Metal grating is a versatile, open grid structure commonly used to create floors, platforms, stair treads, and walkways, primarily in industrial and architectural settings. It is fabricated from metal bars that are welded or locked together to form a panel that is strong yet lightweight, allowing for efficient airflow and drainage. The diverse applications range from factory floors and rooftop walkways to architectural façades and decorative installations. Understanding the importance of metal grating weight is crucial for engineers, architects, and planners. Accurate knowledge of metal grating weight ensures safe load-bearing capacity, assists with structural design, and impacts both the transportation logistics and installation process. It facilitates precise engineering calculations and helps determine whether modifications to supporting structures are required, optimizing both project cost and safety. Accurate metal grating weight data optimizes designs, with heavy-duty gratings handling extreme loads as covers or decking for walkways and ramps.
What is Metal Grating?
Metal grating is a foundational component used across a myriad of applications, offering a unique blend of strength, openness, and versatility. From industrial platforms to architectural accents, metal grating, often fabricated into metal grate sheets, serves not just as a functional element but also adds aesthetic value. These sheets are prefabricated panels that simplify installation and provide consistency in design. Central to their application is the concept of metal grating weight, which plays a critical role in considerations around structural support, material efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. The weight of metal grate sheets must be carefully evaluated to ensure they meet the specific demands of a project while optimizing performance and cost.
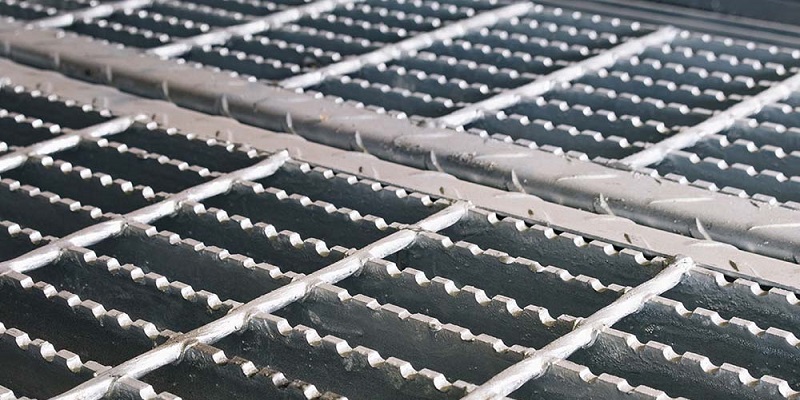

Types of Metal Grating
Metal grating comes in a variety of forms, each suited to specific load-bearing, aesthetic, and environmental requirements. Understanding these types is essential for selecting the right grating for your project, especially when considering the balance between metal grating weight, strength, and functionality.
Welded Bar Grating
Characterized by its high strength and affordability, this type is produced by welding intersecting metal bars.
Press-Locked Steel Grating
Known for its neat appearance, this variation involves pressing bars together, achieving a high degree of precision and uniformity.
Heavy-Duty Grating
Designed to bear heavy loads and high traffic, this type features thicker and deeper bearing bars for increased durability.
Swage-Locked Grating
Utilizes a mechanical locking of the bars through swaging, balancing load-bearing capabilities with aesthetic qualities.
Riveted Grating
Distinguished by its resistance to impact and fatigue, making it ideal for applications with heavy use, such as bridge walkways and steel walkway grating, which offers a similar level of durability for pedestrian paths in industrial settings.
Offers the advantages of being lightweight and resistant to corrosion, suitable for specialty applications where these attributes are prized.
Stainless Steel Grating
Favoured for its corrosion resistance and strength, often used in aggressive environments like food processing facilities.
Galvanized Steel Grating
This involves coating steel grating with zinc to protect it against corrosion, extending its usefulness in outdoor settings.
Materials in Metal Grating
The material selection for metal grating not only impacts its durability and corrosion resistance but also affects the metal grating weight—a crucial factor in design and logistics.
Carbon Steel
By far the most commonly used material thanks to its optimal blend of strength and cost-effectiveness, though it requires protective coatings to prevent corrosion.
Stainless Steel
This material offers enhanced corrosion resistance, making it suitable for use in harsh environments or where hygiene is a priority.
Galvanized Steel
Through a process of zinc coating, this material option provides added protection against corrosion, making it ideal for outdoor or industrial use.
Aluminum
Light, strong, and resistant to corrosion, aluminum grating is perfect for applications where weight reduction is a key consideration.
Fiberglass
Although not a metal, fiberglass is included for its non-conductive and anti-corrosive properties, suitable for specialized environments.
Alloy Materials
For specific needs, metal gratings can be manufactured from various alloys, offering unique properties for challenging applications.
The choice of material not only determines the structural and aesthetic qualities of the grating but also significantly influences the metal grating weight. Each material offers a distinct balance of weight, strength, and corrosion resistance, making it crucial to select the right type for your project’s specific needs.
Applications of Metal Grating
Metal grating is widely used in various industries due to its versatility and durability. Common applications include:
Industrial Flooring
Provides safe, non-slip surfaces for factories and workshops.
Walkways and Platforms
Used in warehouses, refineries, and offshore rigs for durability and ventilation.
Bridges and Ramps
Strong enough to bear heavy loads while ensuring drainage.
Stairs and Stair Treads
Ensures safety and grip in industrial or public spaces.
Drain Covers and Gutters
Facilitates water flow while preventing debris accumulation.
Fencing and Barriers
Provides secure and transparent boundaries in industrial areas.
Advantages of Metal Grating
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Offers durability without excessive weight.
Corrosion Resistance
Materials like stainless steel and galvanized coatings extend lifespan.
Slip Resistance
Serrated surfaces ensure safety in wet or oily conditions.
Customizability
Available in various sizes, patterns, and materials to meet specific needs.
Ventilation and Drainage
The open design allows air, light, and fluids to pass through, preventing accumulation.
Low Maintenance
Easy to clean and requires minimal upkeep over time.
Characteristics of Metal Grating
Material Versatility
Manufactured using carbon steel, stainless steel, or aluminum for different applications.
Design Options
Available in welded, press-locked, or swaged forms for specific structural requirements.
Load Capacity
Engineered to handle light pedestrian traffic or heavy-duty industrial equipment.
Aesthetic Appeal
Combines functionality with modern industrial aesthetics, often used in architectural projects.
In summary, metal grating’s adaptability, strength, and safety features make it indispensable across numerous industries, ensuring convenience and reliability for users.
Structural Advantages of Using 4 Inch Fiberglass Angle Products
Factors Influencing Metal Grating Weight
The functionality and practicality of a metal grating system are highly dictated by its weight. Metal grating weight is an essential element, affecting not only the ease of installation and transportation but also the structural design and material cost of supporting structures. The following ten factors contribute significantly to the weight variations found in metal grating products.
- Type of Material: The constitution of the metal used plays a dominant role. Stainless steel gratings are usually heavier than aluminum but provide higher strength and durability, whereas carbon steel is heavier than stainless steel due to its increased density.
- Density of Material: Different metals and alloys have varying densities, which directly correlate to the overall weight of the grating. For instance, gratings made from high-density materials will weigh more than those made from materials with a lower density.
- Bar Size: The cross-sectional dimensions of the bearing and cross bars influence the weight, with larger bars leading to a heavier grating.
- Bar Thickness: Thicker bars result in a greater amount of metal used in the grating, thus increasing its weight.
- Bar Spacing: Closely spaced bars render a grating heavier due to the greater number of bars per unit area. Conversely, wider spacing reduces weight but may also decrease load-bearing capacity.
- Design Pattern: The arrangement of the bars (e.g., open-ended or trim banded) can also influence the final weight of the grating.
- Grating Type: A standard-duty grating is designed for lighter loads and is consequently lighter in weight, whereas a heavy-duty grating is manufactured to handle more substantial loads, adding to the overall weight.
- Surface Treatment: Coatings such as galvanization add additional mass to the grating. Painted or powder-coated surfaces also contribute to the weight, albeit less significantly.
- Manufacturing Technique: Techniques like welding or swaging add little to the metal grating weight, while a fully forged grating can be heavier due to its manufacturing process which might use thicker bars for achieving desired sturdiness.
- Overall Dimensions: The total area of the grating directly affects its weight. For example, weight per square foot/m2 will vary; a larger piece of grating will weigh more, and this effect is magnified in heavy-duty gratings compared to standard-duty ones given the same area.
Metal grating weight can significantly vary based on multiple intersecting factors. For instance, a standard-duty steel bar grate with wide bar spacing might weigh less than a heavy-duty stainless steel grating with narrow bar spacing, despite carbon steel’s higher density. Each application challenges designers to carefully consider these factors to strike the right balance between structural integrity, functionality, and cost when choosing the appropriate grating product.
What Are Metal Grating Weight Calculations
The calculation of metal grating weight is vital for structural engineering, logistics, and cost estimation. A precise understanding of how weight is computed is necessary for professionals in the field to make informed decisions. Let’s delve deeper into the intricacies of metal grating weight calculations.
- Understanding Units: Metal grating weight is often measured in kilograms (kg) per square meter (m2) or pounds (lb) per square foot (ft2). Ensuring the correct units are used is vital for accurate calculations.
- Basic Formula: The fundamental weight calculation of metal grating involves multiplying the volume of the grating by the grating density of the material. This formula is: Weight = Volume x Grating Density.
- Volume Calculation: The volume of a grating section is calculated by multiplying the area covered by the grating by the thickness of the bars.
- Density Factor: Each metal has a specific density, which can be found in material data sheets. For instance, carbon steel has a density of around 7.85 g/cm3, while stainless steel has a density of approximately 8.00 g/cm3.
- Area of Grating: When calculating weight, it is important to consider the entire area that the grating will cover, including any cut-outs or pattern arrangements.
- Uniform Load-Bearing: Understand that weight calculations can influence the load-bearing capacity of the installation area. Engineers must ensure that the metal grating weight is manageable for the supporting structure.
Metal Grating Weight Calculators
- Accessibility: Metal grating weight calculators are accessible online and can be used to estimate the weight of a grating quickly.
- User-Friendly Interface: Most calculators offer a straightforward interface where users can input their grating specifications, including dimensions, material type, and bar spacing.
- Accuracy: These calculators use standardized densities and formulas to provide users with accurate weight estimations for their specific grating configurations.
- Time Efficiency: Instead of manual calculations, which can be time-consuming, weight calculators expedite the process, thereby enhancing productivity.
- Customization: Advanced calculators allow for customized inputs, such as unique bar sizes and shapes, to accommodate non-standard grating designs.
- Documenting Results: Many weight calculators enable users to save or print calculation results, which helps in maintaining accurate project documentation.
Examples and Hypothetical Calculations
- Standard-Duty Grating: For a section of standard-duty carbon steel grating measuring 1m2 with a bar thickness of 25mm and a density of 7.85 g/cm3:Volume = 1m x 1m x 0.025m = 0.025 m3
Weight = Volume x Density = 0.025 m3 x 7,850 kg/m3 = 196.25 kg - Heavy-Duty Grating: A stainless steel heavy-duty grating piece measuring 3 ft2 with a bar thickness of 1 inch and a density of 8.00 g/cm3:Volume = 3 ft x 3 ft x 1/12 ft = 0.75 ft3 Weight = Volume x Density (converted to lb/ft3) = 0.75 ft3 x 498.16 lb/ft3 = 373.62 lb
- Aluminum Grating: An aluminum grating section of 2m2 with a bar size of 30mm, and density of 2.70 g/cm3:Volume = 2m x 1m x 0.03m = 0.060 m3
Weight = Volume x Density = 0.060 m3 x 2,700 kg/m3 = 162 kg
These hypothetical examples illustrate the diverse nature of metal grating weight calculations involving different materials, sizes, and densities. As the complexity of the design increases, this process ensures professionals can accurately ascertain the weight for project requirements.
Metal Grating Weight Calculator
How to calculate the weight of steel grating?Here, we introduce some convenient formulas for calculating the weight of steel grating. The weight here refers to the theoretical weight after banding, which may differ slightly from the actual weight. This calculator is suitable for welded steel grating and press-locked steel grating in stainless steel and carbon steel materials.

Metal Grating Weight Charts
In the world of construction and design, accurately estimating the weight of metal grating is essential for planning, budgeting, and execution of projects. This section explores the critical tools and methodologies used to measure and predict the weight of metal gratings, including weight charts, calculators, and the understanding of theoretical versus actual weights. These resources are pivotal in ensuring projects meet their design specifications, budgetary constraints, and timeline.
Metal Grating Weight Charts: A Quick Reference
Metal grating weight charts are indispensable tools that offer quick access to the weight of standard and custom metal gratings. These charts are crucial for architects, engineers, and project managers who need to make prompt and accurate decisions regarding material specifications.
- Ease of Access: These charts provide immediate access to weight specifications based on various factors such as grating type, size, and material.
- Diverse Applications: They span a range of applications, addressing the needs of different projects whether for industrial, architectural, or other purposes.
- Customization Reference: For projects with unique requirements, these charts are a starting point for estimating the impact of custom sizes and shapes on weight.
- Material Selection Guide: They assist in selecting the appropriate material by detailing the weight differences among options, aiding in making informed choices.
- Standard Compliance: The charts are aligned with industry standards, ensuring compliance and safety in project designs.
- Efficiency in Planning: By providing a quick reference, they streamline material planning and procurement processes.
Utilizing Calculators for Enhanced Planning
The advent of calculators specifically designed for estimating metal grating weight has revolutionized project planning, allowing for precision and customization in calculations.
- Accurate Estimations: These calculators provide exact weight estimations, factoring in specific configurations and material density.
- Budgeting Aid: Precise weight calculations are instrumental in budget preparation, facilitating accurate cost predictions.
- Real-time Updates: They offer adjustments based on the most current material costs and availability, boosting planning agility.
- Visualization of Specifications: Certain calculators provide visuals of the grating design, enhancing understanding and decision-making.
- Integration with Project Tools: Many calculators can be integrated with project management tools, improving efficiency across the planning process.
- Custom Solutions: They accommodate special project requirements, enabling feasibility assessments for custom designs.
Best Fiberglass Hot Rod Bodies For Custom Car Building Projects
The Importance of Theoretical vs. Actual Weight
When planning projects, a distinction between the theoretical weight of metal grating and its actual weight is crucial. This understanding is foundational for accurate budgeting, risk management, and quality assurance.
- Expectation Management: Understanding the potential for variance between theoretical and actual weights sets realistic expectations.
- Budgeting Considerations: Variances, even minor, can influence shipping costs and the overall project budget.
- Engineering Accuracy: Anticipating weight discrepancies ensures that projects adhere to safety and compliance standards.
- Material Efficiency: Planning for potential variances minimizes the risks associated with over or under-ordering materials.
- Quality Control: Awareness of weight differences may reflect the quality control measures in place during manufacturing.
- Risk Management: Factoring in potential weight variances enables better mitigation strategies for related risks.
The combination of metal grating weight charts, calculators, and an understanding of weight variances forms a comprehensive toolkit for professionals. These resources, when adeptly utilized, ensure that projects not only meet their design and functional requirements but do so within the constraints of budget and timeline, all while maintaining safety and compliance standards.
Selection and Ordering Tips of Metal Grating Weight
Selecting the right type of metal grating for your project involves careful consideration of various factors, including metal grating weight. These decisions can influence safety, durability, project cost, and installation ease. Below are some tips to guide you through the selection of metal grating and helpful reminders when specifying and ordering your materials.

Guide on Choosing the Right Type of Metal Grating
To choose the most suitable metal grating while considering metal grating weight, load capacity, and application area, keep in mind the following points:
- Assess Load Requirements: Determine the maximum load the grating must support. High-traffic areas may require heavier-duty grating.
- Consider Weight Constraints: For structures with weight limitations, opt for lighter-weight materials that still meet load specifications.
- Evaluate Application Area: Match the types of grating to the environment—stainless steel for corrosion resistance, aluminum for lightweight properties, etc.
- Check for Compliance: Ensure the grating meets relevant industry standards and building codes for safety and performance.
- Determine Slip Resistance Needs: For areas where slip resistance is critical, select gratings with appropriate surface textures or coatings.
- Review Accessibility: In public spaces, consider grating that is ADA-compliant to accommodate wheelchairs and pedestrians.
- Analyze Environmental Factors: In outdoor or harsh industrial environments, choose a grating that withstands the elements without compromising on metal grating weight.
- Balance Aesthetic and Function: If visual appearance is a priority, consider gratings with pleasing patterns that also fulfill structural needs.
- Consult Technical Experts: When in doubt, seek advice from manufacturers or engineers who can provide insights based on vast experience with weight of metal grating considerations.
Tips on Specifying and Ordering Metal Grating
Once you’ve determined the right type of grating, specifying and ordering requires attention to detail. Follow these points to ensure you get the exact metal grating that your project demands:
- Specify Exact Dimensions: Precise measurements are crucial for a seamless installation. Include length, width, and depth in your specifications.
- Select the Material: Choose a material that corresponds to environmental conditions and load-bearing requirements.
- Determine the Finish: Protective finishes can extend the life of metal grating. Consider galvanization or powder coating for enhanced durability.
- Clarify Span Direction: Indicate the bearing bar direction necessary for proper installation and load distribution.
- Detail the Grating Type: From welded to riveted, the type of grating will affect performance and metal grating weight.
- Note Special Fabrication: If your project requires cutouts or custom fabrication, provide detailed drawings and instructions.
- Define Load Bar Sizes: The thickness and spacing of the load bars will define the strength and weight of the grating.
- Address Tolerance Levels: Make certain that the manufacturer understands permissible deviation levels from the specified dimensions.
- Confirm Delivery Details: Ensure that delivery schedules align with project timelines and check if the metal grating weight affects shipping options.
By giving meticulous attention to these points when making your metal grating selection and order specifications, you can avoid costly mistakes and delays. Proper planning and a clear understanding of the project’s needs regarding metal grating weight will result in a successful installation and a durable, effective grating solution.
Long Fiberglass Rods: Essential Uses For Gardening
FAQs about Metal Grating Weight
The weight of metal grating can vary widely depending on several factors including the type of material (e.g., carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum), the dimensions and thickness of the bars, and the spacing between bars. For instance, a standard carbon steel grating with a 1″ x 3/16″ bearing bar on centers of 1-3/16″ and cross bars at 4″ could weigh approximately 7.4 lbs per square foot. However, the exact weight can only be determined by taking into account the specific dimensions and materials of the grating in question. It’s important to consult with a manufacturer or use a detailed weight chart or calculator specific to the type of grating for precise figures.
The weight of a steel grid deck, which also falls under the category of steel grating, largely depends on its construction, size, and the steel material’s thickness. Heavy-duty gratings designed for high-load applications like bridges or highways weigh more due to thicker and denser steel. For example, a heavy-duty welded steel grid deck might weigh between 10 to 20 pounds per square foot, depending on its design and specifications. Accurate weight determination is essential for engineering calculations, and as such, precise weights should be obtained from product specifications or direct inquiries to manufacturers.
Metal grating comes in a variety of sizes, designed to suit a wide range of applications. Common dimensions for metal grating panels can vary greatly with lengths and widths ranging from 24 inches up to 36 inches or more, with custom sizes available. The bearing bar size can also vary, with common heights being 1 inch or more and thickness around 3/16 inch or 1/4 inch. Cross bar dimensions and spacing can further define the size, contributing to the overall structural integrity and application suitability of the grating. Specific sizes should be chosen based on the load requirements and the environmental conditions of the application area.
Expanded metal grating weight per foot is determined by the thickness of the sheet metal from which it’s made, as well as the size and weight of the raw sheet before expansion. Generally, lighter materials like aluminum can weigh as little as a few pounds per square foot, while heavier materials like steel can weigh significantly more. For example, a common grade of expanded metal grating made from carbon steel might weigh approximately 5 lbs per square foot, depending on the thickness and strand dimensions. It’s crucial to refer to a manufacturer’s catalog or a weight chart for expanded metal gratings for accurate weight data, as these figures can influence the support structures’ design and the overall project cost.
The weight of metal grates depends on their material, dimensions, and design. Commonly used materials include steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, each having different densities. The weight is typically measured in pounds per square foot (psf) or kilograms per square meter (kg/m²). For example, standard steel grating might weigh 15–60 psf depending on the bar size, spacing, and load-bearing capacity. Manufacturers often provide weight charts to help determine the exact weight of a grate based on its specifications. Factors like surface coatings, such as galvanization, can also slightly increase the weight. Proper weight assessment is crucial in applications like bridges, industrial flooring, and drainage systems, where structural integrity and load distribution are vital.
The density of steel grating refers to the mass per unit volume of the steel material, typically measured in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or pounds per cubic inch. Standard carbon steel used in grating has a density of approximately 7.85 g/cm³ (490 lbs/ft³). The overall density of a steel grating panel also depends on the design—whether it’s open grid, serrated, or solid-surfaced. While the material density is constant, grating density (effective weight per unit area) varies due to bar spacing and cross-bar patterns. This makes steel grating lightweight compared to solid metal sheets but still provides high strength, ensuring it is suitable for platforms, catwalks, and other industrial uses.
To calculate the load a metal grating can support, consider factors such as bar size, spacing, span length, and material properties. Grating load capacity is typically evaluated as a uniform load (e.g., lbs/ft²) or concentrated load (e.g., lbs at a specific point). Manufacturers also provide load tables specifying maximum loads for different configurations, ensuring safety and performance under specific conditions. For heavy loads or unusual spans, custom design or expert consultation is recommended. Compliance with safety factors and codes is essential when calculating grating load capacity.
The term “19 W/4 grating” refers to a specific bar grating type defined by its spacing and material properties. The “19” indicates a bearing bar spacing of 1-3/16 inches (center-to-center), and the “W” denotes that the grating is made of steel with a welded construction. The “4” signifies the cross-bar spacing of 4 inches (center-to-center). This standardized nomenclature helps users identify grating types for industrial or architectural applications. 19 W/4 grating is common for walkways, platforms, and mezzanines, providing high strength-to-weight ratios and good slip resistance. It’s versatile and suitable for most light to heavy load applications.
Grating density refers to the weight of the grating per unit area, typically expressed in pounds per square foot (psf) or kilograms per square meter (kg/m²). It depends on factors like bar thickness, spacing, and material density. Grating with tighter bar spacing and thicker materials will have a higher density, affecting weight and load capacity. For instance, a dense grating design may be required for pedestrian walkways to ensure safety, while lighter density grating may suffice for drainage covers. Manufacturers provide detailed specifications, allowing users to select the right grating density based on structural needs and application constraints.

As the editor of GangLong Fiberglass, I have years of experience and in-depth research, focusing on cable tray products, fiberglass solutions, and grille systems. I incorporate years of industry insights and practical experience into every content, committed to promoting the progress of the industry. At GangLong Fiberglass, my commitment is reflected in every product, from innovative cable trays to durable fiberglass solutions and sturdy grille systems. As an authoritative voice in the industry, my goal is to provide valuable information to professionals and businesses and promote forward-looking solutions.