roofs and are often selected for their ability to provide a long-lasting, low-maintenance roofing solution.
Benefits of Using Fiberglass Sheets for Roofing
Fiberglass sheets offer several benefits when used in roofing applications:
Durability: Fiberglass sheets are highly durable and can withstand harsh weather conditions, including heavy rain, snow, and high winds. Their resistance to cracking and warping ensures a longer lifespan compared to some other roofing materials.
Weather Resistance: The inherent properties of fiberglass make it resistant to moisture and UV degradation. This weather resistance helps prevent issues such as leaks and deterioration, contributing to a more reliable roofing system.
Lightweight: Fiberglass sheets are lighter than traditional roofing materials, which makes them easier to handle and install. This lightweight nature also reduces the load on the building’s structure.
Low Maintenance: Once installed, fiberglass roofing requires minimal maintenance. Its resistance to mold and mildew, combined with its ease of cleaning, makes it a low-maintenance option for homeowners and building managers.
Installation and Maintenance
Basic Installation Tips for Fiberglass Roofing Sheets
Preparation: Before installing fiberglass sheets, ensure that the roofing surface is clean, dry, and free of any debris. It’s important to remove any old roofing materials or contaminants that could affect the adhesion of the sheets.
Cutting and Shaping: Fiberglass sheets can be cut to size using a utility knife or specialized cutting tools. Measure and cut the sheets carefully to fit the dimensions of your roofing area.
Fastening: Secure the fiberglass sheets to the roofing structure using appropriate fasteners or adhesives. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for spacing and type of fasteners to ensure a secure and stable installation.
Sealing: Apply a compatible sealant around the edges and seams of the fiberglass sheets to prevent water infiltration. Proper sealing is crucial to maintaining the integrity of the roofing system.
Maintenance Practices
Regular Inspections: Conduct periodic inspections of your fiberglass roofing to check for any signs of damage or wear. Look for cracks, loose fasteners, or areas where the sealant may have deteriorated.
Cleaning: Clean the fiberglass roofing sheets regularly to remove debris, leaves, and other contaminants. Regular maintenance ensures longevity, and sourcing materials from reputable suppliers, such as China FRP fiberglass roof sheet factories, can provide high-quality options that are durable and reliable.Use a mild detergent and water solution to avoid damaging the surface.
Repairs: Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage. Repair any cracks or holes with appropriate patching materials and reseal any areas where the sealant has worn away.
GangLong Fiberglass Supply Fiberglass Sheets
GangLong Fiberglass is a manufacturer or distributor focused on providing fiberglass sheets for commercial, industrial, and construction applications. Companies in this field usually offer various grades of fiberglass sheets with different thicknesses, resins, and finishes to meet specific customer needs.
Key Offerings by Fiberglass Sheet Suppliers
Fiberglass Sheet Types:
- Standard Fiberglass Sheets: These are used in a wide variety of industries, including construction, automotive, and marine. They may come in various sizes and thicknesses.
- Reinforced Fiberglass Sheets: Used in applications requiring additional strength and durability, these sheets are often reinforced with other materials, such as polyester resin, for added resilience.
- Custom-Made Fiberglass Sheets: Some suppliers, like GangLong, might offer customized solutions, producing sheets tailored to the specifications of the client, such as specific dimensions or resin choices for particular applications.
Product Specifications:
- Thickness & Size Variability: Fiberglass sheets are typically available in different thicknesses ranging from thin sheets for insulation purposes to thick, robust sheets for structural applications.
- Surface Finishes: Fiberglass sheets can be offered with different surface finishes, such as smooth or textured, depending on their intended use. Some suppliers might also provide UV-resistant coatings to protect the material from sun exposure.
- Resin Options: The type of resin used can vary based on the application. For instance, polyester resin is commonly used for general purposes, while epoxy resin is preferred in applications requiring enhanced chemical resistance.
Benefits of Purchasing Fiberglass Sheets from Suppliers like GangLong
- Quality Assurance: Reputable suppliers like GangLong typically maintain strict quality control procedures to ensure the durability, strength, and reliability of their fiberglass sheets. This ensures that the products meet the standards required for various industrial applications.
- Customization: Suppliers often offer the ability to customize fiberglass sheets in terms of size, thickness, and finish, allowing businesses to find the right material for specific projects.
- Competitive Pricing: Established suppliers usually offer competitive pricing, making it easier for businesses to source fiberglass sheets in bulk while staying within budget.
- Technical Support: Suppliers like GangLong may offer technical support to help customers select the right type of fiberglass sheet for their needs. This support can include guidance on material properties, applications, and installation tips.
Fiberglass sheet suppliers like GangLong Fiberglass play an important role in providing high-quality materials to meet the diverse needs of industries such as construction, automotive, marine, and more. By offering customizable products, competitive pricing, and robust customer support, companies can ensure that they receive the right type of fiberglass sheet for their specific needs, ultimately contributing to the success of their projects.
FAQs about Fiberglass Sheets
What are the two types of fiberglass?
How thick is a fiberglass sheet?
Why is fiberglass banned?
What is fiberglass sheeting used for?
What are the disadvantages of fiberglass panels?
Is fiberglass cancerous?
Is glass fiber the same as fiberglass?
What is stronger fiberglass mat or cloth?
Can you buy fiberglass in sheets?
Is fiberglass cheap?
ls fiberglass safe to touch?
How do you lay fiberglass sheets?
Surface Preparation: Clean and smooth the surface where the sheets will be applied.
Apply Resin: Coat the surface with resin, usually epoxy or polyester, to act as an adhesive.
Lay the Fiberglass Sheet: Place the sheet onto the wet resin, smoothing it out to remove air bubbles.
Apply Additional Resin: A top layer of resin is applied to saturate the fiberglass and bond it firmly to the surface.
Curing: Allow the resin and fiberglass to cure, which typically involves hardening under specific temperature conditions.
This method is commonly used in industrial applications such as boat hulls, tanks, and construction materials.
ls fiberglass worth the money?
Is fiberglass an expensive material?
Can you wash fiberglass out of sheets?
What can be mistaken for fiberglass?
How thick are fiberglass sheets?
Is fiberglass sheet fireproof?
What are fiberglass sheets used for?
Construction: For roofing, wall panels, and reinforcement.
Automotive: In body panels, truck beds, and parts of boats and RVs.
Aerospace: For lightweight, high-strength components in aircraft.
Marine: As hull material for boats, decks, and docks due to their water resistance.
Electrical Insulation: Used in electrical panels and circuit boards for insulation purposes.
Chemical Processing: In environments requiring corrosion resistance, such as tanks and pipes.
Is fiberglass toxic to humans?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of fiberglass sheet?
Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Fiberglass is lightweight yet strong, making it ideal for industries like aerospace and marine.
Corrosion Resistance: It resists chemicals, water, and environmental degradation, making it durable in harsh environments.
Versatility: It can be molded into complex shapes for custom applications.
Cost-Effective: Compared to materials like carbon fiber or metal, fiberglass is relatively affordable.
Disadvantages:
Health Risks: Handling fiberglass without protection can lead to skin and respiratory irritation.
Brittleness: Fiberglass can be brittle under impact or high-stress conditions, leading to cracks or fractures.
UV Degradation: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can cause fiberglass to degrade over time if not properly treated.
What is fiberglass mainly used for?
Marine: Boat hulls, decks, and marine equipment.
Construction: Reinforcement for concrete, roofing materials, and insulation.
Automotive and Aerospace: Lightweight components in cars, trucks, and aircraft.
Chemical Industry: Tanks and pipes resistant to corrosive substances.
How do you cut fiberglass?
Tools: Use a fine-toothed saw, jigsaw, or specialized diamond blade for cutting fiberglass.
Protection: Wear protective gear such as gloves, goggles, and a dust mask to prevent inhalation of fiberglass dust.
Cutting Process: Mark the cutting line, stabilize the sheet, and make slow, steady cuts to avoid chipping or cracking the fiberglass.
Does fiberglass break down?
Does your skin absorb fiberglass?
How strong is a sheet of fiberglass?
Is fiberglass waterproof?
ls fiberglass safe in beds?
What is the difference between fiberglass and acrylic sheeting?
Fiberglass: Made from woven glass fibers and resin, it is stronger and more durable, used in construction, marine, and industrial applications. Fiberglass is also more resistant to heat and chemicals.
Acrylic: Made from a transparent plastic polymer (PMMA), it is lighter and often used in applications where clarity is important, like windows, displays, and signage. However, acrylic is more prone to scratching and less resistant to high heat or chemical exposure compared to fiberglass.
Is it OK to sleep on fiberglass?
Is fiberglass toxic to breathe?
Does fiberglass ever leave your skin?
Does fiberglass break down in lungs?
What is the danger of fiberglass in a mattress?
Skin Irritation: Fiberglass particles can cause itching, rashes, and irritation if they come into contact with the skin.
Respiratory Issues: Inhalation of fiberglass particles can lead to coughing, throat irritation, and potentially more severe respiratory problems.
Environmental Contamination: Fiberglass fibers can spread to other parts of your home, contaminating surfaces and making them difficult to clean up. Exposure to fiberglass in a mattress can affect overall health and well-being.
Can you sleep in a room with exposed fiberglass?
How do l tell if my mattress has fiberglass?
Label Information: Check the mattress label or manufacturer's information for materials listed as ""glass fiber"" or ""fiberglass"" under the fire-retardant layer.
Price Point: Low-cost memory foam mattresses often contain fiberglass as a cheaper fire-resistant material.
Visible Damage: If the outer cover is damaged or torn, and you see shiny, thread-like particles, this could indicate fiberglass exposure.
If you're concerned about fiberglass, contact the manufacturer for confirmation.
How does fiberglass get on your bed?
What to do if you have fiberglass in your room?
Isolate the Area: Close off the contaminated area to prevent further spread of the fibers.
Protective Gear: Wear gloves, long sleeves, and a mask to avoid direct contact with the fiberglass.
Vacuum: Use a vacuum with a HEPA filter to clean surfaces, as regular vacuums can spread the fibers.
Wash Clothing and Bedding: Wash affected bedding and clothes separately to remove fiberglass particles.
Consult a Professional: If the contamination is severe, consider hiring professional cleaners who specialize in fiberglass removal.
How to tell if something is fiberglass?
Visual Inspection: Fiberglass often has a woven, shiny, thread-like appearance. In some cases, the fibers are embedded in resin, giving a smooth finish.
Touch: Fiberglass feels slightly rough to the touch and may cause itching or irritation.
Product Information: Check the product label or manufacturer's materials list for references to ""fiberglass,"" ""glass fiber,"" or similar terms.
Light Test: If the material is exposed and thin, shining a light through it can reveal the characteristic fiber patterns of fiberglass.
Which is stronger fiberglass mat or fiberglass cloth?
How many layers of fiberglass cloth should l use?
Can fiberglass cloth stop a bullet?
Do i need to sand between layers of fiberglass?
Is fiberglass as strong as Kevlar?
What is the strongest type of fiberglass cloth?
What is better than fiberglass?
Carbon Fiber: Stronger and lighter than fiberglass, used in high-performance applications like aerospace and racing.
Kevlar: More impact-resistant than fiberglass, often used in bulletproof vests and military gear. Both materials, however, are more expensive than fiberglass, making fiberglass still a cost-effective option for many industrial applications.
What can l use instead of fiberglass cloth?
Carbon Fiber Cloth: Stronger and lighter but more expensive. Ideal for high-performance applications.
Kevlar Fabric: Highly impact-resistant and used in armor and other protective equipment.
Natural Fiber Composites: Hemp or flax fibers can be used as an eco-friendly alternative in some non-structural applications. These materials offer different benefits depending on the application’s requirements for strength, weight, and cost.
Is fiberglass worth the money?
Is fiberglass easily breakable?
What weakens fiberglass?
UV Exposure: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can degrade the resin, making the fiberglass brittle.
Moisture: Water intrusion can weaken fiberglass over time, especially in poorly cured or improperly sealed applications.
Physical Impact: Repeated stress or impacts can cause fiberglass to crack or fracture.
Chemical Exposure: Certain chemicals, especially strong acids or bases, can corrode the resin, weakening the fiberglass structure. Proper maintenance and UV-resistant coatings can help mitigate these weaknesses.
What material is stronger than fiberglass?
Carbon Fiber: Much stronger and lighter than fiberglass, with high tensile strength and stiffness.
Kevlar: Superior in impact resistance, often used in body armor and protective gear.
Steel: Though heavier, steel offers greater strength and is more resistant to impact than fiberglass. These materials are often used in industries where high performance or extreme durability is needed, though they come at a higher cost compared to fiberglass.
Is there anything better than fiberglass insulation?
Spray Foam Insulation: Offers better air sealing and higher R-values for improved energy efficiency, but is more expensive.
Mineral Wool (Rock Wool): Fire-resistant and offers higher soundproofing capabilities compared to fiberglass.
Cellulose Insulation: Made from recycled materials, it's eco-friendly and has excellent thermal resistance. These alternatives may offer better performance in terms of insulation, fire resistance, or environmental impact, but at a higher cost.